Lung
| Lung | |
|---|---|
 Diagram of the lungs with the respiratory tract visible, and different colours for each lobe | |
| Details | |
| System | Respiratory system |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | pulmo |
| Greek | πνεύμων (pneumon) |
| MeSH | A04.411 |
| TA | A06.5.01.001 |
| FMA | 68877 |

The lungs are the primary organs of respiration in humans and many other animals including a few fish and some snails. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the atmosphere and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their musculoskeletal systems to support and foster breathing. In early tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the primary muscle that drives breathing is the diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes vocal sounds including human speech possible.
Humans have two lungs, a right lung and a left lung. They are situated within the thoracic cavity of the chest. The right lung is bigger than the left, which shares space in the chest with the heart. The lungs together weigh approximately 1.3 kilograms (2.9 lb), and the right is heavier. The lungs are part of the lower respiratory tract that begins at the trachea and branches into the bronchi and bronchioles and which receive air breathed in via the conducting zone. These divide until air reaches microscopic alveoli, where the process of gas exchange takes place. Together, the lungs contain approximately 2,400 kilometres (1,500 mi) of airways and 300 to 500 million alveoli. The lungs are enclosed within a sac called the pleural sac which allows the inner and outer walls to slide over each other whilst breathing takes place, without much friction. This sac encloses each lung and also divides each lung into sections called lobes. The right lung has three lobes and the left has two. The lobes are further divided into bronchopulmonary segments and lobules. The lungs have a unique blood supply, receiving deoxygenated blood sent from the heart for the purposes of receiving oxygen (the pulmonary circulation) and a separate supply of oxygenated blood (the bronchial circulation).
The tissue of the lungs can be affected by a number of diseases, including pneumonia and lung cancer. Chronic diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and emphysema can be related to smoking or exposure to harmful substances. Diseases such as bronchitis can also affect the respiratory tract.
In embryonic development, the lungs begin to develop as an outpouching of the foregut, a tube which goes on to form the upper part of the digestive system. When the lungs are formed the fetus is held in the fluid-filled amniotic sac and so they do not function to breathe. Blood is also diverted from the lungs through the ductus arteriosus. At birth however, air begins to pass through the lungs, and the diversionary duct closes, so that the lungs can begin to respire. The lungs only fully develop in early childhood.
Medical terms related to the lung often begin with pulmo-, from the Latin pulmonarius (of the lungs) as in pulmonology, or with pneumo- (from Greek πνεύμων "lung") as in pneumonia.
Structure

Gross anatomy

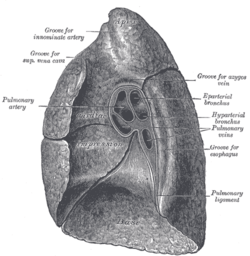
The lungs are located in the chest on either side of the heart in the rib cage. They are conical in shape with a narrow rounded apex at the top and a broad base that rests on the diaphragm.[1] The apex of the lung extends into the root of the neck, reaching shortly above the level of the sternal end of the first rib. The lungs stretch from close to the backbone in the rib cage to the front of the chest and downwards from the lower part of the trachea to the diaphragm.[1] The left lung shares space with the heart, with an impression in its medial surface called the cardiac impression.[2] The front and outer sides of the lung face the ribs, which make light indendations on their surfaces. The bottom of the lungs is smooth and rests on the diaphragm, matching its concavity. The medial surface of the lungs faces towards the centre of the chest, and lies against the heart, great vessels, and the carina where the two main bronchi branch off from the base of the trachea.[2]
Both lungs have a central recession called the hilum at the root of the lung, where the blood vessels and airways pass into the lungs.[1] There are also bronchopulmonary lymph nodes on the hilum.[2]
The lungs are surrounded by the pulmonary pleurae. The pleurae are two serous membranes; the outer parietal pleura lines the inner wall of the rib cage and the inner visceral pleura directly lines the surface of the lungs. Between the pleurae is a potential space called the pleural cavity containing pleural fluid. Each lung is divided into lobes by the invaginations of the pleura as fissures. The fissures are double folds of pleura that section the lungs and help in their expansion.[3]
The lobes of the lungs are further divided into bronchopulmonary segments based on the locations of bronchioles. Segments for the left and right lung are shown in the table.[4] The segmental anatomy is useful clinically for localising disease processes in the lungs.[4]
Right lung
| Right lung | Left lung |
|---|---|
Upper
|
Upper
Lower
Lingula
|
The right lung has both more lobes and segments than the left. It is divided into three lobes, an upper, middle, and a lower, by two fissures, one oblique and one horizontal. The upper, horizontal fissure, separates the upper from the middle lobe. It begins in the lower oblique fissure near the posterior border of the lung, and, running horizontally forward, cuts the anterior border on a level with the sternal end of the fourth costal cartilage; on the mediastinal surface it may be traced backward to the hilum.[1]
The lower, oblique fissure, separates the lower from the middle and upper lobes, and is closely aligned with the oblique fissure in the left lung.[1][3]
The mediastinal surface of the right lung is indented by a number of nearby structures. The heart sits in an impression called the cardiac impression. Above the hilum of the lung is an arched groove for the azygos vein, and above this is a wide groove for the superior vena cava and right innominate vein; behind this, and close to the top of the lung is a groove for the innominate artery. There is a groove for the esophagus behind the hilum and the pulmonary ligament, and near the lower part of the esophageal groove is a deeper groove for the inferior vena cava before it enters the heart.[2]
