Ancien Régime
 |
| Kingdom of France |
|---|
| Structure |

The Ancien Régime (French pronunciation: [ɑ̃.sjɛ̃ ʁeʒim], Old Regime or Former Regime) was the monarchic, aristocratic, social and political system established in the Kingdom of France from approximately the 15th century until the latter part of the 18th century ("early modern France") under the late Valois and Bourbon dynasties. The term is occasionally used to refer to the similar feudal social and political order of the time elsewhere in Europe. The administrative and social structures of the Ancien Régime were the result of years of state-building, legislative acts (like the Ordinance of Villers-Cotterêts), internal conflicts and civil wars, but they remained a patchwork of local privilege and historic differences until the French Revolution ended the system.
Much of the medieval political centralization of France had been lost in the Hundred Years' War, and the Valois Dynasty's attempts at re-establishing control over the scattered political centres of the country were hindered by the Wars of Religion. Much of the reigns of Henry IV, Louis XIII and the early years of Louis XIV were focused on administrative centralisation. Despite, however, the notion of "absolute monarchy" (typified by the king's right to issue lettres de cachet) and the efforts by the kings to create a centralized state, Ancien Régime France remained a country of systemic irregularities: administrative (including taxation), legal, judicial, and ecclesiastic divisions and prerogatives frequently overlapped, while the French nobility struggled to maintain their own rights in the matters of local government and justice, and powerful internal conflicts (like the Fronde) protested against this centralization.
The need for centralization in this period was directly linked to the question of royal finances and the ability to wage war. The internal conflicts and dynastic crises of the 16th and 17th centuries (the Wars of Religion, the conflict with the Habsburgs) and the territorial expansion of France in the 17th century demanded great sums which needed to be raised through taxes, such as the taille and the gabelle and by contributions of men and service from the nobility.
One key to this centralization was the replacing of personal "clientele" systems organized around the king and other nobles by institutional systems around the state.[1] The creation of the Intendants—representatives of royal power in the provinces—did much to undermine local control by regional nobles. The same was true of the greater reliance shown by the royal court on the "noblesse de robe" as judges and royal counselors. The creation of regional parlements had initially the same goal of facilitating the introduction of royal power into newly assimilated territories, but as the parlements gained in self-assurance, they began to be sources of disunity.
Terminology
The term in French means "old regime" or "former regime". However, most English language books use the French term Ancien Régime. The term first appeared in print in English in 1794, and was originally pejorative in nature: Simon Schama has observed: "virtually as soon as the term was coined, 'old regime' was automatically freighted with associations of both traditionalism and senescence. It conjured up a society so encrusted with anachronisms that only a shock of great violence could free the living organism within. Institutionally torpid, economically immobile, culturally atrophied and socially stratified, this 'old regime' was incapable of self-modernization."[2]
More generally, ancien régime refers to any political and social system having the principal features of the French Ancien Régime. Europe's other anciens régimes had similar origins, but diverse fates: some eventually evolved into constitutional monarchies, whereas others were torn down by wars and revolutions.
Provinces and administrative divisions
Territorial expansion

In the mid-15th century, France was significantly smaller than it is today,[3] and numerous border provinces (such as Roussillon, Cerdagne, Conflent, Vallespir, Capcir, Calais, Béarn, Navarre, County of Foix, Flanders, Artois, Lorraine, Alsace, Trois-Évêchés, Franche-Comté, Savoy, Bresse, Bugey, Gex, Nice, Provence, Dauphiné, and Brittany) were either autonomous or belonged to the Holy Roman Empire, the Crown of Aragon or the Kingdom of Navarra; there were also foreign enclaves, like the Comtat Venaissin.
In addition, certain provinces within France were ostensibly personal fiefs of noble families (like the Bourbonnais, Marche, Forez and Auvergne provinces held by the House of Bourbon until the provinces were forcibly integrated into the royal domain in 1527 after the fall of Charles III, Duke of Bourbon).
From the late fifteenth century up to the late seventeenth century (and again in the 1760s), France underwent a massive territorial expansion and an attempt to better integrate its provinces into an administrative whole.
French acquisitions from 1461–1768:
- under Louis XI – Provence (1482), Dauphiné (1461, under French control since 1349)
- under Louis XII – Milan (1500, lost in 1521), Naples (1500, lost in 1504)
- under Francis I – Brittany (1532)
- under Henry II – de facto "Trois-Évêchés" (Metz, Toul, Verdun) (1552), Calais (1559)
- under Henry IV – County of Foix (1607)
- under Louis XIII – Béarn and Navarre (1620, under French control since 1589 as part of Henry IV's possessions)
- under Louis XIV
- Treaty of Westphalia (1648) – Alsace and de jure "Trois-Evêchés"
- Treaty of the Pyrenees (1659) – Artois, Northern Catalonia (Roussillon, Cerdagne)
- Treaty of Nijmegen (1678–79) – Franche-Comté, Flanders
- under Louis XV – Lorraine (1766), Corsica (1768)
Administration
Despite efforts by the kings to create a centralized state out of these provinces, France in this period remained a patchwork of local privileges and historical differences. The arbitrary power of the monarch (as implied by the expression "absolute monarchy") was in fact much limited by historic and regional particularities. Administrative (including taxation), legal (parlement), judicial, and ecclesiastic divisions and prerogatives frequently overlapped (for example, French bishoprics and dioceses rarely coincided with administrative divisions).
Certain provinces and cities had won special privileges (such as lower rates in the gabelle or salt tax). The south of France was governed by written law adapted from the Roman legal system, the north of France by common law (in 1453 these common laws were codified into a written form).
