Stockholm
| Stockholm, Sweden | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Aerial view of the Old Town, Skeppsbron, Stockholm City Hall, Hötorget buildings, Ericsson Globe and Stockholm Palace. | ||
| ||
| Nickname(s): Eken, the Venice of the North, the Venice of Scandinavia,[1] Mälardrottningen | ||
 Stockholm, Sweden | ||
| Coordinates: 59°19′46″N 18°4′7″E / 59.32944°N 18.06861°ECoordinates: 59°19′46″N 18°4′7″E / 59.32944°N 18.06861°E | ||
| Country | Sweden | |
| Province | Södermanland and Uppland | |
| County | Stockholm County | |
| Municipalities | ||
| First mention | 1252 | |
| Charter | 13th century | |
| Area[2] | ||
| • City | 188 km2 (73 sq mi) | |
| • Urban | 381.63 km2 (147.35 sq mi) | |
| • Metro | 6,519 km2 (2,517 sq mi) | |
| Elevation | 0 m (0 ft) | |
| Population (31 December 2015)[3][4][5] | ||
| • City | 932,917 | |
| • Density | 5,000/km2 (13,000/sq mi) | |
| • Urban | 1,515,017 | |
| • Urban density | 3,597/km2 (9,320/sq mi) | |
| • Metro | 2,226,795 | |
| • Metro density | 340/km2 (880/sq mi) | |
| Demonym(s) | Stockholmare | |
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | |
| • Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | |
| Postal code | 100 00-199 99 | |
| Area code(s) | +46-8 | |
| Website | www.stockholm.se | |
Stockholm (/ˈstɒkhoʊm, -hoʊlm/;[6] Swedish pronunciation: [²stɔkːɔlm] or [²stɔkhɔlm])[7] is the capital of Sweden and the most populous city in the Nordic countries;[8][lower-alpha 1] 932,917 people live in the municipality,[3] approximately 1.5 million in the urban area,[5] and 2.3 million in the metropolitan area.[3] The city is spread across 14 islands on the coast in the southeast of Sweden at the mouth of Lake Mälaren, by the Stockholm archipelago and the Baltic Sea. The area has been settled since the Stone Age, in the 6th millennium BC, and was founded as a city in 1252 by a Swedish statesman Birger Jarl. It is also the capital of Stockholm County.
Stockholm is the cultural, media, political, and economic centre of Sweden. The Stockholm region alone accounts for over a third of the country's GDP,[9] and is among the top 10 regions in Europe by GDP per capita.[10] It is an important global city,[11][12] and the main centre for corporate headquarters in the Nordic region.[13] The city is home to some of Europe's top ranking universities, such as the Stockholm School of Economics, Karolinska Institute and Royal Institute of Technology (KTH).[14] It hosts the annual Nobel Prize ceremonies and banquet at the Stockholm Concert Hall and Stockholm City Hall. One of the city's most prized museums, the Vasa Museum, is the most visited non-art museum in Scandinavia.[15][16] The Stockholm metro, opened in 1950, is well known for its decoration of the stations; it has been called the longest art gallery in the world.[17][18][19] Sweden's national football arena is located north of the city centre, in Solna. Ericsson Globe, the national indoor arena, is in the southern part of the city. The city was the host of the 1912 Summer Olympics, and hosted the equestrian portion of the 1956 Summer Olympics otherwise held in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.
Stockholm is the seat of the Swedish government and most of its agencies,[20] including the highest courts in the judiciary,[21][22] and the official residencies of the Swedish monarch and the Prime Minister. The government has its seat in the Rosenbad building, the Riksdag is seated in the Parliament House, and the Prime Minister's residence is adjacent at the Sager House.[23][24][25] The Stockholm Palace is the official residence and principal workplace of the Swedish monarch, while the Drottningholm Palace, a World Heritage Site on the outskirts of Stockholm, serves as the Royal Family's private residence.[26][27]
History



After the Ice Age, around 8,000 BCE, there were already a large number of people living in the present-day Stockholm area, but, as temperatures dropped, inhabitants moved towards the South. Thousands of years later, as the ground thawed, the climate became tolerable, and the lands became fertile, some life moved back to the North. At the intersection of the Baltic Sea and lake Mälaren is an archipelago site where the Old Town of Stockholm was first built from about 1000 CE by Vikings. They had a positive trade impact on the area because of the trade routes they created.
Stockholm's location appears in Norse sagas as Agnafit, and in Heimskringla in connection with the legendary king Agne. The earliest written mention of the name Stockholm dates from 1252, by which time the mines in Bergslagen made it an important site in the iron trade. The first part of the name (stock) means log in Swedish, although it may also be connected to an old German word (Stock) meaning fortification. The second part of the name (holm) means islet, and is thought to refer to the islet Helgeandsholmen in central Stockholm. According to Eric Chronicles the city is said to have been founded by Birger Jarl to protect Sweden from sea invasions made by Karelians after the pillage of Sigtuna on Lake Mälaren in the summer of 1187.[28]
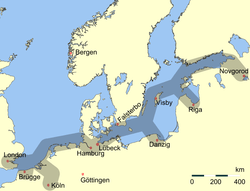
Stockholm's core, the present Old Town (Gamla Stan) was built on the central island next to Helgeandsholmen from the mid 13th century onward. The city originally rose to prominence as a result of the Baltic trade of the Hanseatic League. Stockholm developed strong economic and cultural linkages with Lübeck, Hamburg, Gdańsk, Visby, Reval, and Riga during this time. Between 1296 and 1478 Stockholm's City Council was made up of 24 members, half of whom were selected from the town's German-speaking burghers.
The strategic and economic importance of the city made Stockholm an important factor in relations between the Danish Kings of the Kalmar Union and the national independence movement in the 15th century. The Danish King Christian II was able to enter the city in 1520. On 8 November 1520 a massacre of opposition figures called the Stockholm Bloodbath took place and set off further uprisings that eventually led to the breakup of the Kalmar Union. With the accession of Gustav Vasa in 1523 and the establishment of a royal power, the population of Stockholm began to grow, reaching 10,000 by 1600.
The 17th century saw Sweden grow into a major European power, reflected in the development of the city of Stockholm. From 1610 to 1680 the population multiplied sixfold. In 1634, Stockholm became the official capital of the Swedish empire. Trading rules were also created that gave Stockholm an essential monopoly over trade between foreign merchants and other Swedish and Scandinavian territories.
In 1710, a plague killed about 20,000 (36 percent) of the population.[29] After the end of the Great Northern War the city stagnated. Population growth halted and economic growth slowed. The city was in shock after having lost its place as the capital of a Great power. However Stockholm maintained its role as the political centre of Sweden and continued to develop culturally under Gustav III.
By the second half of the 19th century, Stockholm had regained its leading economic role. New industries emerged and Stockholm was transformed into an important trade and service centre as well as a key gateway point within Sweden. The population also grew dramatically during this time, mainly through immigration. At the end of the 19th century, less than 40% of the residents were Stockholm-born. Settlement began to expand outside the city limits. The 19th century saw the establishment of a number of scientific institutes, including the Karolinska Institutet. The General Art and Industrial Exposition was held in 1897.