Left lung
The left lung is divided into two lobes, an upper and a lower, by the oblique fissure, which extends from the costal to the mediastinal surface of the lung both above and below the hilum.[1] The left lung, unlike the right, does not have middle lobe, though it does have a homologous feature, a projection of the upper lobe termed the “lingula”. Its name means “little tongue”. The lingula on the left serves as an anatomic parallel to the right middle lobe, with both areas being predisposed to similar infections and anatomic complications.[5][6] There are two bronchopulmonary segments of the lingula: superior and inferior.[1]
The mediastinal surface of the left lung has a large cardiac impression where the heart sits. This is deeper and larger than that on the right lung, at which level the heart projects to the left.[2]
On the same surface, immediately above the hilum, is a well-marked curved groove for the aortic arch, and a groove below it for the descending aorta. The left subclavian artery, a branch off the aortic arch, sits in a groove from the arch to near the apex of the lung. A shallower groove in front of the artery and near the edge of the lung, lodges the left innominate vein. The esophagus may sit in a wider shallow impression at the base of the lung.[2]

Respiratory system
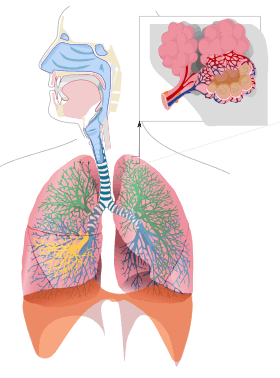
The lung is part of the respiratory system, and contains the majority of the lower respiratory tract after the trachea.[7] The trachea receives air from the pharynx and travels down to a place where it splits (the carina) into a right and left bronchus. These supply air to the right and left lungs, splitting progressively into the secondary and tertiary bronchi for the lobes of the lungs, and into smaller and smaller bronchioles until they become the respiratory bronchioles. These in turn supply air through alveolar ducts into the alveoli, where the exchange of gases take place.[7] Oxygen diffuses through the walls of the alveoli into the enveloping capillaries (small blood vessels).[8]
Estimates of the total surface area of lungs vary from 50 to 75 square metres (540 to 810 sq ft);[7][9] roughly the same area as one side of a tennis court.[9][10]
The bronchi in the conducting zone are reinforced with hyaline cartilage in order to hold open the airways. The bronchioles have no cartilage and are surrounded instead by smooth muscle.[9] Air is warmed to 37 °C (99 °F), humidified and cleansed by the conduction zone; particles from the air being removed by the cilia on the respiratory epithelium lining the passageways.[11]
Blood supply
The human lung has a dual blood supply.[7]
The tissue of the lungs receive oxygenated blood via the bronchial circulation, a series of arteries that leave the aorta and are part of the systemic circulation. There are usually three arteries, and they branch alongside the bronchi and bronchioles.[7] The blood volume of the lungs is about 450 millilitres on average, about 9 per cent of the total blood volume of the entire circulatory system. This quantity can easily fluctuate from between one-half and twice the normal volume.[12]
The lungs also receive deoxygenated blood from the heart and supply it with oxygen, in a process known as respiration. In this process, venous blood in the body collects in the right atrium and is pumped from the right ventricle through the pulmonary trunk and the pulmonary arteries into the left and right lungs. Blood passes through small capillaries next to the alveoli in the lung, receives oxygen, and travels back to the heart. This is called the pulmonary circulation. The oxygenated blood is then pumped to the rest of the body.[7]
Nerve supply
The lungs are supplied by nerves of the autonomic nervous system. Input from the parasympathetic nervous system occurs via the vagus nerve. When stimulated by acetylcholine, this causes constriction of the smooth muscle lining the bronchus and bronchioli, and increases the secretions from glands.[13] The lungs also have a sympathetic tone from norepinephrine acting on the beta 2 receptors in the respiratory tract, which causes bronchodilation.[13]
The action of breathing takes place because of nerve signals sent by the respiratory centres in the brainstem, along the phrenic nerve to the diaphragm. This is described in more detail below.[14]
Microanatomy

The lungs contain the respiratory tract and its lining, which terminate in alveoli, the tissue in between (called interstitium or parenchyma), and veins, arteries, nerves and lymphatic vessels.[2][15]
The respiratory tract begins with the trachea and bronchi. These structures are lined with columnar epithelial cells that possess cilia, small frond-like projections. Interspersed with the epithelial cells are goblet cells which produce mucous, and club cells with actions similar to macrophages. Surrounding these in the trachea and bronchi are cartilage rings, which help to maintain stability.[9] Bronchioles possess the same columnar epithelial lining, but are not surrounded by cartilage rings. Instead, they are encircled by a layer of smooth muscle.[9] The respiratory tract ends in lobules. These consist of a respiratory bronchiole, which branches into alveolar ducts and alveolar sacs, which in turn divide into alveoli.[2]
The epithelial cells throughout the respiratory tract secrete epithelial lining fluid (ELF), the composition of which is tightly regulated and determines how well mucociliary clearance works.[16][17]:Section 4 pages 7–8 (Page 4–7ff) which in turn is coated with a layer of surfactant.[7]
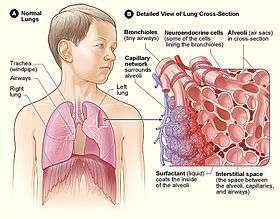
Alveoli consist of two types of alveolar cell and an alveolar macrophage. The two types of cell are known as type I and type II alveolar cells[7] (also known as pneumocytes).[2] Types I and II make up the walls and septa of the alveoli. Type I cells provide 95% of the surface area of each alveoli and are flat ("squamous"), and Type II cells generally cluster in the corners of the alveoli and have a cuboidal shape.[9] Despite this, cells occur in a roughly equal ratio of 1:1 or 6:4.[7][9]