The representative of the king in his provinces and cities was the gouverneur. Royal officers chosen from the highest nobility, provincial and city governors (oversight of provinces and cities was frequently combined) were predominantly military positions in charge of defense and policing. Provincial governors — also called "lieutenants généraux" — also had the ability of convoking provincial parlements, provincial estates and municipal bodies.
The title "gouverneur" first appeared under Charles VI. The ordinance of Blois of 1579 reduced their number to 12, and an ordinance of 1779 increased their number to 39 (18 first-class governors, 21 second-class governors). Although in principle they were the king's representatives and their charges could be revoked at the king's will, some governors had installed themselves and their heirs as a provincial dynasty.
The governors were at the height of their power from the middle of the 16th to the mid-17th century. Their role in provincial unrest during the civil wars led Cardinal Richelieu to create the more tractable positions of intendants of finance, policing and justice, and in the 18th century the role of provincial governors was greatly curtailed.
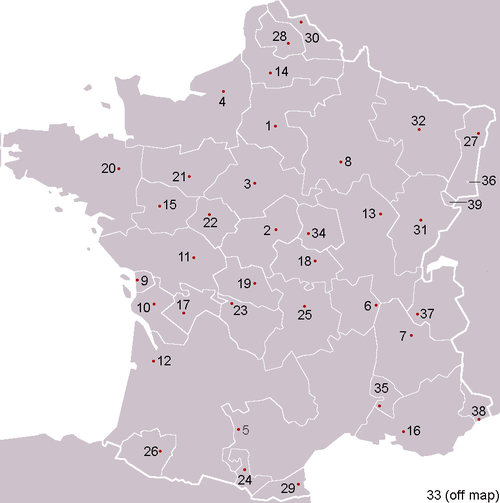
| Major provinces of France, with provincial capitals. Cities in bold had provincial "parlements" or "conseils souverains" during the Ancien Régime. Note: The map reflects France's modern borders and does not indicate the territorial formation of France over time. Provinces on this list may encompass several other historic provinces and counties (for example, at the time of the Revolution, Guyenne was made up of eight smaller historic provinces, including Quercy and Rouergue). For a more complete list, see Provinces of France. | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
 |
In an attempt to reform the system, new divisions were created. The recettes générales, commonly known as "généralités", were initially only taxation districts (see State finances below). The first sixteen were created in 1542 by edict of Henry II. Their role steadily increased and by the mid-17th century, the généralités were under the authority of an "intendant", and they became a vehicle for the expansion of royal power in matters of justice, taxation and policing. By the Revolution, there were 36 généralités; the last two were created in 1784.
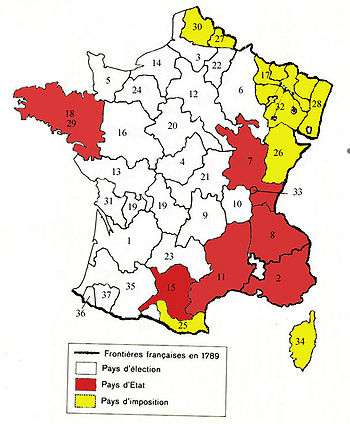
| Généralités of France by city (and province). Areas in red are "pays d'état" (note: should also include 36, 37 and parts of 35); white "pays d'élection"; yellow "pays d'imposition" (see State finances below). | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
 |
State finances
The desire for more efficient tax collection was one of the major causes for French administrative and royal centralization in the early modern period. The taille became a major source of royal income. Exempted from the taille were clergy and nobles (except for non-noble lands they held in "pays d'état", see below), officers of the crown, military personnel, magistrates, university professors and students, and certain cities ("villes franches") such as Paris.
The provinces were of three sorts, the "pays d'élection", the "pays d'état" and the "pays d'imposition". In the "pays d'élection" (the longest held possessions of the French crown; some of these provinces had had the equivalent autonomy of a "pays d'état" in an earlier period, but had lost it through the effects of royal reforms) the assessment and collection of taxes were trusted to elected officials (at least originally, later these positions were bought), and the tax was generally "personal", meaning it was attached to non-noble individuals.
In the "pays d'état" ("provinces with provincial estates"), Brittany, Languedoc, Burgundy, Auvergne, Béarn, Dauphiné, Provence and portions of Gascony, such as Bigorre, Comminges and the Quatre-Vallées, recently acquired provinces which had been able to maintain a certain local autonomy in terms of taxation, the assessment of the tax was established by local councils and the tax was generally "real", meaning that it was attached to non-noble lands (meaning that nobles possessing such lands were required to pay taxes on them). "Pays d'imposition" were recently conquered lands which had their own local historical institutions (they were similar to the "pays d'état" under which they are sometimes grouped), although taxation was overseen by the royal intendant.
Taxation history
Taxation districts had gone through a variety of mutations from the 14th century on. Before the 14th century, oversight of the collection of royal taxes fell generally to the baillis and sénéchaux in their circumscriptions. Reforms in the 14th and 15th centuries saw France's royal financial administration run by two financial boards which worked in a collegial manner: the four Généraux des finances (also called "général conseiller" or "receveur général" ) oversaw the collection of taxes (taille, aides, etc.) by tax-collecting agents (receveurs) and the four Trésoriers de France (Treasurers) oversaw revenues from royal lands (the "domaine royal").
Together they were the Messieurs des finances. The four members of each board were divided by geographical circumscriptions (although the term généralité isn't found before the end of the 15th century). The areas were named Languedoïl, Languedoc, Outre-Seine-and-Yonne, and Nomandy (the latter was created in 1449; the other three were created earlier), with the directors of the "Languedoïl" region typically having an honorific preeminence. By 1484, the number of généralités had increased to 6.