Stockholm became a modern, technologically advanced, and ethnically diverse city in the latter half of the 20th century. Many historical buildings were torn down during the modernist era, including substantial parts of the historical district of Klara, and replaced with modern architecture. However, in many other parts of Stockholm (such as in Gamla stan, Södermalm, Östermalm, Kungsholmen and Vasastan), many "old" buildings, blocks and streets built before the modernism and functionalism movements took off in Sweden (around 1930–1935) survived this era of demolition. Throughout the century, many industries shifted away from work-intensive activities into more high-tech and service industry areas.
Currently, Stockholm's metropolitan area is one of the fastest-growing regions in Europe, and its population is expected to number 2.5 million by 2024. As a result of this massive population growth, it has been proposed to build densely-packed high-rise building in the city centre connected by high-rise walkways.[30]
Geography

Location
Stockholm is located on Sweden's south-central east coast, where the freshwater Lake Mälaren — Sweden's third largest lake — flows out into the Baltic Sea. The central parts of the city consist of fourteen islands that are continuous with the Stockholm archipelago. The geographical city centre is situated on the water, in Riddarfjärden bay. Over 30% of the city area is made up of waterways and another 30% is made up of parks and green spaces.
The biome Stockholm belongs to is the Temperate Deciduous Forest, which means the climate is very similar to that of the far north-eastern area of the United States and coastal Nova Scotia in Canada. The average annual temperature is 10 °C (50 °F). The average rainfall is 30 to 60 inches a year. The deciduous forest has four distinct seasons, spring, summer, autumn, and winter. In the autumn the leaves change colour. During the winter months the trees lose their leaves.
For details about the other municipalities in the Stockholm area, see the pertinent articles. North of Stockholm Municipality: Järfälla, Solna, Täby, Sollentuna, Lidingö, Upplands Väsby, Österåker, Sigtuna, Sundbyberg, Danderyd, Vallentuna, Ekerö, Upplands-Bro, Vaxholm, and Norrtälje. South of Stockholm: Huddinge, Nacka, Botkyrka, Haninge, Tyresö, Värmdö, Södertälje, Salem, Nykvarn and Nynäshamn.
Stockholm Municipality
Stockholm Municipality is an administrative unit defined by geographical borders. The semi-officially adopted name for the municipality is City of Stockholm (Stockholms stad in Swedish).[31] As a municipality, the City of Stockholm is subdivided into district councils, which carry responsibility for primary schools, social, leisure and cultural services within their respective areas. The municipality is usually described in terms of its three main parts: Innerstaden (Stockholm City Centre), Söderort (Southern Stockholm) and Västerort (Western Stockholm). The districts of these parts are:
The modern centre Norrmalm, (concentrated around the town square Sergels torg), is the largest shopping district in Sweden. It is the most central part of Stockholm in business and shopping.
Climate
Stockholm, with a February mean of −3.0 °C (26.6 °F), had a humid continental climate (Köppen Dfb) for the most recent official reference period. Due to the city's high northerly latitude, daylight varies widely from more than 18 hours around midsummer, to only around 6 hours in late December. Despite its northern location, Stockholm has relatively mild weather compared to other locations at similar latitude, or even farther south. With an average of just over 1800 hours of sunshine per year, it is also one of the sunniest cities in Northern Europe, receiving more sunshine than Paris,[32] London[33] and a few other major European cities of a more southerly latitude. Due to recent mildening of the climate it could be classified as cold marine with significant continental influence if the −3 °C (27 °F) isotherm is used. The urban heat island combined with prevailing wind travelling over land rather than sea during summer renders Stockholm to have the warmest summers in the Nordic countries.
In spite of its mild climate it is actually located further to the north of where areas of Canada are above the Arctic tree line at sea level.[34] Winter in Stockholm is more than 20 °C (68 °F) milder than in many areas this far north.
Summers average daytime high temperatures of 20–25 °C (68–77 °F) and lows of around 13 °C (55 °F), but temperatures can reach 30 °C (86 °F) on some days. Days above 30 °C (86 °F) occur on average 1.55 days per year (1992–2011).[35] Days between 25 °C (77 °F) and 30 °C (86 °F) are relatively common especially in July and August. Night-time lows of above 20 °C (68 °F) are rare, and the hot summer nights roam around 17 to 18 °C (63 to 64 °F). Winters generally bring cloudy weather with the most precipitation falling in December and January (as rain or as snow). The average winter temperatures range from −3 to −1 °C (27 to 30 °F), and occasionally drop below −20 °C (−4 °F). Spring and autumn are generally cool to mild.
The climate table below presents weather data from the years 1981–2010 although the official Köppen reference period was from 1961–1990. According to ongoing measurements, the temperature has increased during the years 1991–2009 as compared with the last series. This increase averages about 1.0 °C (1.8 °F) over all months. Warming is most pronounced during the winter months, with an increase of more than 2.0 °C (3.6 °F) in January.[36] For the 2002–2014 measurements some further increases have been found, although some months such as June have been relatively flat.
The highest temperature ever recorded in Stockholm was 36 °C (97 °F) on 3 July 1811; the lowest was −32 °C (−26 °F) on 20 January 1814.[37] The temperature has not dropped to below −25.1 °C (−13.2 °F) since 10 January 1987.[38][39]
Annual precipitation is 539 mm (21.2 in) with around 170 wet days and light to moderate rainfall throughout the year. Snowfall occurs mainly from December through March. Snowfall may occasionally occur in late October as well as in April.
In Stockholm, the aurora borealis can occasionally be observed.
| Climate data for Stockholm, 1961–1990 (Extremes 1756–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 11.0 (51.8) |
12.2 (54) |
17.8 (64) |
26.1 (79) |
29.0 (84.2) |
32.2 (90) |
36.0 (96.8) |
35.4 (95.7) |
27.9 (82.2) |
20.2 (68.4) |
14.0 (57.2) |
12.7 (54.9) |
36.0 (96.8) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −0.7 (30.7) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
3.0 (37.4) |
8.6 (47.5) |
15.7 (60.3) |
20.7 (69.3) |
21.9 (71.4) |
20.4 (68.7) |
15.1 (59.2) |
9.9 (49.8) |
4.5 (40.1) |
1.1 (34) |
10.0 (50) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −2.8 (27) |
−3.0 (26.6) |
0.1 (32.2) |
4.6 (40.3) |
10.7 (51.3) |
15.6 (60.1) |
17.2 (63) |
16.2 (61.2) |
11.9 (53.4) |
7.5 (45.5) |
2.6 (36.7) |
−1.0 (30.2) |
6.6 (43.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −5 (23) |
−5.3 (22.5) |
−2.7 (27.1) |
1.1 (34) |
6.3 (43.3) |
11.3 (52.3) |
13.4 (56.1) |
12.7 (54.9) |
9.0 (48.2) |
5.3 (41.5) |
0.7 (33.3) |
−3.2 (26.2) |
3.6 (38.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −32 (−26) |
−30 (−22) |
−25.5 (−13.9) |
−22.0 (−7.6) |
−6.5 (20.3) |
0.0 (32) |
4.3 (39.7) |
2.0 (35.6) |
−3.5 (25.7) |
−9.0 (15.8) |
−18 (0) |
−22.5 (−8.5) |
−32.0 (−25.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 39 (1.54) |
27 (1.06) |
29 (1.14) |
29 (1.14) |
32 (1.26) |
55 (2.17) |
65 (2.56) |
59 (2.32) |
52 (2.05) |
49 (1.93) |
47 (1.85) |
45 (1.77) |
531 (20.91) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 9 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 100 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 40 | 72 | 135 | 185 | 276 | 292 | 260 | 221 | 154 | 99 | 54 | 33 | 1,821 |
| Source #1: NOAA[40] | |||||||||||||
| Source #2: SMHI[41] | |||||||||||||
Daylight hours
Stockholm's location just south of the 60th latitude means that the number of daylight hours is relatively small during winter — about six hours, while in June and the first half of July, the nights are relatively short, with about 18 hours of daylight. Around the Summer solstice the sun never reaches further below the horizon than 7.3 degrees.[42] This gives the sky a bright blue colour in summer once the sun has set, because it does not get any darker than nautical twilight. Also, when looking straight up towards the zenith, few stars are visible after the sun has gone down. This is not to be confused with the midnight sun, which occurs north of the Arctic Circle, around 7 degrees farther north.
City governance