Type I are squamous epithelial cells that make up the alveolar wall structure. They have extremely thin walls that enable an easy gas exchange.[7] These type I cells also make up the alveolar septa which separate each alveolus. The septa consist of an epithelial lining and associated basement membranes.[9] Type I cells are not able to divide, and consequently rely on differentiation from Type II cells.[9]
Type II are larger and they line the alveoli and produce and secrete ELF and surfactant.[7] Type II cells are able to divide and differentiate to Type 1 cells.[9]
The alveolar macrophages have an important immunological role. They remove substances which deposit in the alveoli including loose red blood cells that have been forced out from blood vesels.[9]
The lung is surrounded by a serous membrane of visceral pleura, which has an underlying layer of loose connective tissue attached to the substance of the lung.[18]
Development

The development of the human lungs arise from the laryngotracheal groove and develop to maturity over several weeks in the foetus and for several months following birth.[19] The larynx, trachea, bronchi and lungs begin to form during the fourth week of embryogenesis.[20] from the respiratory bud (or diverticulum) which appears ventrally to the caudal portion of the foregut.[21]
At the end of the fourth week the lung bud divides into two, the right and left primary bronchial buds.[22] During the fifth week the right bud branches into three secondary bronchial buds and the left branches into two secondary bronchial buds. These give rise to the lobes of the lungs, three on the right and two on the left. Over the following week, the secondary buds branch into tertiary buds, about ten on each side.[22] From the sixth week to the sixteenth week, the major elements of the lungs appear except the alveoli.[23] From week 16 to week 26, the bronchi enlarge and lung tissue becomes highly vascularised. Bronchioles and alveolar ducts also develop. During the period covering the 26th week until birth the important blood-air barrier is established. Specialised type I alveolar cells where gas exchange will take place, together with the type II alveolar cells that secrete pulmonary surfactant, appear. The surfactant reduces the surface tension at the air-alveolar surface which allows expansion of the terminal saccules. These saccules form at the end of the bronchioles and their appearance marks the point at which limited respiration would be possible.[24]
First breath
At birth, the baby's lungs are filled with fluid secreted by the lungs and are not inflated. After birth its central nervous system reacts to the sudden change in temperature and environment. This triggers the first breath, within about 10 seconds after delivery.[25] Before birth, the lungs are filled with fetal lung fluid.[26] After the first breath, the fluid is quickly absorbed into the body or exhaled. The resistance in the lung's blood vessels decreases giving an increased surface area for gas exchange, and the lung begins to breathe spontaneously. This accompanies other changes which result in an increased amount of blood entering the lung tissues.[25]
At birth the lungs are very undeveloped with only a fraction of the alveoli present. The alveoli continue to form until the third year. Inter alveoli septa have a double capillary network instead of the single network of the developed lung. Only after the maturation of the capillary network can the lung enter a normal phase of growth. Following the early growth in numbers of alveoli there is another stage of the alveoli being enlarged.[27]
Function
Breathing

Breathing refers to the process by which air enters and leaves the lungs.[28] It is largely driven by the muscular diaphragm at the bottom of the thorax. Contraction of the diaphragm pulls the bottom of the cavity in which the lung is enclosed downward, increasing volume and thus decreasing pressure, causing air to flow into the airways. A number of muscles assist in this action, including the intercostal muscles and muscles that line the abdominal wall. The lung is not capable of expanding itself, and only expands because of a negative pressure between the two pleural walls outside the lung. The lungs are pulled by this negative pressure and expand or contract to fill it out.[29] This draws air into the lungs, which passes through the respiratory tract and into the alveoli, where respiration occurs.[13]
During normal breathing, exhalation is passive and no muscles are contracted (the diaphragm relaxes).[13]
The process of breathing occurs because of signals sent along the phrenic nerve in the respiratory centres situated in the medulla of the brainstem. The respiratory centres are situated below the fourth ventricle and contains two main groups of neurons, a ventral respiratory group and a dorsal respiratory group. The ventral respiratory group is responsible for muscle movements associated with respiration (such as of the pharynx, larynx and intercostal muscles) and may contain the "pacemaker" cells responsible for driving the rate of respiration in the pre-Botzinger complex. The dorsal respiratory group seems primarily responsible for control of the diaphragm and integration of signals transmitted back via the vagus nerve that affect the rate of respiration.[14] Within these two groups are mixed groups of nerves, inspiratory neurons, and expiratory neurons. These spontaneously generate signals (action potentials) responsible for inspiration and expiration which are then transmitted to the diaphragm by the phrenic nerve.[14]
A number of factors influence the rate of breathing. Carbon dioxide levels, particularly the arterial and cerebrospinal fluid levels, detected by medullary central chemoreceptors, cause an increase in the rate of breathing when high and a decrease when low. The acidity of blood, detected by peripheral chemoreceptors, causes an increase in the rate of breathing when low and a decrease when high. Significant hypoxia, primarily detected by peripheral chemoreceptors in the aortic body, can cause an increase in the rate of breathing. Factors internal to the lung, including pulmonary stretch or detection of irritants, can also stimulate breathing.[14]
Respiration

Respiration is the process by which oxygen is taken into the body and carbon dioxide is expelled.[30] Respiration is divided into 'inspiration, in which air is taken into the lungs, and expiration, in which it is expelled from them. This gas exchange takes place in the alveoli during breathing.[7]