In the 16th century, the kings of France, in an effort to exert more direct control over royal finances and to circumvent the double-board (accused of poor oversight) – instituted numerous administrative reforms, including the restructuring of the financial administration and an increase in the number of "généralités". In 1542, Henry II, France was divided into 16 "généralités". The number increased to 21 at the end of the 16th century, and to 36 at the time of the French Revolution; the last two were created in 1784.
The administration of the généralités of the Renaissance went through a variety of reforms. In 1577, Henry III established 5 treasurers ("trésoriers généraux") in each généralité who formed a bureau of finances. In the 17th century, oversight of the généralités was subsumed by the intendants of finance, justice and police, and the expression "généralité" and "intendance" became roughly synonymous.
Until the late 17th century, tax collectors were called receveurs. In 1680, the system of the Ferme Générale was established, a franchised customs and excise operation in which individuals bought the right to collect the taille on behalf of the king, through 6-years adjudications (certain taxes like the aides and the gabelle had been farmed out in this way as early as 1604). The major tax collectors in that system were known as the fermiers généraux (farmers-general in English).
The taille was only one of a number of taxes. There also existed the "taillon" (a tax for military purposes), a national salt tax (the gabelle), national tariffs (the "aides") on various products (wine, beer, oil, and other goods), local tariffs on speciality products (the "douane") or levied on products entering the city (the "octroi") or sold at fairs, and local taxes. Finally, the church benefited from a mandatory tax or tithe called the "dîme".
Louis XIV created several additional tax systems, including the "capitation" (begun in 1695) which touched every person including nobles and the clergy (although exemption could be bought for a large one-time sum) and the "dixième" (1710–17, restarted in 1733), enacted to support the military, which was a true tax on income and on property value. In 1749, under Louis XV, a new tax based on the "dixième", the "vingtième" (or "one-twentieth"), was enacted to reduce the royal deficit, and this tax continued through the remaining years of the Ancien Régime.
Fees for holding state positions
Another key source of state financing was through charging fees for state positions (such as most members of parlements, magistrates, maître des requêtes and financial officers). Many of these fees were quite elevated, but some of these offices conferred nobility and could be financially advantageous. The use of offices to seek profit had become standard practice as early as the 12th and 13th centuries. A law in 1467 made these offices irrevocable, except through the death, resignation or forfeiture of the title holder, and these offices, once bought, tended to become hereditary charges (with a fee for transfer of title) passed on within families.[4]
In an effort to increase revenues, the state often turned to the creation of new offices. Before it was made illegal in 1521, It had been possible to leave open-ended the date that the transfer of title was to take effect. In 1534, the "forty days rule" was instituted (adapted from church practice), which made the successor's right void if the preceding office holder died within forty days of the transfer and the office returned to the state;however, a new fee, called the survivance jouissante protected against the forty days rule.[4] In 1604, Sully created a new tax, the "paulette" or "annual tax" (1/60 of the amount of the official charge), which permitted the title-holder to be free of the 40-day rule. The "paulette" and the venality of offices became key concerns in the parlementarian revolts of the 1640s (La Fronde).
The state also demanded of the church a "free gift", which the church collected from holders of eccleciastic offices through taxes called the "décime" (roughly 1/20th of the official charge, created under Francis I).
State finances also relied heavily on borrowing, both private (from the great banking families in Europe) and public. The most important public source for borrowing was through the system of rentes sur l'Hôtel de Ville of Paris, a kind of government bond system offering investors annual interest. This system first came to use in 1522 under Francis I.
Until 1661, the head of the financial system in France was generally the surintendant des finances. In that year, the surintendant Nicolas Fouquet fell from power and the position was replaced by the less powerful contrôleur général des finances.
Justice
Lower courts
Justice in seigneurial lands (including those held by the church or within cities) was generally overseen by the seigneur or his delegated officers. Since the 15th century, much of the seigneur's legal purview had been given to the bailliages or sénéchaussées and the présidiaux (see below), leaving only affairs concerning seigneurial dues and duties, and small affairs of local justice. Only certain seigneurs—those with the power of haute justice (seigneurial justice was divided into "high" "middle" and "low" justice) – could enact the death penalty, and only with the consent of the présidiaux.
Crimes of desertion, highway robbery, and mendicants (so-called cas prévôtaux) were under the supervision of the prévôt des maréchaux, who exacted quick and impartial justice. In 1670, their purview was overseen by the présidiaux (see below).
The national judicial system was made-up of tribunals divided into bailliages (in northern France) and sénéchaussées (in southern France); these tribunals (numbering around 90 in the 16th century, and far more at the end of the 18th) were supervised by a lieutenant général and were subdivided into:
- prévôtés supervised by a prévôt;
- or (as was the case in Normandy) into vicomtés supervised by a vicomte (the position could be held by non-nobles);
- or (in parts of northern France) into châtellenies supervised by a châtelain (the position could be held by non-nobles);
- or, in the south, into vigueries or baylies supervised by a viguier or a bayle.
In an effort to reduce the case load in the parlements, certain bailliages were given extended powers by Henry II of France: these were called présidiaux.
The prévôts or their equivalent were the first-level judges for non-nobles and ecclesiastics. In the exercise of their legal functions, they sat alone, but had to consult with certain lawyers (avocats or procureurs) chosen by themselves, whom, to use the technical phrase, they "summoned to their council". The appeals from their sentences went to the bailliages, who also had jurisdiction in the first instance over actions brought against nobles. Bailliages and présidiaux were also the first court for certain crimes (so-called cas royaux; these cases had formerly been under the supervision of the local seigneurs): sacrilege, lèse-majesté, kidnapping, rape, heresy, alteration of money, sedition, insurrections, and the illegal carrying of arms. To appeal a bailliage's decisions, one turned to the regional parlements.