The Stockholm Municipal Council (Swedish: Stockholms kommunfullmäktige) is the name of the local assembly. Its 101 councillors are elected concurrently with general elections, held at the same time as the elections to the Riksdag and county councils. The Council convene twice every month at Stockholm City Hall, and the meetings are open to the public. The matters on which the councillors decide have generally already been drafted and discussed by various boards and committees. Once decisions are referred for practical implementation, the employees of the City administrations and companies take over.[43]
The elected majority has a Mayor and eight Vice Mayors. The Mayor and each majority Vice Mayor is a head of a department, with responsibility for a particular area of operation, such as City Planning. The opposition also has four Vice Mayors, but they hold no executive power. Together the Mayor and the 12 Vice Mayors form the Council of Mayors, and they prepare matters for the City Executive Board. The Mayor holds a special position among the Vice Mayors, chairing both the Council of Mayors and the City Executive Board.[43]
The City Executive Board (Swedish: Kommunstyrelsen) is elected by the City Council and can be thought of as the equivalent of a cabinet. The City Executive Board renders an opinion in all matters decided by the Council and bears the overall responsibility for follow-up, evaluation and execution of its decisions. The Board is also responsible for financial administration and long-term development. The City Executive Board consists of 13 members, who represent both the majority and the opposition. Its meetings are not open to the public.[43]
Following the Stockholm municipal election, 2014 a majority of seats in the municipal council is at present held by a left-wing majority (following two terms of a center-right majority) and the Mayor of Stockholm (Swedish: Finansborgarråd) is Karin Wanngård from the Social Democrats. In addition to the eight political parties which are also represented on the national level in the Riksdag, the Feminist Initiative also hold seats in the municipal council and is part of the ruling majority.
Economy


The vast majority of Stockholm residents work in the service industry, which accounts for roughly 85% of jobs in Stockholm. The almost total absence of heavy industry (and fossil fuel power plants) makes Stockholm one of the world's cleanest metropolises. The last decade has seen a significant number of jobs created in high technology companies. Large employers include IBM, Ericsson, and Electrolux. A major IT centre is located in Kista, in northern Stockholm.
Stockholm is Sweden's financial centre. Major Swedish banks, such as Nordea, Swedbank, Handelsbanken, and Skandinaviska Enskilda Banken, are headquartered in Stockholm, as are the major insurance companies Skandia, Folksam and Trygg-Hansa. Stockholm is also home to Sweden's foremost stock exchange, the Stockholm Stock Exchange (Stockholmsbörsen). Additionally, about 45% of Swedish companies with more than 200 employees are headquartered in Stockholm.[44] Noted clothes retailer H&M is also headquartered in the city. In recent years, tourism has played an important part in the city's economy. Stockholm County is ranked as the 10th largest visitor destination in Europe, with over 10 million commercial overnight stays per year. Among 44 European cities Stockholm had the 6th highest growth in number of nights spent in the period 2004–2008.[45]
The largest companies by number of employees:[46]
- Ericsson — 8,430
- Posten AB (national postal service) — 4,710
- Skandinaviska Enskilda Banken (SEB) — 4,240
- Swedbank — 3,610
- Södersjukhuset (Southern Hospital) — 3,610
- MTR Stockholm (Stockholm Subway operator) — 3,000
- Nordea — 2,820
- Handelsbanken — 2,800
- IBM Svenska — 2,640
- Capgemini — 2,500
- Securitas AB — 2,360
- Veolia Transport — 2,300
- ISS Facility Services — 2,000
- Sveriges Television (public television) — 1,880
- Nobina Sverige AB — 1,873 (2012)
- Sodexo — 1,580
Fibre optic network
The city-owned company Stokab started in 1994 to build a fiber-optic network throughout the municipality as a level playing field for all operators (City of Stockholm, 2011). Around a decade later, the network was 1.2 million kilometres (0.7 million miles) long making it the longest optic fiber network in the world and now has over 90 operators and 450 enterprises as customers. 2011 was the final year of a three-year project which brought fiber to 100% of public housing, meaning an extra 95,000 houses were added. (City of Stockholm, 2011)
Education
Research and higher education in the sciences started in Stockholm in the 18th century, with education in medicine and various research institutions such as the Stockholm Observatory. The medical education was eventually formalized in 1811 as the Karolinska Institutet. The Royal Institute of Technology (Kungliga Tekniska högskolan, or KTH) was founded in 1827 and is currently Scandinavia's largest higher education institute of technology with 13,000 students. Stockholm University, founded in 1878 with university status granted in 1960, has 52,000 students as of 2008. It also incorporates many historical institutions, such as the Observatory, the Swedish Museum of Natural History, and the botanical garden Bergianska trädgården. The Stockholm School of Economics, founded in 1909, is one of the few private institutions of higher education in Sweden.
In the fine arts, educational institutions include the Royal College of Music, which has a history going back to the conservatory founded as part of the Royal Swedish Academy of Music in 1771, the Royal University College of Fine Arts, which has a similar historical association with the Royal Swedish Academy of Arts and a foundation date of 1735, and the Swedish National Academy of Mime and Acting, which is the continuation of the school of the Royal Dramatic Theatre, once attended by Greta Garbo. Other schools include the design school Konstfack, founded in 1844, the University College of Opera (founded in 1968, but with older roots), the University College of Dance, and the Stockholms Musikpedagogiska Institut (the University College of Music Education).
The Södertörn University College was founded in 1995 as a multi-disciplinary institution for southern Metropolitan Stockholm, to balance the many institutions located in the northern part of the region.
Other institutes of higher education are:
- Military Academy Karlberg, the world's oldest military academy to remain in its original location, inaugurated in 1792 and housed in Karlberg Palace.
- Ersta Sköndal University College
- The Stockholm School of Theology (Teologiska Högskolan, Stockholm)
- The Swedish School of Sport and Health Sciences (Gymnastik- och idrottshögskolan, or GIH)
- Stockholm University (Stockholms universitet)
The biggest complaint from students of higher education in Stockholm is the lack of student accommodations, the difficulty in finding other accommodations and the high rent.[47][48]
Demographics
| Estimated population, 1252–1775 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: Stockholms Stads Utrednings- och Statistikkontor AB Befolkningen i Stockholm 1252–2005, p. 55 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Historical population in 10-year intervals, 1800–Present | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: Stockholms Stads Utrednings- och Statistikkontor AB Befolkningen i Stockholm 1252–2005, p. 55 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Stockholm region is home to around 22% of Sweden's total population, and accounts for about 29% of its gross domestic product.[49] The geographical notion of "Stockholm" has changed throughout the times. By the turn of the 19th century, Stockholm largely consisted of the area today known as City Centre, roughly 35 km2 (14 sq mi) or one-fifth of the current municipal area. In the ensuing decades several other areas were incorporated (such as Brännkyrka Municipality in 1913, at which time it had 25,000 inhabitants, and Spånga in 1949). The municipal border was established in 1971; with the exception of Hansta, in 1982 purchased by Stockholm Municipality from Sollentuna Municipality and today a nature reserve.[50]
| Largest groups of foreign residents[51] | |
| Nationality | Population (2014) |
|---|---|
| 17,576 | |
| 16,374 | |
| 11,429 | |
| 10,612 | |
| 7,429 | |
| 7,364 | |
| 5,440 | |
| 4,791 | |
| 4,785 | |
| 4.556 | |
| 1,913 | |
Of the population of 765,044 in 2004, 370,482 were men and 394,562 women. The average age is 39.8 years; 40.5% of the population is between 20 and 44 years.[50] 309,480 people, or 40.4% of the population, over the age 15 were unmarried. 211,115 people, or 27.5% of the population, were married. 85,373, or 11.1% of the population, had been married but divorced.[50] Approximately 27% of Stockholm's residents are of an immigrant or non-Swedish background.[52] Residents of Stockholm are known as Stockholmers. Some of the suburbs have large populations of immigrants. Languages spoken in Greater Stockholm outside of Swedish include Finnish, one of the official minority languages of Sweden; and English, as well as Bosnian, Syriac, Arabic, Turkish, Kurdish, Persian, Dutch, Spanish, Serbian and Croatian.
As of December 2012, there were 201,821 foreign-born persons in Stockholm. The largest group of them are the Finns (17,579), followed by Iraqis (16,374) and Iranian people (11,429).
The entire Stockholm metropolitan area, consisting of 26 municipalities, has a population of over 2,2 million,[53] making it the most populous city in the Nordic region.[8] The Stockholm urban area, defined only for statistical purposes, had a total population of 1,630,738 in 2015. In the following municipalities some of the districts are contained within the Stockholm urban area, though not all:[4][5]
|
 Stockholm Municipality population development years 1570–2012[54] |
Culture
Apart from being Sweden's capital, Stockholm houses many national cultural institutions. The Stockholm region is home to three of Sweden's World Heritage Sites – spots judged as invaluable places that belong to all of humanity: The Drottningholm Palace, Skogskyrkogården (The Woodland Cemetery) and Birka.[27][55][56] In 1998, Stockholm was named European Capital of Culture.
Literature
Authors connected to Stockholm include the poet and songwriter Carl Michael Bellman (1740–1795), novelist and dramatist August Strindberg (1849–1912), and novelist Hjalmar Söderberg (1869–1941), all of whom made Stockholm part of their works.
Other authors with notable heritage in Stockholm were the Nobel Prize laureate Eyvind Johnson (1900–1976) and the popular poet and composer Evert Taube (1890–1976). The novelist Per Anders Fogelström (1917–1998) wrote a popular series of historical novels depicting life in Stockholm from the mid-18th to mid-20th century.
Architecture