In humans, the trachea divides into the two main bronchi that enter the roots of the lungs. The bronchi continue to divide within the lung, and after multiple divisions, give rise to bronchioles. The bronchial tree continues branching until it reaches the level of terminal bronchioles, which lead to respiratory bronchioles and alveolar sacs. Alveolar sacs, are made up of clusters of alveoli, like individual grapes within a bunch. The individual alveoli are tightly wrapped in capillaries and it is here that gas exchange actually occurs. Deoxygenated blood from the heart is pumped through the pulmonary artery to the lungs, where oxygen diffuses into blood and is exchanged for carbon dioxide in the hemoglobin of the erythrocytes. The oxygen-rich blood returns to the heart via the pulmonary veins to be pumped back into systemic circulation.[7]
Protection
The lungs possess several characteristics which protect against infection. The lung tract is lined by epithelia with hair-like projections called cilia that beat rhythmically and carry mucous. This mucociliary clearance is an important defence system against air-borne infection. The dust particles and bacteria in the inhaled air are caught in the mucous layer present at the mucosal surface of respiratory passages and are moved up towards the pharynx by the rhythmic upward beating action of the cilia.[9][31][32] The lining of the lung also secretes immunoglobulin A which protects against respiratory infections;[31] goblet cells secrete mucous[9] which also contains contains several antimicrobial compounds such as defensins, antiproteases, and antioxidates.[31] In addition, the lining of the lung also contains macrophages, immune cells which engulf and destroy debris and microbes that enter the lung in a process known as phagocytosis; and dendritic cells which present antigens to activate components of the adaptive immune system such as T-cells and B-cells.[31]
The size of the respiratory tract and the flow of air also protect the lungs from larger particles. Smaller particles deposit in and behind the mouth, and larger particles are trapped after inhalation by nose hairs.[31]
Other
In addition to their function in respiration, the lungs also have a number of other functions. They are involved in the maintenance of homeostasis. They help in the regulation of blood pressure as part of the renin-angiotensin system. The inner lining of the blood vessels secretes angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) an enzyme that catalyses the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II.[33] The lungs are involved in the blood's acid-base homeostasis by expelling carbon dioxide when breathing.[29][34]
The lungs also serve a protective role. Several blood-borne substances, such as a few types of prostaglandins, leukotrienes, serotonin and bradykinin, are excreted through the lungs.[33] Drugs and other substances can be absorbed, modified or excreted in the lungs.[29][35] The lungs filter out small blood clots from veins and prevent them from entering arteries and causing strokes.[34]
The lungs also play a pivotal role in speech by providing air and airflow for the creation of vocal sounds.[29][36]
Clinical significance
Human lungs can be affected by a variety of diseases. Pulmonology is the medical speciality that deals with diseases involving the respiratory tract,[37] and cardiothoracic surgery is the surgical field that deals with surgery of the lungs.[38]
Infections of the lung tissue are called pneumonia, of the respiratory tract are called bronchitis or bronchiolitis, and of the pleurae surrounding the lungs pleurisy. Many infections are due to bacteria or viruses, however not all causes of pneumonia or bronchial tree inflammation are caused by infection. One important cause of bacterial pneumonia is tuberculosis.[31] Chronic infections often occur in those with immunodeficiency and can include a fungal infection by Aspergillus fumigatus that can lead to an aspergilloma forming in the lung.[31][39]
A pulmonary embolism is a blood clot that becomes lodged in the pulmonary arteries. The majority of emboli arise because of deep vein thrombosis in the legs. Pulmonary emboli may be investigated using a ventilation/perfusion scan, a CT scan of the arteries of the lung, or blood tests such as the D-dimer.[31] Pulmonary hypertension describes an increased pressure at the beginning of the pulmonary artery that has a large number of differing causes.[31] Other rarer conditions may also affect the blood supply of the lung, such as granulomatosis with polyangiitis, which causes inflammation of the small blood vessels of the lungs and kidneys.[31]
A lung contusion is a bruise caused by chest trauma. It results in hemorrhage of the alveoli causing a build-up of fluid which can impair breathing, and this can be either mild or severe. The function of the lungs can also be affected by compression from fluid in the pleural cavity pleural effusion, or other substances such as air (pneumothorax), blood (hemothorax), or rarer causes. These may be investigated using a chest X-ray or CT scan, and may require the insertion of a surgical drain until the underlying cause is identified and treated.[31]
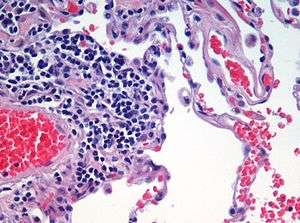
Asthma, chronic bronchitis, bronchiectasis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are all obstructive lung diseases characterised by airway obstruction. This limits the amount of air that is able to enter alveoli because of constriction of the bronchial tree, due to inflammation. Obstructive lung diseases are often identified because of symptoms and diagnosed with pulmonary function tests such as spirometry. Many obstructive lung diseases are managed by avoiding triggers (such as dust mites or smoking), with symptom control such as bronchodilators, and with suppression of inflammation (such as through corticosteroids) in severe cases. One common cause of COPD and emphysema is smoking, and common causes of bronchiectasis include severe infections and cystic fibrosis. The definitive cause of asthma is not yet known.[31]