The most important of these royal tribunals was the prévôté[5] and présidial of Paris, the Châtelet, which was overseen by the prévôt of Paris, civil and criminal lieutenants, and a royal officer in charge of maintaining public order in the capital, the Lieutenant General of Police of Paris.
Superior courts
The following were cours souveraines, or superior courts, whose decisions could only be revoked by "the king in his conseil" (see administration section below).
- Parlements – eventually 14 in number: Paris, Languedoc (Toulouse), Provence (Aix), Franche-Comté (Besançon), Guyenne (Bordeaux), Burgundy (Dijon), Flanders (Douai), Dauphiné (Grenoble), Trois-Évêchés (Metz), Lorraine (Nancy), Navarre (Pau), Brittany (Rennes, briefly in Nantes), Normandy (Rouen) and (from 1523–1771) Dombes (Trévoux). There was also parlement in Savoy (Chambéry) from 1537–59. The parlements were originally only judicial in nature (appellate courts for lower civil and ecclesiastical courts), but began to subsume limited legislative functions (see administration section below). The most important of the parlements, both in administrative area (covering the major part of northern and central France) and prestige, was the parliament of Paris, which also was the court of first instance for peers of the realm and for regalian affairs.
- Conseils souverains – Alsace (Colmar), Roussillon (Perpignan), Artois (a conseil provincial, Arras) and (from 1553–59) Corsica (Bastia); formerly Flanders, Navarre and Lorraine (converted into parlements). The conseils souverains were regional parliaments in recently conquered lands.
- Chambre des comptes – Paris, Dijon, Blois, Grenoble, Nantes. The chambre des comptes supervised the spending of public funds, the protection of royal lands (domaine royal), and legal issues involving these areas.
- Cours des aides – Paris, Clermont, Bordeaux, Montauban. The cours des aides supervised affairs in the pays d'élections, often concerning taxes on wine, beer, soap, oil, metals, etc.
- Chambre des comptes combined with Cours des aides – Aix, Bar-le-Duc, Dole, Nancy, Montpellier, Pau, Rouen
- Cours des monnaies – Paris; additionally Lyon (1704–71), and (after 1766), the chambre des comptes of Bar-le-Duc and Nancy. The cours des monnaies oversaw money, coins and precious metals.
- Grand Conseil – created in 1497 to oversee affairs concerning ecclesiastical benefices; occasionally the king sought the Grand Conseil's intervention in affairs considered to be too contentious for the parliament.
The head of the judicial system in France was the chancellor.
Administration
One of the established principles of the French monarchy was that the king could not act without the advice of his counsel; the formula "le roi en son conseil" expressed this deliberative aspect. The administration of the French state in the early modern period went through a long evolution, as a truly administrative apparatus – relying on old nobility, newer chancellor nobility ("noblesse de robe") and administrative professionals – was substituted to the feudal clientel system.
King's counsel
Under Charles VIII and Louis XII the king's counsel was dominated by members of twenty or so noble or rich families; under Francis I the number of counsellors increased to roughly 70 individuals (although the old nobility was proportionally more important than in the previous century). The most important positions in the court were those of the Great Officers of the Crown of France, headed by the connétable (chief military officer of the realm; position eliminated in 1627) and the chancellor.
The royal administration during the Renaissance was divided between a small counsel (the "secret" and later "high" counsel) of 6 or fewer members (3 members in 1535, 4 in 1554) for important matters of state; and a larger counsel for judicial or financial affairs. Francis I was sometimes criticized for relying too heavily on a small number of advisors, while Henry II, Catherine de Medici and their sons found themselves frequently unable to negotiate between the opposing Guise and Montmorency families in their counsel.
Over time, the decision-making apparatus of the King's Council was divided into several royal counsels. The subcouncils of the King's Council can be generally grouped as "governmental councils", "financial councils" and "judicial and administrative councils". With the names and subdivisions of the 17–18th century, these subcouncils were:
Governmental Councils:
- Conseil d'en haut ("High Council", concerning the most important matters of state) – composed of the king, the crown prince (the "dauphin"), the chancellor, the contrôleur général des finances, and the secretary of state in charge of foreign affairs.
- Conseil des dépêches ("Council of Messages", concerning notices and administrative reports from the provinces) – composed of the king, the chancellor, the secretaries of state, the contrôleur général des finances, and other councillors according to the issues discussed.
- Conseil de Conscience
Financial Councils:
- Conseil royal des finances ("Royal Council of Finances") – composed of the king, the "chef du conseil des finances" (an honorary post), the chancellor, the contrôleur général des finances and two of his consellors, and the intendants of finance.
- Conseil royal de commerce
Judicial and Administrative Councils:
- Conseil d'État et des Finances or Conseil ordinaire des Finances – by the late 17th century, its functions were largely taken over by the three following sections.
- Conseil privé or Conseil des parties or Conseil d'État ("Privy Council" or "Council of State", concerning the judicial system, officially instituted in 1557) – the largest of the royal councils, composed of the chancellor, the dukes with peerage, the ministers and secretaries of state, the contrôleur général des finances, the 30 councillors of state, the 80 maître des requêtes and the intendants of finance.
- Grande Direction des Finances
- Petite Direction des Finances
In addition to the above administrative institutions, the king was also surrounded by an extensive personal and court retinue (royal family, valet de chambres, guards, honorific officers), regrouped under the name "Maison du Roi".