The city's oldest section is Gamla stan (Old Town), located on the original small islands of the city's earliest settlements and still featuring the medieval street layout. Some notable buildings of Gamla Stan are the large German Church (Tyska kyrkan) and several mansions and palaces: the Riddarhuset (the House of Nobility), the Bonde Palace, the Tessin Palace and the Oxenstierna Palace.
The oldest building in Stockholm is the Riddarholmskyrkan from the late 13th century. After a fire in 1697 when the original medieval castle was destroyed, Stockholm Palace was erected in a baroque style. Storkyrkan Cathedral, the episcopal seat of the Bishop of Stockholm, stands next to the castle. It was founded in the 13th century but is clad in a baroque exterior dating to the 18th century.
As early as the 15th century, the city had expanded outside of its original borders. Some pre-industrial, small-scale buildings from this era can still be found in Södermalm. During the 19th century and the age of industrialization Stockholm grew rapidly, with plans and architecture inspired by the large cities of the continent such as Berlin and Vienna. Notable works of this time period include public buildings such as the Royal Swedish Opera and private developments such as the luxury housing developments on Strandvägen.
In the 20th century, a nationalistic push spurred a new architectural style inspired by medieval and renaissance ancestry as well as influences of the Jugend/Art Nouveau style. A key landmark of Stockholm, the Stockholm City Hall, was erected 1911–1923 by architect Ragnar Östberg. Other notable works of these times are the Stockholm Public Library and the World Heritage Site Skogskyrkogården.[56]

In the 1930s modernism characterized the development of the city as it grew. New residential areas sprang up such as the development on Gärdet while industrial development added to the growth, such as the KF manufacturing industries on Kvarnholmen located in the Nacka Municipality. In the 1950s, suburban development entered a new phase with the introduction of the Stockholm metro. The modernist developments of Vällingby and Farsta were internationally praised. In the 1960s this suburban development continued but with the aesthetic of the times, the industrialized and mass-produced blocks of flats received a large amount of criticism.
At the same time that this suburban development was taking place, the most central areas of the inner city were being redesigned, known as Norrmalmsregleringen. Sergels torg, with its five high-rise office towers was created in the 1960s, followed by the total clearance of large areas to make room for new development projects. The most notable buildings from this period is the ensemble of the House of Culture, City Theatre and National Bank at Sergels Torg, designed by architect Peter Celsing.
In the 1980s, the planning ideas of modernism were starting to be questioned, resulting in suburbs with a denser planning, such as Skarpnäck. In the 1990s this idea was taken further with the development of and old industrial area close to the inner city, resulting in a sort of mix of modernistic and urban planning in the new area of Hammarby Sjöstad.
The municipality has appointed an official "board of beauty" called "Skönhetsrådet" to protect and preserve the beauty of the city.[57]
Stockholm's architecture (along with Visby, Gotland[58]) provided the inspiration for Japanese anime director Hayao Miyazaki as he sought to evoke an idealized city untouched by World War. His creation, called Koriko, draws directly from what Miyazaki felt was Stockholm's sense of well-established architectural unity, vibrancy, independence, and safety.[59]
One of the most unusual pieces of "architecture" in Stockholm is the Jumbohostel, housed in a converted Boeing 747-200 located at Stockholm-Arlanda Airport.[60]
Museums


Stockholm is one of the most crowded museum-cities in the world with around 100 museums, visited by millions of people every year.[61]
The Vasa Museum (Swedish: Vasamuseet) is a maritime museum on Djurgården which displays the only almost fully intact 17th century ship that has ever been salvaged, the 64-gun warship Vasa that sank on her maiden voyage in 1628.
The Nationalmuseum houses the largest collection of art in the country: 16,000 paintings and 30,000 objects of art handicraft. The collection dates back to the days of Gustav Vasa in the 16th century, and has since been expanded with works by artists such as Rembrandt, and Antoine Watteau, as well as constituting a main part of Sweden's art heritage, manifested in the works of Alexander Roslin, Anders Zorn, Johan Tobias Sergel, Carl Larsson, Carl Fredrik Hill and Ernst Josephson.
Moderna Museet (Museum of Modern Art) is Sweden's national museum of modern art. It has works by noted modern artists such as Picasso and Salvador Dalí.
Skansen (in English: the Sconce) is a combined open-air museum and zoo, located on the island of Djurgården. It was founded in 1891 by Artur Hazelius (1833–1901) to show the way of life in the different parts of Sweden before the industrial era.
Other notable museums (in alphabetical order):
- ABBA: The Museum, an interactive exhibit about the pop-group ABBA
- Fotografiska, museum of photography
- Livrustkammaren, the royal armoury, located at Stockholm Palace
- Nobel Museum, devoted to the Nobel Prize, Nobel laureates, and the founder of the prize, Alfred Nobel (1833–1896)
- Nordic Museum, dedicated to the cultural history and ethnography of Sweden
- Royal Coin Cabinet, dedicated to the history of money and economic history in general
- Stockholm City Museum
- Swedish Museum of Natural History
Art galleries
Stockholm has a vibrant art scene with a number of internationally recognized art centres and commercial galleries. Amongst others privately sponsored initiatives such as Bonniers Konsthall, Magasin 3, and state supported institutions such as Tensta Konsthall and Index all show leading international and national artists. In the last few years a gallery district has emerged around Hudiksvallsgatan where leading galleries such as Andréhn-Schiptjenko, Brändström & Stene have located. Other important commercial galleries include Nordenhake, Milliken Gallery and Galleri Magnus Karlsson.
Suburbs
The Stockholm suburbs are places with diverse cultural background. Some areas in the inner suburbs, including those of Skärholmen, Tensta, Jordbro, Fittja, Husby, Brandbergen, Rinkeby, Rissne, Hallonbergen, Kista, Hagsätra, Hässelby, Farsta, Rågsved, Flemingsberg, and the outer suburb of Södertälje, have high percentages of immigrants or second generation immigrants. These mainly come from the Middle East (Assyrians, Syriacs, Turks and Kurds) and former Yugoslavia, but there are also immigrants from Africa, Southeast Asia and Latin America. Other parts of the inner suburbs, such as Täby, Danderyd, Lidingö, Flysta and, as well as some of the suburbs mentioned above, have a majority of ethnic Swedes.
Theatres
Distinguished among Stockholm's many theatres are the Royal Dramatic Theatre (Kungliga Dramatiska Teatern), one of Europe's most renowned theatres, and the Royal Swedish Opera, inaugurated in 1773.
Other notable theatres are the Stockholm City Theatre (Stockholms stadsteater), the Peoples Opera (Folkoperan), the Modern Theatre of Dance (Moderna dansteatern), the China Theatre, the Göta Lejon Theatre, the Mosebacke Theatre, and the Oscar Theatre.
Amusement park
Gröna Lund is an amusement park located on the island of Djurgården. This amusement park has over 30 attractions and many restaurants. It is a popular tourist attraction and visited by thousands of people every day. It is open from the end of April to the middle of September. Gröna Lund also serves as a concert venue.
Media