Some types of chronic lung diseases are classified as restrictive lung disease, because of a restriction in the amount of lung tissue involved in respiration. These include pulmonary fibrosis which can occur when the lung is inflamed for a long period of time. Fibrosis in the lung replaces functioning lung tissue with fibrous connective tissue. This can be due to a large variety of occupational diseases such as Coalworker's pneumoconiosis, autoimmune diseases or more rarely to a reaction to medication.[31]
Lung cancer can can either arise directly from lung tissue or as a result of metastasis from another part of the body. There are two main types of primary tumour described as either small-cell or non-small-cell lung carcinomas. The major risk factor for cancer is smoking. Once a cancer is identified it is staged using scans such as a CT scan and a sample of tissue (a biopsy) is taken. Cancers may be treated by surgically removing the tumour, radiotherapy, chemotherapy or combinations thereof, or with the aim of symptom control.[31]Lung cancer screening is being recommended in the United States for high-risk populations.[40]
Congenital disorders include cystic fibrosis, pulmonary hypoplasia (an incomplete development of the lungs)[41]congenital diaphragmatic hernia, and infant respiratory distress syndrome caused by a deficiency in lung surfactant. An azygos lobe is a congenital anatomical variation which though usually without effect can cause problems in thoracoscopic procedures.[42]
Lung function testing

Lung function testing is carried out by evaluating a person's capacity to inhale and exhale in different circumstances.[43] The inhaled and exhaled by a person at rest is the tidal volume (normally 500-750mL); the inspiratory reserve volume and expiratory reserve volume are the additional amounts a person is able to forcibly inhale and exhale respectively. The summed total of forced inspiration and expiration is a person's vital capacity. Not all air is expelled from the lungs even after a forced breath out; the remainder of the air is called the residual volume. Together these terms are referred to as lung volumes.[43]
Pulmonary plethysmographs are used to measure functional residual capacity.[44] Functional residual capacity cannot be measured by tests that rely on breathing out, as a person is only able to breathe a maximum of 80% of their total functional capacity.[45] The total lung capacity depends on the person's age, height, weight, and sex, and normally ranges between 4 and 6 litres.[43] Females tend to have a 20–25% lower capacity than males. Tall people tend to have a larger total lung capacity than shorter people. Smokers have a lower capacity than nonsmokers. Thinner persons tend to have a larger capacity, and capacity can be increased by physical training as much as 40%.[45]
Other lung function tests include spirometry, measuring the amount (volume) and flow of air that can be inhaled and exhaled. The maximum volume of breath that can be exhaled is called the vital capacity. In particular, how much a person is able to exhale in one minute (called FEV1) as a proportion of how much they are able to exhale in total (FEV). This ratio, the FEV1/FEV ratio, is important to distinguish whether a disease is restrictive or obstructive.[31][43]
Other animals
Birds

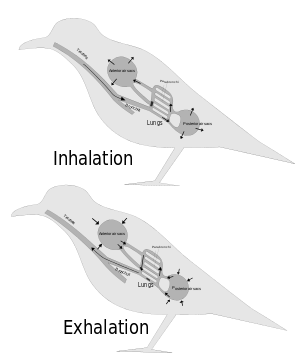
The lungs of birds are relatively small, but are connected to 8–9 air sacs that extend through much of the body, and are in turn connected to air spaces within the bones. On inspiration, air travels through the trachea of a bird into the 8–9 air sacs. Air then travels continuously from the air sacs at the back, through the lungs, and to the air sacs at the front. From here, air is expelled. This type of lung construction is called a circulatory lung, as distinct from the bellows lung possessed by other animals.[46] Lungs are relatively fixed in size, unlike the fluctuating size of a bellows-type lung.[47] This means that birds are able to extract a greater concentration of oxygen from inhaled air. Birds are thus equipped to fly at altitudes at which mammals would succumb to hypoxia. This also allows them to sustain a higher metabolic rate than most equivalent weight mammals.[46]
The lungs of birds are honeycomb-like and contain millions of tiny passages called parabronchi. Small sacs called called atria radiate from the walls of the tiny passages, and are the site of gas exchange. Gas exchange occurs by diffusion in these walls, as gas travels between the blood vessels and the lumen of each parabronchus.[47]
The air sacs, which hold air, do not contribute much to gas exchange, despite being thin-walled, as they are poorly vascularised. The air sacs expand and contract due to changes in the volume in the thorax and abdomen. This volume change is caused by the movement of the sternum and ribs and this movement is often synchronised with movement of the flight muscles.[48]
This typical system is one of two types of parabronchi found in birds, called paleopulmonic parabronchi and is found in all birds. Some bird species also have a lung structure where the air flow is bidirectional, called neopulmonic parabronchi.[47]
Reptiles
The lung of most reptiles has a single bronchus running down the centre, from which numerous branches reach out to individual pockets throughout the lungs. These pockets are similar to alveoli in mammals, but much larger and fewer in number. These give the lung a sponge-like texture. In tuataras, snakes, and some lizards, the lungs are simpler in structure, similar to that of typical amphibians.[48]
Snakes and limbless lizards typically possess only the right lung as a major respiratory organ; the left lung is greatly reduced, or even absent. Amphisbaenians, however, have the opposite arrangement, with a major left lung, and a reduced or absent right lung.[48]
Both crocodilians and monitor lizards have developed lungs similar to those of birds, providing an unidirectional airflow and even possessing air sacs.[49] The now extinct pterosaurs have seemingly even further refined this type of lung, extending the airsacs into the wing membranes and, in the case of lonchodectids, tupuxuara, and azhdarchoids, the hindlimbs.[50]