At the death of Louis XIV, the Regent Philippe II, Duke of Orléans abandoned several of the above administrative structures, most notably the Secretaries of State, which were replaced by Counsels. This system of government, called the Polysynody, lasted from 1715–18.
17th-century state positions
Under Henry IV and Louis XIII the administrative apparatus of the court and its councils was expanded and the proportion of the "noblesse de robe" increased, culminating in the following positions during the 17th century:
- First Minister: ministers and secretaries of state — such as Sully, Concini (who was also governor of several provinces), Richelieu, Mazarin, Jean-Baptiste Colbert, Cardinal de Fleury, Turgot, etc. – exerted a powerful control over state administration in the 17th and 18th century. The title "principal ministre de l'état" was however only given six times in this period and Louis XIV himself refused to choose a "prime minister" after the death of Mazarin.
- Chancellor of France (also called the "garde des sceaux", or "Keeper of the Seals"; in the case of incapacity or disfavor, the Chancellor was generally permitted to retain his title, but the royal seals were passed to a deputy, called the "garde des sceaux"[6])
- Controller-General of Finances (contrôleur général des finances, formerly called the surintendant des finances).
- Secretaries of State: created in 1547 by Henry II, of greater importance after 1588, generally 4 in number, but occasionally 5:
- Secretary of State for Foreign Affairs
- Secretary of State for War, also oversaw France's border provinces.
- Secretary of State of the Navy
- Secretary of State of the Maison du Roi (the king's royal entourage and personal military guard), who also oversaw the clergy, the affairs of Paris and the non-border provinces.
- Secretary of State for Protestant Affairs (combined with the secretary of the Maison du Roi in 1749).
- Councillors of state (generally 30)
- Maître des requêtes (generally 80)
- Intendants of finance (6)
- Intendants of commerce (4 or 5)
- Ministers of State (variable)
- Treasurers
- Farmers-General
- Superintendent of the postal system
- Directeur général of buildings
- Directeur général of fortifications
- Lieutenant General of Police of Paris (in charge of public order in the capital)
- Archbishop of Paris
- Royal confessor
Royal administration in the provinces had been the role of the bailliages and sénéchaussées in the Middle Ages, but this declined in the early modern period, and by the end of the 18th century, the bailliages served only a judicial function. The main source of royal administrative power in the provinces in the 16th and early 17th centuries fell to the gouverneurs (who represented "the presence of the king in his province"), positions which had long been held by only the highest ranked families in the realm. With the civil wars of the early modern period, the king increasing turned to more tractable and subservient emissaries, and this was the reason for the growth of the provincial intendants under Louis XIII and Louis XIV. Indendants were chosen from among the maître des requêtes. Intendants attached to a province had jurisdiction over finances, justice and policing.
By the 18th century, royal administrative power was firmly established in the provinces, despite protestations by local parlements. In addition to their role as appellate courts, regional parlements had gained the privilege to register the edicts of the king and to present the king with official complaints concerning the edicts; in this way, they had acquired a limited role as the representative voice of (predominantly) the magistrate class. In case of refusal on parliament's part to register the edicts (frequently concerning fiscal matters), the king could impose registration through a royal assize ("lit de justice").
The other traditional representatives bodies in the realm were the Etats généraux (created in 1302) which reunited the three estates of the realm (clergy, nobility, the third estate) and the "États provinciaux" (Provincial Estates). The "Etats généraux" (convoked in this period in 1484, 1560–61, 1576–77, 1588–89, 1593, 1614, and 1789) had been reunited in times of fiscal crisis or convoked by parties malcontent with royal prerogatives (the Ligue, the Huguenots), but they had no true power, the dissensions between the three orders rendered them weak and they were dissolved before having completed their work. As a sign of French absolutism, they ceased to be convoked from 1614 to 1789. The provincial estates proved more effective, and were convoked by the king to respond to fiscal and tax policies.
The Church

The French monarchy was irrevocably linked to the Catholic Church (the formula says "la France est la fille aînée de l'église", or "France is the eldest daughter of the church"), and French theorists of the divine right of kings and sacerdotal power in the Renaissance had made these links explicit: Henry IV was able to ascend to the throne only after abjuring Protestantism. The symbolic power of the Catholic monarch was apparent in his crowning (the king was anointed by blessed oil in Rheims) and he was popularly believed to be able to cure scrofula by the laying on of his hands (accompanied by the formula "the king touches you, but God heals you").
In 1500, France had 14 archbishoprics (Lyon, Rouen, Tours, Sens, Bourges, Bordeaux, Auch, Toulouse, Narbonne, Aix-en-Provence, Embrun, Vienne, Arles, and Rheims) and 100 bishoprics. By the 18th century, archbishoprics and bishoprics had expanded to a total of 139 (see List of Ancien Régime dioceses of France). The upper levels of the French church were made up predominantly of old nobility, both from provincial families and from royal court families, and many of the offices had become de facto hereditary possessions, with some members possessing multiple offices. In addition to fiefs that church members possessed as seigneurs, the church also possessed seigneurial lands in its own right and enacted justice upon them.
At the start of the 16th century, the secular clergy (curates, vicars, canons, etc.) numbered around 100,000 individuals in France.[7]
Other temporal powers of the church included playing a political role as the first estate in the "États Généraux" and the "États Provinciaux" (Provincial Assemblies) and in Provincial Conciles or Synods convoked by the king to discuss religious issues. The church also claimed a prerogative to judge certain crimes, most notably heresy, although the Wars of Religion did much to place this crime in the purview of the royal courts and parliament. Finally, abbots, cardinals and other prelates were frequently employed by the kings as ambassadors, members of his councils (such as Richelieu and Mazarin) and in other administrative positions.