Stockholm is the media centre of Sweden. It has four nationwide daily newspapers and is also the central location of the publicly funded radio (SR) and television (SVT). In addition, all other major television channels have their base in Stockholm, such as: TV3, TV4 and TV6. All major magazines are also located to Stockholm, as are the largest literature publisher, the Bonnier group. The hit PC game Minecraft was created in Stockholm by Markus 'Notch' Persson in 2009.
Sports

The most popular spectator sports are football and ice hockey. The three most popular football clubs in Stockholm are AIK, Djurgårdens IF and Hammarby IF, who all play in the first tier, Allsvenskan. AIK play at Sweden's national stadium for football, Friends Arena in Solna, with a capacity of 54,329. Djurgårdens IF and Hammarby play at Tele2 Arena in Johanneshov, with a capacity of 30,000 spectators.
All three clubs have ice hockey teams; Djurgårdens IF plays in the first tier, AIK in the second and Hammarby in the third tier.
Historically, the city was the host of the 1912 Summer Olympics. From those days stem the Stockholms Olympiastadion which has since hosted numerous sports events, notably football and athletics. Other major sport arenas are Friends Arena the new national football stadium, Stockholm Globe Arena, a multi-sport arena and one of the largest spherical buildings in the world and the nearby indoor arena Hovet.
Beside the 1912 Summer Olympics, Stockholm hosted the 1956 Summer Olympics Equestrian Games and the UEFA Euro 1992. The city was also second runner up in the 2004 Summer Olympics bids.
Stockholm also hosted all but one of the Nordic Games, a winter multi-sport event that predated the Winter Olympics.
In 2015, the Stockholms Kungar Rugby league club were formed. They are Stockholms first Rugby league team and will play in Sweden's National Rugby league championship.
Cuisine
There are over 1000 restaurants in Stockholm.[62] As of 2013 Stockholm boasts a total of eight Michelin star restaurants, two of which have two stars.

Yearly events
- Stockholm Jazz Festival is one of Sweden's oldest festivals. The festival takes place at Skeppsholmen in July.[63]
- Stockholm Pride is the largest Pride event in the Nordic countries and takes place in the last week of July every year. The Stockholm Pride festival always ends with a parade and in 2007, 50,000 people marched with the parade and about 500,000 watched.[64]
- The Stockholm Marathon takes place on a Saturday in early June each year.
- The Nobel Banquet takes place at Stockholm City Hall every year on 10 December.
- The Stockholm Culture Festival (Swe: Stockholms kulturfestival) is a summer festival held annually around the middle of August.
- The Stockholm Water Festival (Swe: Vattenfestivalen) was a popular summer festival held annually in Stockholm between 1991 and 1999.
- Manifestation, a yearly ecumenical Christian festival with up to 25,000 participants.
- Summerburst Music festival
- The Stockholm International Film Festival is an annual film festival held in Stockholm each year since 1990.
Environment

Green city with a national urban park
Stockholm is one of the cleanest capitals in the world. The city was granted the 2010 European Green Capital Award by the EU Commission; this was Europe’s first "green capital".[65] Applicant cities were evaluated in several ways: climate change, local transport, public green areas, air quality, noise, waste, water consumption, waste water treatment, sustainable utilisation of land, biodiversity and environmental management.[66] Out of 35 participant cities, eight finalists were chosen: Stockholm, Amsterdam, Bristol, Copenhagen, Freiburg, Hamburg, Münster, and Oslo.[67] Some of the reasons why Stockholm won the 2010 European Green Capital Award were: its integrated administrative system, which ensures that environmental aspects are considered in budgets, operational planning, reporting, and monitoring; its cut in carbon dioxide emissions by 25% per capita in ten years; and its decision towards being fossil fuel free by 2050.[66] Stockholm has long demonstrated concern for the environment. The city’s current environmental program is the fifth since the first one was established in the mid-1970s.[68] In 2011, Stockholm passed the title of European Green Capital to Hamburg, Germany.[67]
Role model
In the beginning of 2010, Stockholm launched the program Professional Study Visits[69] in order to share the city’s green best practices. The program provides visitors with the opportunity to learn how to address issues such as waste management, urban planning, carbon dioxide emissions, and sustainable and efficient transportation system, among others.[65]
According to the European Cities Monitor 2010,[70] Stockholm is the best city in terms of freedom from pollution. Surrounded by 219 nature reserves, Stockholm has around 1,000 green spaces, which corresponds to 30% of the city’s area.[71] Founded in 1995, the Royal National City Park is the world’s first legally protected "national urban park".[72][73] For a description of the formation process, value assets and implementation of the legal protection of The Royal National Urban Park, see Schantz 2006 The water in Stockholm is so clean that people can dive and fish in the centre of the city.[71] In fact the waters of downtown Stockholm serve as spawning grounds for multiple fish species including trout and salmon. As for carbon dioxide emissions, the government goal is to have only clean vehicles in the city by 2011.[71]
Transport
Public transport

Stockholm has an extensive public transport system. It consists of the Stockholm Metro (Swedish: Tunnelbanan), which consist of three color-coded main lines (green, red and blue) with seven actual lines (10, 11, 13, 14, 17, 18, 19); the Stockholm commuter rail (Swedish: Pendeltågen) which runs on the State-owned railroads on four lines (35, 36, 37, 38); four light rail/tramway lines (7, 12, 21, and 22); the 891 mm narrow-gauge railway Roslagsbanan, on three lines (27, 28, 29) in the northeastern part; the local railway Saltsjöbanan, on two lines (25, 26) in the southeastern part; a large number of bus lines, and the inner-city boat line Djurgårdsfärjan. The overwhelming majority of the land-based public transport in Stockholm County (save for the airport buses/airport express trains and other few commercially viable bus lines) is organized under the common umbrella of Storstockholms Lokaltrafik (SL), an aktiebolag wholly owned by Stockholm County Council. Since the 1990s, the operation and maintenance of the SL public transport services are contracted out to independent companies bidding for contracts, such as MTR, which currently operate the Metro. The archipelago boat traffic is handled by Waxholmsbolaget, which is also wholly owned by the County Council.