Reptilian lungs typically receive air via expansion and contraction of the ribs driven by axial muscles and buccal pumping. Crocodilians also rely on the hepatic piston method, in which the liver is pulled back by a muscle anchored to the pubic bone (part of the pelvis), which in turn pulls the bottom of the lungs backward, expanding them. Turtles, which are unable to move their ribs, instead use their forelimbs and pectoral girdle to force air in and out of the lungs.[48]
Amphibians

The lungs of most frogs and other amphibians are simple and balloon-like, with gas exchange limited to the outer surface of the lung. This is not very efficient, but amphibians have low metabolic demands and can also quickly dispose of carbon dioxide by diffusion across their skin in water, and supplement their oxygen supply by the same method. Amphibians employ a positive pressure system to get air to their lungs, forcing air down into the lungs by buccal pumping. This is distinct from most higher vertebrates, who use a breathing system driven by negative pressure where the lungs are inflated by expanding the rib cage.[51] In buccal pumping, the floor of the mouth is lowered, filling the mouth cavity with air. The throat muscles then presses the throat against the underside of the skull, forcing the air into the lungs.[52]
Due to the possibility of respiration across the skin combined with small size, all known lungless tetrapods are amphibians. The majority of salamander species are lungless salamanders, which respirate through their skin and tissues lining their mouth. This necessarily restrict their size: all are small and rather thread-like in appearance, maximising skin surface relative to body volume.[53] Other known lungless tetrapods are the Bornean flat-headed frog[54] and Atretochoana eiselti, a caecilian.[55]
The lungs of amphibians typically have a few narrow internal walls (septa) of soft tissue around the outer walls, increasing the respiratory surface area and giving the lung a honey-comb appearance. In some salamanders even these are lacking, and the lung has a smooth wall. In caecilians, as in snakes, only the right lung attains any size or development.[48]
Lungfish
The lungs of lungfish are similar to those of amphibians, with few, if any, internal septa. In the Australian lungfish, there is only a single lung, albeit divided into two lobes. Other lungfish and Polypterus, however, have two lungs, which are located in the upper part of the body, with the connecting duct curving around and above the esophagus. The blood supply also twists around the esophagus, suggesting that the lungs originally evolved in the ventral part of the body, as in other vertebrates.[48]
Invertebrates

Some invertebrates have "lungs" that serve a similar respiratory purpose as, but are not evolutionarily related to, vertebrate lungs. Some arachnids, spiders and scorpions, have structures called "book lungs" used for atmospheric gas exchange. Some species of spider have four pairs of book lungs but most have two pairs.[56] Scorpions have spiracles on their body for the entrance of air to the book lungs.[57]
The coconut crab is terrestrial and uses structures called branchiostegal lungs to breathe air.[58] They cannot swim and would drown in water, yet they possess a rudimentary set of gills. They can breathe on land and hold their breath underwater.[59] The branchiostegal lungs are seen as a developmental adaptive stage from water-living to enable land-living, or from fish to amphibian.[60]
Pulmonates are mostly land snails and slugs that have developed a simple lung from the mantle cavity. An externally located opening called the pneumostome allows air to be taken into the mantle cavity lung.[61][62]
Evolutionary origins
The lungs of today's terrestrial vertebrates and the gas bladders of today's fish are believed to have evolved from simple sacs, as outpocketings of the esophagus, that allowed early fish to gulp air under oxygen-poor conditions.[63] These outpocketings first arose in the bony fish. In most of the ray-finned fish the sacs evolved into closed off gas bladders, while a number of carps, trouts, herrings, catfish, and eels have retained the physostome condition with the sack being open to the esophagus. In more basal bony fish, such as the gar, bichir, bowfin and the lobe-finned fish, the bladders have evolved to primarily function as lungs.[63] The lobe-finned fish gave rise to the land-based tetrapods. Thus, the lungs of vertebrates are homologous to the gas bladders of fish (but not to their gills).[64]
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to lungs. |
Further reading
- Dr D.R. Johnson: Introductory anatomy, respiratory system, leeds.ac.uk
- Franlink Institute Online: The Respiratory System, sln.fi.edu
- Avian lungs and respiration, people.eku.edu
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Mitchell, Adam W.M. (2014). Gray's anatomy for students (3rd ed.). Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. pp. 167–174. ISBN 978-0-7020-5131-9.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Standring, Susan (2008). Borley, Neil R., ed. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (40 ed.). Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. pp. 992–1000. ISBN 978-0-443-06684-9. Archived from the original on 10 March 2014.
- 1 2 Hacking, Craig; Knipe, Henry. "Lung fissures". Radiopaedia. Retrieved 8 February 2016.
- 1 2 3 Arakawa, H; Niimi, H; Kurihara, Y; Nakajima, Y; Webb, WR (December 2000). "Expiratory high-resolution CT: diagnostic value in diffuse lung diseases.". AJR. American journal of roentgenology. 175 (6): 1537–43. doi:10.2214/ajr.175.6.1751537. PMID 11090370.
- ↑ Yu, J. A.; Pomerantz, M; Bishop, A; Weyant, M. J.; Mitchell, J. D. (2011). "Lady Windermere revisited: Treatment with thoracoscopic lobectomy/segmentectomy for right middle lobe and lingular bronchiectasis associated with non-tuberculous mycobacterial disease". European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery. 40 (3): 671–5. doi:10.1016/j.ejcts.2010.12.028. PMID 21324708.
- ↑ Ayed, A. K. (2004). "Resection of the right middle lobe and lingula in children for middle lobe/lingula syndrome". Chest. 125 (1): 38–42. doi:10.1378/chest.125.1.38. PMID 14718418.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Stanton, editors, Bruce M. Koeppen, Bruce A. (2008). Berne & Levy physiology (6th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Mosby/Elsevier. pp. 418–422. ISBN 978-0-323-04582-7.