The faculty of theology of Paris (often called the Sorbonne), maintained a censor board which reviewed publications for their religious orthodoxy. The Wars of Religion saw this control over censorship however pass to the parliament, and in the 17th century to the royal censors, although the church maintained a right to petition.
The church was the primary provider of schools (primary schools and "colleges") and hospitals ("hôtel-Dieu", the Sisters of Charity) and distributor of relief to the poor in pre-revolutionary France.
The Pragmatic Sanction of Bourges (1438, suppressed by Louis XI but brought back by the États Généraux of Tours in 1484) gave the election of bishops and abbots to the cathedral chapter houses and abbeys of France, thus stripping the pope of effective control of the French church and permitting the beginning of a Gallican church. However, in 1515, Francis I signed a new agreement with Pope Leo X, the Concordat of Bologna, which gave the king the right to nominate candidates and the pope the right of investiture; this agreement infuriated gallicans, but gave the king control over important ecclesiastical offices with which to benefit nobles.
Although exempted from the taille, the church was required to pay the crown a tax called the "free gift" ("don gratuit"), which it collected from its office holders, at roughly 1/20 the price of the office (this was the "décime", reapportioned every five years). In its turn, the church exacted a mandatory tithe from its parishioners, called the "dîme".
The Counter-Reformation saw the French church create numerous religious orders (such as the Jesuits) and make great improvements on the quality of its parish priests; the first decades of the 17th century were characterized by a massive outpouring of devotional texts and religious fervor (exemplified in Saint Francis of Sales, Saint Vincent de Paul, etc.). Although the Edict of Nantes (1598) permitted the existence of Protestant churches in the realm (characterized as "a state within a state"), the next eighty years saw the rights of the Huguenots slowly stripped away, until Louis XIV finally revoked the edict in 1685, producing a massive emigration of Huguenots to other countries. Religious practices which veered too close to Protestantism (like Jansenism) or to the mystical (like Quietism) were also severely suppressed, as too libertinage or overt atheism.
Regular clergy (i.e. those in Catholic religious orders) in France numbered into the tens of thousands in the 16th century. Some orders, like the Benedictines, were largely rural; others, like the Dominicans (also called "Jacobins") and the Franciscans (also called "cordeliers") operated in cities.[7]
Although the church came under attack in the eighteenth century by the philosophers of the Enlightenment and recruitment of clergy and monastic orders dropped after 1750, figures show that, on the whole, the population remained a profoundly Catholic country (absenteeism from services did not exceed 1% in the middle of the century[8]). At the eve of the revolution, the church possessed upwards of 7% of the country's land (figures vary) and generated yearly revenues of 150 million livres.
Gallicanism
Louis XIV supported the Gallican cause that gave the government a greater role than the pope in choosing bishops, and gave the government the revenues when a bishopric was vacant. There would be no inquisition in France, and papal decrees could operate only after the government approved them. Louis avoided schism – he wanted more royal power over the French Church but did not want to break free of Rome. The pope likewise recognized the "most Christian king" was a powerful ally who could not be alienated.[9]
Monasteries
Until the French Revolution, the monastic community constituted a central element of the economic, social, and religious life of many localities under the Old Regime. From the end of the Wars of Religion to the French Revolution, Menat, a Cluniac abbey dating back to 1107, ruled over the Sioule Valley in the northwest region of the Clermont diocese. The monks were large landholders and developed a diversified and complex set of links with their neighbors; they received seigniorial rights, provided work to the rural poor, and were in daily contact with notaries public, merchants, and surgeons. While they did not directly manage the religious life of the faithful (parish priests did that), monks did constitute a motivating force in it through their setting up of a parish clergy, providing alms and social services, and playing the role of intercessors.
Convents
Communities of nuns in France on the eve of Revolution had, on average, 25 members and a median age of 48 years. Nuns were both entering the profession later and living longer than before. In general, they had little wealth. Recruitment varied from region to region and by convent lifestyle (active or contemplative, austere or opulent, lower class or middle class). The nature of male and female monasticism differed greatly in France both before and during the revolution. Convents tended to be more isolated and less centrally controlled. This made for greater diversity among them than among male monasteries.[10]
Reformation and the Protestant minority
French Protestantism, which was largely Calvinist, derived its support from the lesser nobles and trading classes. Its two main strongholds were south west France and Normandy, but even in these districts the Catholics were a majority. Protestantism in France was considered a grave threat to national unity, as the Huguenot minority felt a closer affinity with German and Dutch Calvinists than with their fellow Frenchmen. In an effort to cement their position they often allied with French enemies. The animosity between the two sides led to the French Wars of Religion and the tragic St. Bartholomew's Day Massacre. The religious wars ended in 1593, when the Huguenot Henry of Navarre (1553–1610), who was already effectively king of France became a Catholic and was recognized by both Catholics and Protestants as King Henry IV (reigned 1589–1610).
The main provisions of the Edict of Nantes (1598), which Henry IV had issued as a charter of religious freedoms for the Huguenots, were as follows; first) Huguenots were allowed to hold religious services in certain towns in each province; second) They were allowed to control and fortify eight cities; third) Special courts were established to try Huguenot offenders; d) Huguenots were to have equal civil rights with the Catholics.
The military privileges were incorporated in the Edict in order to allay the fears of the minority. Over time it became clear these privileges were open to abuse and when in 1620 the Huguenots proclaimed a constitution for the "Republic of the Reformed Churches of France", the Prime Minister Cardinal Richelieu (1585–1642) invoked the full powers of the state; He captured La Rochelle after a long siege in 1628. The subsequent Treaty of Alais left the Huguenots their religious freedom but revoked their military freedoms.