SL has a common ticket system in the entire Stockholm County, which allows for easy travel between different modes of transport. The tickets are of two main types, single ticket and travel cards, both allowing for unlimited travel with SL in the entire Stockholm County for the duration of the ticket validity. Starting 1 April 2007, a new zone system (A, B, C) and price system applies for single tickets. Single tickets are now available in forms of cash ticket, individual unit pre-paid tickets, pre-paid ticket slips of 8, sms-ticket and machine ticket. Cash tickets bought at the point of travel are the most expensive and pre-paid tickets slips of 8 are the cheapest. A single ticket is valid for 75 minutes. The duration of the travel card validity depends on the exact type; they are available from 24 hours up to a year. A 30-day card costs 790 SEK (83 EUR; 130 USD). Tickets of all these types are available with reduced prices for students and persons under 20 and over 65 years of age
The City Line Project
With an estimated cost of SEK 16.8 billion (January 2007 price level), which equals 2.44 billion US dollars, the City Line, an environmentally certified project, comprises a 6 km (3.7 mi)-long commuter train tunnel (in rock and water) beneath Stockholm, with two new stations (Stockholm City and Stockholm Odenplan), and a 1.4 km (0.87 mi)-long railway bridge at Årsta. The City Line is being built by the Swedish Transport Administration in co-operation with the City of Stockholm, Stockholm County Council, and Stockholm Transport, SL. As Stockholm Central Station is overloaded, the purpose of this project is to double the city’s track capacity and improve service efficiency. Operations are scheduled to begin in 2017.[74]
Between Riddarholmen and Söder Mälarstrand, the City Line will run through a submerged concrete tunnel.[74] As a green project, the City Line includes the purification of waste water; noise reduction through sound-attenuating tracks; the use of synthetic diesel, which provides users with clean air; and the recycling of excavated rocks.[74]
Roads
Stockholm is at the junction of the European routes E4, E18 and E20. A half-completed motorway ring road exists on the south and west sides of the City Centre. A north section of the ring road will open for traffic in 2015 while the final subsea eastern section is being discussed as a future project. A bypass motorway for traffic between Northern and Southern Sweden will be built west of Stockholm 2013–2023. The many islands and waterways make extensions of the road system both complicated and expensive, and new motorways are often built as systems of tunnels and bridges.
Congestion charges

Stockholm has a congestion pricing system, Stockholm congestion tax,[75] in use on a permanent basis since 1 August 2007,[76][77] after having had a seven-month trial period in the first half of 2006.[78] The City Centre is within the congestion tax zone. All the entrances and exits of this area have unmanned control points operating with automatic number plate recognition. All vehicles entering or exiting the congestion tax affected area, with a few exceptions, have to pay 10–20 SEK (1.09–2.18 EUR, 1.49–2.98 USD) depending on the time of day between 06:30 and 18:29. The maximum tax amount per vehicle per day is 60 SEK (6.53 EUR, ).[79] Payment is done by various means within 14 days after one has passed one of the control points; one cannot pay at the control points.[80]
After the trial period was over, consultative referendums were held in Stockholm Municipality and several other municipalities in Stockholm County. The then-reigning government (Persson Cabinet) stated that they would only take into consideration the results of the referendum in Stockholm Municipality. The opposition parties (Alliance for Sweden) stated that if they were to form a cabinet after the general election—which was held the same day as the congestion tax referendums—they would take into consideration the referendums held in several of the other municipalities in Stockholm County as well. The results of the referendums were that the Stockholm Municipality voted for the congestion tax, while the other municipalities voted against it. The opposition parties won the general election and a few days before they formed government (Reinfeldt Cabinet) they announced that the congestion tax would be reintroduced in Stockholm, but that the revenue would go entirely to road construction in and around Stockholm. During the trial period and according to the agenda of the previous government the revenue went entirely to public transport.
Ferries