- ↑ Pocock, Gillian; Richards, Christopher D. (2006). Human physiology : the basis of medicine (3rd ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 315–318. ISBN 978-0-19-856878-0.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Pawlina, W (2015). Histology a Text & Atlas (7th ed.). pp. 670–678. ISBN 978-1451187427.
- ↑ Notter, Robert H. (2000). Lung surfactants: basic science and clinical applications. New York, N.Y: Marcel Dekker. p. 120. ISBN 0-8247-0401-0. Retrieved 2008-10-11.
- ↑ Ahmadi, Jiyuan Tu, Kiao Inthavong, Goodardz (2013). Computational fluid and particle dynamics in the human respiratory system (1st ed.). Dordrecht: Springer. pp. 23–24. ISBN 9789400744875.
- ↑ Hall, John E. (2012). Pocket companion to Guyton and Hall textbook of medical physiology (12th ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier/Saunders. p. Blood volume of the lungs (p. 478). ISBN 9781455711949.
- 1 2 3 4 Levitzky, Michael G. (2013). Pulmonary physiology (Eighth ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. p. Chapter 2. Mechanics of Breathing. ISBN 978-0071793131.
- 1 2 3 4 Levitzky, Michael G. (2013). Pulmonary physiology (Eighth ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. p. Chapter 9. Control of Breathing. ISBN 978-0071793131.
- ↑ Young B, Lowe JS, Stevens A, Heath JW (2006). Wheater's functional histology : a text and colour atlas. Deakin PJ (illust) (5th ed.). [Edinburgh?]: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. pp. 234–250. ISBN 9780443068508.
- ↑ Stanke, F (2015). "The Contribution of the Airway Epithelial Cell to Host Defense". Mediators Inflamm. 2015: 463016. doi:10.1155/2015/463016. PMC 4491388
 . PMID 26185361.
. PMID 26185361. - ↑ U.S. EPA. Integrated Science Assessment for Oxides of Nitrogen – Health Criteria (2016 Final Report). U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, EPA/600/R-15/068, 2016. Federal Register Notice Jan 28, 2016 Free download available at Report page at EPA website.
- ↑ Dorland (2011-06-09). Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary (32 ed.). Elsevier. p. 1077. ISBN 978-1-4160-6257-8. Retrieved 11 February 2016.
- ↑ Sadler T (2003). Langman's Medical Embryology (9th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0-7817-4310-9.
- ↑ Moore KL, Persaud TVN (2002). The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (7th ed.). Saunders. ISBN 0-7216-9412-8.
- ↑ Hill, Mark. "Respiratory System Development". UNSW Embryology. Retrieved 23 February 2016.
- 1 2 Larsen, William J. (2001). Human embryology (3. ed.). Philadelphia, Pa.: Churchill Livingstone. p. 144. ISBN 9780443065835.
- ↑ Kyung Won, PhD. Chung (2005). Gross Anatomy (Board Review). Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 156. ISBN 0-7817-5309-0.
- ↑ Dorland (2011-06-09). Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary (32 ed.). Elsevier. p. 1660. ISBN 978-1-4160-6257-8. Retrieved 11 February 2016.
- 1 2 Medline Plus (4 December 2013). "Changes in the newborn at birth". NIH. Archived from the original on 5 January 2016. Retrieved 13 February 2016.
- ↑ "Fetal lung liquid secretion". doi:10.1165/ajrcmb.25.1.f211#.Vsa_p8f8E3g (inactive 2016-06-02). Retrieved 19 February 2016.
- ↑ Burri, PH (1984). "Fetal and postnatal development of the lung". Annual Review of Physiology. 46: 617–28. doi:10.1146/annurev.ph.46.030184.003153. PMID 6370120.
- ↑ Oxford Dictionary. "Breathing". Retrieved 11 February 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 Levitzky, Michael G. (2013). Pulmonary physiology (Eighth ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. p. Chapter 1. Function and Structure of the Respiratory System. ISBN 978-0071793131.
- ↑ Oxford Dictionary. "Respiration". Retrieved 11 February 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Britton, edited by Brian R. Walker, Nicki R. Colledge, Stuart H. Ralston, Ian D. Penman ; illustrations by Robert (2014). Davidson's principles and practice of medicine (22nd ed.). ISBN 978-0-7020-5035-0.
- ↑ Britton, edited by Brian R. Walker, Nicki R. Colledge, Stuart H. Ralston, Ian D. Penman ; illustrations by Robert (2014). Davidson's principles and practice of medicine (22nd ed.). pp. 661–730. ISBN 978-0-7020-5035-0.
- 1 2 Walter F., PhD. Boron (2004). Medical Physiology: A Cellular And Molecular Approach. Elsevier/Saunders. p. 605. ISBN 1-4160-2328-3.
- 1 2 Hoad-Robson, Rachel; Tim Kenny. "The Lungs and Respiratory Tract". Patient.info. Patient UK. Archived from the original on 16 October 2012. Retrieved 11 February 2016.
- ↑ Smyth, Hugh D.C. (2011). Controlled pulmonary drug delivery. New York: Springer. pp. Chapter 2. ISBN 9781441997449.
- ↑ Mannell, Robert. "Introduction to Speech Production". Macquarie University. Retrieved 8 February 2016.
- ↑ American College of Physicians. "Pulmonology". ACP. Archived from the original on 9 September 2015. Retrieved 9 February 2016.
- ↑ "The Surgical Specialties: 8 – Cardiothoracic Surgery". Royal College of Surgeons. Retrieved 9 February 2016.
- ↑ "Aspergilloma". Medical Dictionary. TheFreeDictionary.