Montpellier was among the most important of the 66 "villes de sûreté" that the Edict of 1598 granted to the Huguenots. The city's political institutions and the university were all handed over to the Huguenots. Tension with Paris led to a siege by the royal army in 1622. Peace terms called for the dismantling of the city's fortifications. A royal citadel was built and the university and consulate were taken over by the Catholic party. Even before the Edict of Alès (1629), Protestant rule was dead and the ville de sûreté was no more.
By 1620 the Huguenots were on the defensive, and the government increasingly applied pressure. A series of small civil wars that broke out in southern France between 1610 and 1635 were long considered by historians to be regional squabbles between rival noble families. New analysis shows that these civil wars were in fact religious in nature, remnants of the French Wars of Religion that largely ended with the Edict of Nantes in 1598. Small wars in the provinces of Languedoc and Guyenne show Catholic and Calvinist groups using destruction of churches, iconoclasm, forced conversions, and the execution of heretics as weapons of choice.
Louis XIV acted more and more aggressively to force the Huguenots to convert. At first he sent missionaries to convert them, backed by a fund to financially reward converts to Catholicism. Then he imposed penalties and closed their schools and excluded them from favorite professions. Escalating the attack, he tried to forcibly re-Catholicize the Huguenots by the employment of armed dragonnades (soldiers) to occupy and loot their houses, and finally by the revocation (Oct. 18, 1685) of the liberal Edict of Nantes of 1598.[11]
The revocation forbade Protestant services, the children were to be educated as Catholics, and emigration was prohibited. It proved disastrous to the Huguenots and costly for France. It precipitated civil bloodshed, ruined commerce, and resulted in the illegal flight from the country of about 180,000 Protestants, many of whom became intellectuals, doctors and business leaders in Britain as well as Holland, Prussia and South Africa. 4000 went to the American colonies.[11]
The English welcomed the French refugees, providing money from both government and private agencies to aid their relocation. Those Huguenots who stayed in France became Catholics and were called "new converts." Only a few Protestant villages remained in isolated areas.[11]
By the 1780s, Protestants comprised about 700,000 people, or 2% of the population. Theirs was no longer a favorite religion of the elite; most Protestants were peasants. To be a Protestant was still illegal. Although the law was seldom enforced it could be a threat or a nuisance to Protestants. Calvinists lived primarily in the Midi; about 200,000 Lutherans lived in Alsace, where the 1648 Treaty of Westphalia still protected them.[12] In addition, there were about 40,000 to 50,000 Jews in France, chiefly centered in Bordeaux, Metz and a few other cities. They had very limited rights and opportunities, apart from the money-lending business, but their status was not illegal.[13]
Downfall

In 1789, the Ancien Régime was violently overthrown by the French Revolution. Although France in 1785 faced economic difficulties, mostly concerning the equitability of taxation, it was one of the richest and most powerful nations of Europe.[14] The French people also enjoyed more political freedom and a lower incidence of arbitrary punishment than many of their fellow Europeans.
However, Louis XVI, his ministers, and the widespread French nobility had become immensely unpopular. This was a consequence of the fact that peasants and, to a lesser extent, the bourgeoisie, were burdened with ruinously high taxes levied to support wealthy aristocrats and their sumptuous lifestyles.
Historians explain the sudden collapse of the Ancien Régime as stemming in part from its rigidity. Aristocrats were confronted by the rising ambitions of merchants, tradesmen, and prosperous farmers, who were allied with aggrieved peasants, wage-earners, and intellectuals influenced by the ideas of Enlightenment philosophers. As the revolution proceeded, power devolved from the monarchy and the privileged-by-birth to more-representative political bodies, like legislative assemblies, but conflicts among the formerly allied republican groups became the source of considerable discord and bloodshed.
A growing number of the French citizenry had absorbed the ideas of "equality" and "freedom of the individual" as presented by Voltaire, Denis Diderot, Turgot, and other philosophers and social theorists of the Enlightenment. The American Revolution had demonstrated that it was possible for Enlightenment ideas about how governance should be organized to actually be put into practice. Some American diplomats, like Benjamin Franklin and Thomas Jefferson, had lived in Paris where they consorted freely with members of the French intellectual class. Furthermore, contact between American revolutionaries and the French troops who served as anti-British mercenaries in North America helped spread revolutionary ideals to the French people. After a time, many of the French began to attack the undemocratic nature of their own government, push for freedom of speech, challenge the Roman Catholic Church, and decry the prerogatives of the nobles.[15]
Revolution was not due to a single event but to a series of events, that together irreversibly changed the organization of political power, the nature of society, and the exercise of individual freedoms.
Nostalgia
For some observers the term came to denote a certain nostalgia. Talleyrand famously quipped:
| “ | Celui qui n'a pas vécu au dix-huitième siècle avant la Révolution ne connaît pas la douceur de vivre:[16] ("Those who have not lived in the eighteenth century before the Revolution do not know the sweetness of living") | ” |
The reason for this affection was the perceived decline in culture and values following the Revolution, where the aristocracy lost much of its economic and political power to what was seen as a rich, but coarse and materialistic bourgeoisie. The theme recurs throughout nineteenth-century French literature, with Balzac and Flaubert alike attacking the mores of the new upper classes. To this mindset, the Ancien Régime expressed a bygone era of refinement and grace, before the Revolution and its associated changes disrupted the aristocratic tradition and ushered in a crude, uncertain modernity.