Stockholm has regular ferry lines to Helsinki and Turku in Finland (commonly called "Finlandsfärjan"); Tallinn, Estonia; Riga, Latvia, Åland islands and to Saint Petersburg. The large Stockholm archipelago is served by the archipelago boats of Waxholmsbolaget (owned and subsidized by Stockholm County Council).
City bikes
Between April and October, during the warmer months, it is possible to rent Stockholm City Bikes by purchasing a bike card online or through retailers.[81] Cards allow users to rent bikes from any Stockholm City Bikes stand spread across the city and return them in any stand.[82] There are two types of cards: the Season Card (valid from 1 April to 31 October) and the 3-day card. When their validity runs out they can be reactivated and are therefore reusable.[83] Bikes can be used for up to three hours per loan and can be rented from Monday to Sunday from 6 am to 10 pm.[82]
Airports
- International and domestic:
- Stockholm-Arlanda International Airport (IATA: ARN, ICAO: ESSA) is the largest and busiest airport in Sweden with 22.5 million passengers in 2014. It is located about 40 km (25 mi) north of Stockholm and serves as a hub for Scandinavian Airlines.
- Stockholm-Bromma Airport (IATA: BMA, ICAO: ESSB) is located about 8 km (5.0 mi) west of Stockholm.
- Only international:
- Stockholm-Skavsta Airport (IATA: NYO, ICAO: ESKN) is located 100 km (62 mi) south of Stockholm. It is located 5 km (3 mi) away from Södermanland County capital Nyköping.
- Stockholm-Västerås Airport (IATA: VST, ICAO: ESOW) is located 110 km (68 mi) west of Stockholm, in the city of Västerås.
Arlanda Express airport rail link runs between Arlanda Airport and central Stockholm. With a journey of 20 minutes, the train ride is the fastest way of travelling to the city center. Additionally, there are also bus lines, Flygbussarna, that run between central Stockholm and all the airports.
As of 2010 there are no airports specifically for general aviation in the Stockholm area.
Inter-city trains
Stockholm Central Station has train connections to many Swedish cities as well as to Oslo, Norway and Copenhagen, Denmark. The popular X 2000 service to Gothenburg takes three hours. Most of the trains are run by SJ AB.
International rankings
Stockholm often performs well in international rankings, some of which are mentioned below:
- In the book The Ultimate Guide to International Marathons (1997), written by Dennis Craythorn and Rich Hanna, Stockholm Marathon is ranked as the best marathon in the world.[84]
- In the 2006 European Innovation Scoreboard, prepared by the Maastricht Economic Research Institute on Innovation and Technology (MERIT) and the Joint Research Centre's Institute for the Protection and the Security of the Citizen of the European Commission, Stockholm was ranked as the most innovative city in Europe.[85]
- In the 2008 World Knowledge Competitiveness Index, published by the Centre for International Competitiveness, Stockholm was ranked as the sixth most competitive region in the world and the most competitive region outside the United States.[86]
- In the 2006 European Regional Growth Index (E-REGI), published by Jones Lang LaSalle, Stockholm was ranked fifth on the list of European cities with the strongest GDP growth forecast. Stockholm was ranked first in Scandinavia and second outside Central and Eastern Europe.[87]
- In the 2007 European Cities Monitor, published by Cushman & Wakefield, Stockholm was ranked as the best Nordic city to locate a business. In the same report, Stockholm was ranked first in Europe in terms of freedom from pollution.[88]
- In a 2007 survey performed by the environmental economist Matthew Kahn for the Reader's Digest magazine, Stockholm was ranked first on its list of the "greenest" and most "livable" cites in the world.[89]
- In a 2008 survey published by Reader's Digest magazine, Stockholm was ranked fourth in the world in its list of the "world's top ten honest cities".[90]
- In a 2008 survey published by the National Geographic Traveler magazine, Gamla stan (the old town) in Stockholm was ranked sixth on its list of rated historic places.[91]
- In a 2008 survey published by the Foreign Policy magazine, Stockholm was ranked twenty-fourth on its list of the world's most global cities.[92]
- In 2009 Stockholm was awarded the title as European Green Capital 2010, as the first Green capital ever in the European Green Capital Award scheme.
- In 2013, Stockholm was named the 8th most competitive city in the world by the Economist Intelligence Unit.[93]
Twin cities and towns
Gallery
 Old Town seen from Skeppsholmen
Old Town seen from Skeppsholmen- Skyline of Old Town
 Ship af Chapman at Skeppsholmen in Stockholm City
Ship af Chapman at Skeppsholmen in Stockholm City
 Front view of Scaniabanken
Front view of Scaniabanken
 View of the two Kungstornen buildings
View of the two Kungstornen buildings
 Northern Södermalm and the bridge to Riddarholmen
Northern Södermalm and the bridge to Riddarholmen Southern Södermalm and Johanneshov
Southern Södermalm and Johanneshov Shopping street, Drottninggatan
Shopping street, Drottninggatan Public square, Stureplan
Public square, Stureplan Nordic Museum, in Djurgården
Nordic Museum, in Djurgården Stockholm Public Library, in Vasastan
Stockholm Public Library, in Vasastan_1333972121.jpg) Sergels torg, commercial square in central Stockholm
Sergels torg, commercial square in central Stockholm Stockholm City Hall, venue of the Nobel Prize banquet
Stockholm City Hall, venue of the Nobel Prize banquet
- Aerial view of central Stockholm
 Skyline of Stockholm Palace
Skyline of Stockholm Palace Entrance of the Stockholm Olympic Stadium, built in 1912
Entrance of the Stockholm Olympic Stadium, built in 1912- Solgränd, common view of several taverns in the old districts of Stockholm
 Gamla stan, listed in Guinness World Records as one of the oldest streets with an unaltered interior
Gamla stan, listed in Guinness World Records as one of the oldest streets with an unaltered interior Hotel Bellevue in Stockholm archipelago, built in 1886
Hotel Bellevue in Stockholm archipelago, built in 1886 Utö Chuch
Utö Chuch
See also
- List of people connected to Stockholm
- Ports of the Baltic Sea
- Stockholm syndrome
- Holmium – a chemical element named after Stockholm
Notes
References
- ↑ "20 Famous Cities You Can Visit Without Breaking The Bank – TripAdvisor Vacation Rentals". TripAdvisor Vacation Rentals. Retrieved 10 February 2016.
- ↑ "Localities 2010, area, population and density in localities 2005 and 2010 and change in area and population". Statistics Sweden. 29 May 2012. Archived from the original on 17 December 2012.
- 1 2 3 "Folkmängd i riket, län och kommuner 31 mars 2016 och befolkningsförändringar 1 januari–31 mars 2016. Totalt". SCB. Retrieved 2 July 2016.
- 1 2 "Stockholm" (in Swedish). Nationalencyklopedin. Retrieved 30 January 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 "Folkmängd per tätort och småort 2010, per kommun" (XLS) (in Swedish). Statistics Sweden. 20 June 2013. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- ↑ "Stockholm". Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.
- ↑ Hedelin, Per (1997). Svenska uttals-lexikon. Stockholm: Norstedts.
- 1 2 "Population". The Nordic Council. Retrieved 31 December 2014.
Stockholm is the largest city with 2.1 million people, followed by Copenhagen and Oslo with 1.2 million each.
- ↑ "Finansiella sektorn bär frukt — Analys av den finansiella sektorn ur ett svenskt perspektiv" (PDF). Government of Sweden. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 July 2014. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ↑ "Regional GDP per capita in the EU in 20 10 : eight capital regions in the ten first places" (PDF). Eurostat. 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 April 2013. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ↑ "The World According to GaWC 2012". Loughborough University/GaWC. 13 January 2014. Retrieved 30 January 2014.
- ↑ "2012 Global Cities Index and Emerging Cities Outlook" (PDF). A.T. Kearney et al. 2012. Retrieved 30 January 2014.
- ↑ Olshov, Anders (2010). The location of nordic and global headquarters 2010. Malmö: Øresundsinstituttet. p. 197. OCLC 706436140.
Stockholm is the main centre of headquarters in the Nordic region
- ↑ "World University Rankings 2011–12: Europe". TSL Education Ltd. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ↑ "Top 5 non-art museums". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ↑ "Who visits Vasa". Vasamuseet. Archived from the original on 27 July 2014. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ↑ "Stockholm's underground subway art". BBC. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ↑ "Stockholm's Subway System is the World's Largest Underground Art Museum". Inhabitat. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ↑ "Magic in the Metro". Businessweek. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ↑ "Allt fler myndigheter hamnar i Stockholm" (in Swedish). Riksdag & Departement. 27 April 2012. Archived from the original on 1 May 2012. Retrieved 1 February 2014.
- ↑ "Kammarrättens hus" (in Swedish). National Property Board of Sweden. Archived from the original on 4 February 2014. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- ↑ "Bondeska palatset" (in Swedish). National Property Board of Sweden. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- ↑ "The Swedish Government Offices — a historical perspective". The Government Offices of Sweden. Archived from the original on 18 February 2014. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- ↑ "How the Riksdag works". The Riksdag. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- ↑ "Sagerska huset" (in Swedish). National Property Board of Sweden. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- ↑ "The Royal Palace of Stockholm". The Royal Court of Sweden. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- 1 2 "Drottningholm Palace". The Royal Court of Sweden. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- ↑ Carlquist, Erik; Hogg, Peter C.; Österberg, Eva (2011-12-01). The Chronicle of Duke Erik: A Verse Epic from Medieval Sweden. Nordic Academic Press. ISBN 9789185509577.