- ↑ "Lung Cancer Screening". U.S. Preventative Services Task Force. 2013.
- ↑ Cadichon, Sandra B. (2007), "Chapter 22: Pulmonary hypoplasia", in Kumar, Praveen; Burton, Barbara K., Congenital malformations: evidence-based evaluation and management
- ↑ Sieunarine, K.; May, J.; White, G. H.; Harris, J. P. (August 1997). "Anomalous azygos vein: a potential danger during endoscopic thoracic sypathectomy". ANZ Journal of Surgery. 67 (8): 578–579. doi:10.1111/j.1445-2197.1997.tb02046.x.
- 1 2 3 4 Kim E., Barrett (2012). Ganong's review of medical physiology. (24th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. p. Chapter 34. Introduction to Pulmonary Structure and Mechanics. ISBN 978-0071780032.
- ↑ Criée, C.P.; Sorichter, S.; Smith, H.J.; Kardos, P.; Merget, R.; Heise, D.; Berdel, D.; Köhler, D.; Magnussen, H.; Marek, W.; Mitfessel, H.; Rasche, K.; Rolke, M.; Worth, H.; Jörres, R.A. (July 2011). "Body plethysmography – Its principles and clinical use". Respiratory Medicine. 105 (7): 959–971. doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2011.02.006. PMID 21356587.
- 1 2 Applegate, Edith (2014). The Anatomy and Physiology Learning System. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 335. ISBN 9780323290821.
- 1 2 Ritchson, G. "BIO 554/754 - Ornithology: Avian respiration". Department of Biological Sciences, Eastern Kentucky University. Retrieved 2009-04-23.
- 1 2 3 Maina, John N. (2005). The lung air sac system of birds development, structure, and function ; with 6 tables. Berlin: Springer. pp. 3.2–3.3 "Lung", "Airway (Bronchiol) System" 66–82. ISBN 9783540255956.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Romer, Alfred Sherwood; Parsons, Thomas S. (1977). The Vertebrate Body. Philadelphia, PA: Holt-Saunders International. pp. 330–334. ISBN 0-03-910284-X.
- ↑ "Unidirectional airflow in the lungs of birds, crocs…and now monitor lizards!?". Sauropod Vertebra picture of the week. Retrieved 9 February 2016.
- ↑ Claessens, Leon P. A. M.; O'Connor, Patrick M.; Unwin, David M.; Sereno, Paul (18 February 2009). "Respiratory Evolution Facilitated the Origin of Pterosaur Flight and Aerial Gigantism". PLoS ONE. 4 (2): e4497. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0004497. PMC 2637988
 . PMID 19223979.
. PMID 19223979. - ↑ Janis, C.M.; Keller, J.C. (2001). "Modes of ventilation in early tetrapods: Costal aspiration as a key feature of amniotes" (PDF). Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 46 (2): 137–170. Retrieved 11 May 2012.
- ↑ Brainerd, E. L. (1999). New perspectives on the evolution of lung ventilation mechanisms in vertebrates. Experimental Biology Online 4, 11-28. http://www.brown.edu/Departments/EEB/brainerd_lab/pdf/Brainerd-1999-EBO.pdf
- ↑ Duellman, W. E.; Trueb, L. (1994). Biology of amphibians. illustrated by L. Trueb. Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 0-8018-4780-X.
- ↑ "First Lungless Frog Discovered in Indonesia". Scientific American (April 15, 2008). http://www.scientificamerican.com/gallery/first-lungless-frog-discovered-in-indonesia/.
- ↑ Wilkinson, M.; et al. (1998). "The largest lungless tetrapod: report on a second specimen of Atretochoana eiselti (Amphibia: Gymnophiona: Typhlonectidae) from Brazil" (PDF). Journal of Natural History (32): 617–627.
- ↑ "book lung | anatomy". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2016-02-24.
- ↑ "spiracle | anatomy". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2016-02-24.
- ↑ C. A. Farrelly & P. Greenaway (2005). "The morphology and vasculature of the respiratory organs of terrestrial hermit crabs (Coenobita and Birgus): gills, branchiostegal lungs and abdominal lungs". Arthropod Structure & Development. 34 (1): 63–87. doi:10.1016/j.asd.2004.11.002.
- ↑ Burggren, Warren W.; McMahon, Brian R. (1988-04-29). Biology of the Land Crabs. Cambridge University Press. p. 25. ISBN 9780521306904.
- ↑ Burggren, Warren W.; McMahon, Brian R. (1988-04-29). Biology of the Land Crabs. Cambridge University Press. p. 331. ISBN 9780521306904.
- ↑ Land Snails (& other Air-Breathers in Pulmonata Subclass & Sorbeconcha Clade). at Washington State University Tri-Cities Natural History Museum. Accessed 25 February 2016. http://shells.tricity.wsu.edu/ArcherdShellCollection/Gastropoda/Pulmonates.html
- ↑ Hochachka, Peter W. (2014-05-10). Mollusca: Metabolic Biochemistry and Molecular Biomechanics. Academic Press. ISBN 9781483276038.
- 1 2 Colleen Farmer (1997). "Did lungs and the intracardiac shunt evolve to oxygenate the heart in vertebrates" (PDF). Paleobiology. 23 (3): 358–372. doi:10.1017/S0094837300019734.
- ↑ Longo, Sarah; Riccio, Mark; McCune, Amy R (June 2013). "Homology of lungs and gas bladders: Insights from arterial vasculature". Journal of Morphology. 274 (6): 687–703. doi:10.1002/jmor.20128. PMID 23378277.