- ↑ Stockholm: A Cultural History. Tony Griffiths (2009). Oxford University Press US. p.9. ISBN 0-19-538638-8
- ↑ Feargus O'Sullivan. "The Sky Walk Plan That Could Change the Face of Stockholm – CityLab". CityLab. Retrieved 17 March 2016.
- ↑ In official contexts, the municipality of Stockholm calls itself "stad" (or City), as do a small number of other Swedish municipalities, and especially the other two Swedish metropolis: Gothenburg and Malmö. However, the term city has administratively been discontinued in Sweden. See also city status in Sweden
- ↑ Paris#Climate
- ↑ London#Climate
- ↑ "Arctic Tree Line Map of Canada". Jackson School of International Studies. Retrieved 8 October 2015.
- ↑ "Stockholm — Bromma". Data.smhi.se. Retrieved 11 April 2014.
- ↑ "Stockholm — Bromma". Data.smhi.se. Retrieved 1 December 2012.
- ↑ "Temperaturrekord i Stockholm och Uppsala | Meteorologi | Kunskapsbanken" (in Swedish). SMHI. 14 November 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2012.
- ↑ "Vintern 2010–2011: Vinterns lägsta temperaturer | Klimatdata | SMHI" (in Swedish). Smhi.se. Retrieved 14 January 2012.
- ↑ "Temperaturrekord i Stockholm och Uppsala" [Temperature Records in Stockholm and Uppsala] (in Swedish). Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute. 2009. Retrieved 13 June 2010.
- ↑ "Stockholm Climate Normals 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 27 November 2013.
- ↑ "Sunshine Hours of Stockholm" (PDF). Sveriges Meteorologiska och Hydrologiska Institut. Retrieved 19 March 2012.
- ↑ Svenska Almanackan published on an annual basis since 1906 by Almanacksförlaget (which holds a Royal warrant) in cooperation with Stockholm's Observatory. Valid for latitude 59 degrees and 21 minutes north (and longitude 12 time minutes east of the Swedish time meridian, which is 15 degrees East)
- 1 2 3 "City Governance". Stockholm City. Retrieved 23 July 2014.
- ↑ "Fakta om företagandet i Stockholm – 2012. page 18, Stockholm Business Region website" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 July 2012. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- ↑ "Fakta om företagandet i Stockholm – 2012. page 6, Stockholm Business Region website" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 July 2012. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- ↑ Statistical Yearbook of Stockholm 2006, section Labour Market and Manufacturing, p. 244 pdf file
- ↑ "Stockholm University — Find Housing On Your Own". Su.se. 11 May 2012. Archived from the original on 4 May 2012. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- ↑ "Emerging housing crisis for students". Stockholmnews.com. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- ↑ "Fakta om företagandet i Stockholm – 2012. page 13, Stockholm Business Region website" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 July 2012. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- 1 2 3 Stockholm Statistical Yearbook, 2006 (Stockholms statistiska årsbok för 2006) City of Stockholm website, May 2006. The numbers provided by Stockholm Office of Research and Statistics, or Utrednings- och statistikkontoret (USK), in Swedish. (USK official web information in English
- ↑ "Statistisk arsbok for Stockholm 2015" (PDF). Statistik om Stockholm. Retrieved 2 September 2015.
- ↑ OECD Territorial Reviews: Stockholm, May 2006
- ↑ "Population in the country, counties and municipalities on 31/12/2012 and Population Change in 2012". Statistics Sweden. 20 February 2013. Archived from the original on 16 December 2013. Retrieved 30 January 2014.
- ↑ "Befolkningen i Stockholm 1252–2005" (PDF) (in Swedish). Stockholm Municipality. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 February 2014. Retrieved 30 January 2014.
- ↑ "Three world heritage sites". Stockholm Visitors Board. Archived from the original on 19 February 2014. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- 1 2 "World Heritage Skogskyrkogården". The Stockholm City Museum. Archived from the original on 9 January 2014. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- ↑ "Skönhetsrådet". Stockholm.se. 17 February 2012. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- ↑ Hayao Miyazaki (director) (3 February 2010). Creating Kiki's Delivery Service (DVD) (in English and Japanese). Disney Presents Studio Ghibli.
- ↑ Helen McCarthy Hayao Miyazaki: Master of Japanese Animation pub Stone Bridge Press (Berkeley, CA) 1999 ISBN 1-880656-41-8, pages 144 and 157
- ↑ "History and curiosities". Jumbohostel. Archived from the original on 12 March 2009. Retrieved 4 September 2009.
- ↑ "Museer & attraktioner — Stockholms officiella besöksguide, kartor, hotell och evenemang". Stockholmtown.com. Archived from the original on 7 March 2009. Retrieved 6 May 2009.
- ↑ 1997 there were 1123 restaurants with permission to serve alcoholic drinks "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 July 2007. Retrieved 18 March 2016.
- ↑ "Stockholm Jazz". Stockholm Jazz. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- ↑ "Stockholm Pride". Stockholm Pride. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- 1 2 "Stockholm – European Green Capital 2010". Ec.europa.eu. 23 February 2009. Archived from the original on 11 May 2012. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- 1 2 "European Green Capital". international.stockholm.se. 1 March 2012. Archived from the original on 24 May 2012. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- 1 2 "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 27 August 2010. Retrieved 18 March 2016.
- ↑ "A sustainable city". international.stockholm.se. Archived from the original on 29 May 2012. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 27 February 2010. Retrieved 18 March 2016.
- ↑ "Cushman & Wakefield. 2010 European Cities Monitor" (PDF). p. 2. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 May 2012. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- 1 2 3 "Environment". international.stockholm.se. 10 February 2012. Archived from the original on 13 March 2012. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- ↑ Ohlsen, B. (2010). ‘‘Stockholm encounter’’ (2nd Ed.). Hong Kong, China: Lonely Planet Publications Pty Ltd (p.163)
- ↑ Schantz, P. 2006. The Formation of National Urban Parks: a Nordic Contribution to Sustainable Development? In: The European City and Green Space; London, Stockholm, Helsinki and S:t Petersburg, 1850–2000 (Ed. Peter Clark), Historical Urban Studies Series (Eds. Jean-Luc Pinol & Richard Rodger), Ashgate Publishing Limited, Aldershot.
- 1 2 3 https://wayback.archive.org/web/20110501132319/http://www.trafikverket.se/Om-Trafikverket/Spraksida/English-Engelska/Railway-construction-projects/Stockholm-City-Line/. Archived from the original on 1 May 2011. Retrieved 16 November 2010. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ "Congestion tax in Stockholm from 1 August". Swedish Road Administration. Archived from the original on 2 March 2007. Retrieved 2 August 2007.
- ↑ "Trängselskatt i Stockholm". Swedish Road Administration. Archived from the original on 9 July 2007. Retrieved 1 August 2007.
- ↑ "Odramatisk start för biltullarna". Dagens Nyheter. 1 August 2007. Archived from the original on 30 September 2007. Retrieved 1 August 2007.
- ↑ "Stockholmsförsöket". Stockholmsförsöket. Retrieved 18 July 2007.
- ↑ "Tider och belopp". Swedish Road Administration. Archived from the original on 3 July 2007. Retrieved 1 August 2007.
- ↑ "Betalning". Swedish Road Administration. Archived from the original on 29 June 2007. Retrieved 1 August 2007.
- ↑ "Traffic and public transport". international.stockholm.se. Archived from the original on 21 June 2012. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- 1 2 Archived 25 September 2010 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "To buy a bike card". Citybikes.se. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- ↑ Craythorn, Dennis; Hanna, Rich (1997). The Ultimate Guide to International Marathons. United States: Capital Road Race Publications. ISBN 978-0-9655187-0-3.
- ↑ "European Innovation Scoreboard" (PDF). Maastricht Economic Research Institute on Innovation and Technology; Institute for the Protection and the Security of the Citizen. 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 December 2008. Retrieved 1 December 2008.
- ↑ "The World Knowledge Competitiveness Index". Centre for International Competitiveness. 2008. Retrieved 1 December 2008.
- ↑ "London takes top spot from Paris in Jones Lang LaSalle's new European Regional Growth Barometer". Jones Lang LaSalle. 7 November 2006. Archived from the original on 8 January 2007. Retrieved 1 December 2008.
- ↑ "European Cities Monitor" (PDF). Cushman & Wakefield. 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 December 2008. Retrieved 1 December 2008.
- ↑ Kahn, Matthew. "Living Green". Reader's Digest. Archived from the original on 29 September 2008. Retrieved 1 December 2008.
- ↑ Marty, Phil (23 November 2008). "Phoning in search of an honest man". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved 3 September 2016.
- ↑ Tourtellot, Jonathan (November–December 2008). "Historic Places Rated". National Geographic Traveler. Retrieved 1 December 2008.
- ↑ "The 2008 Global Cities Index". Foreign Policy. November 2008. Archived from the original on 10 January 2010. Retrieved 9 December 2008.
- ↑ Steven, Perlberg (9 June 2013). "The 17 Most Competitive Cities In The World". Business Insider. Retrieved 30 January 2014.
External links
- Stockholm—official website
- Stockholm Visitors Board—the official visitors' guide
- LUX Magazine: Scandic Sensation