The historian Alexis de Tocqueville argued against this defining narrative in his classic study, L'Ancien Régime et la Révolution, highlighting the continuities between pre- and post-revolutionary French institutions.
References
- ↑ Major 1994, pp. xx–xxi
- ↑ Schama, Simon (1989). Citizens: A Chronicle of the French Revolution. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. p. 184.
- ↑ Bély 1994, p. 21. In 1492, roughly 450,000 km² versus 550,000 km² today.
- 1 2 Salmon 1975, p. 77
- ↑ Despite being called a prévôté, the prévôté of Paris was effectively a bailliage. See Salmon 1975, p. 73
- ↑ Salmon 1975, p. 67
- 1 2 Bély 1994, p. 50
- ↑ Viguerie 1995, p. 280
- ↑ John Wolf, Louis XIV, 388–92
- ↑ Elizabeth Rapley and Robert Rapley, "An Image of Religious Women in the 'Ancien Regime': the 'Etats Des Religieuses' of 1790–1791." French History 1997 11(4): 387–410
- 1 2 3 John Wolf, Louis XIV, ch 24; Bertrand Van Ruymbeke, "Escape from Babylon." Christian History 2001 20(3): 38–42. ISSN 0891-9666 Fulltext: Ebsco
- ↑ Nigel Aston, Religion and Revolution in France, 1780-1804 (2000) pp 61-72
- ↑ Aston, Religion and Revolution in France, 1780-1804 (2000) pp 72-89
- ↑ Norman Gash, Reflections on the revolution – French Revolution, National Review, July 14, 1790: "Yet in 1789 France was the largest, wealthiest, and most powerful state in Western Europe."
- ↑ The Origins of the French Revolution. Historyguide.org (2006-10-30). Retrieved on 2011-11-18.
- ↑ "Celui qui n'a pas vécu au dix-huitième siècle avant la Révolution ne connaît pas la douceur de vivre et ne peut imaginer ce qu'il peut y avoir de bonheur dans la vie. C'est le siècle qui a forgé toutes les armes victorieuses contre cet insaisissable adversaire qu'on appelle l'ennui. L'Amour, la Poésie, la Musique, le Théâtre, la Peinture, l'Architecture, la Cour, les Salons, les Parcs et les Jardins, la Gastronomie, les Lettres, les Arts, les Sciences, tout concourait à la satisfaction des appétits physiques, intellectuels et même moraux, au raffinement de toutes les voluptés, de toutes les élégances et de tous les plaisirs. L'existence était si bien remplie qui si le dix-septième siècle a été le Grand Siècle des gloires, le dix-huitième a été celui des indigestions." Charles-Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord: Mémoires du Prince de Talleyrand: La Confession de Talleyrand, V. 1-5 Chapter: La jeunesse – Le cercle de Madame du Barry.
Further reading
- Baker, Keith Michael (1987). The French Revolution and the creation of modern political culture. Volume 1, The Political Culture of Old Regime. Oxford: Pergamon Press.
- Behrens, C.B.A. Ancien Regime (1989)
- Black, Jeremy. From Louis XIV to Napoleon: The Fate of a Great Power (1999)
- Brockliss, Laurence and Colin Jones. The Medical World of Early Modern France (1997) 984pp; highly detailed survey, 1600–1790s excerpt and text search
- Doyle, William, ed. Old Regime France: 1648–1788 (2001) excerpt and text search
- Doyle, William, ed. The Oxford Handbook of the Ancien Régime (2012) 656pp excerpt and text search; 32 topical chapters by experts
- Goubert, Pierre. Louis XIV and Twenty Million Frenchmen (1972), social history from Annales School
- Goubert, Pierre. The French Peasantry in the Seventeenth Century (1986) excerpt and text search
- Holt, Mack P. Renaissance and Reformation France: 1500–1648 (2002) excerpt and text search
- Jones, Colin. The Great Nation: France from Louis XV to Napoleon, 1715-99 (2002). excerpt and text search
- Kendall, Paul Murray. Louis XI: The Universal Spider. (1971). ISBN 0-393-30260-1
- Kors, Alan Charles. Encyclopedia of the Enlightenment (4 vol. 1990; 2nd ed. 2003), 1984pp excerpt and text search
- Knecht, R.J. The Rise and Fall of Renaissance France. (1996). ISBN 0-00-686167-9
- Le Roy Ladurie, Emmanuel. The Ancien Regime: A History of France 1610–1774 (1999), political survey excerpt and text search
- Lynn, John A. The Wars of Louis XIV, 1667–1714 (1999) excerpt and text search
- Major, J. Russell (1994). From Renaissance Monarchy to Absolute Monarchy: French Kings, Nobles & Estates. ISBN 0-8018-5631-0.
- Mayer, Arno (2010) [1981]. The Persistence of the Old Regime: Europe to the Great War. London & Brooklyn, NY: Verso. ISBN 978-1-844-67636-1.
- O'Gorman, Frank. "Eighteenth-Century England as an Ancien Regime," in Stephen Taylor, ed. Hanoverian Britain and Empire (1998) argues that a close comparison with England shows that France did have an Ancien Régime and England did not (an attack on Jonathan Clark. English Society, 1688–1832 (1985))
- Perkins, James Breck. France under Louis XV (2 vol 1897) online vol 1; online vol 2
- Potter, David. A History of France, 1460–1560: The Emergence of a Nation-State (1995)
- Riley, James C. "French Finances, 1727-1768," Journal of Modern History (1987) 59#2 pp. 209–243 in JSTOR
- Roche, Daniel. France in the Enlightenment (1998), wide-ranging history 1700–1789 excerpt and text search
- Salmon, J.H.M. (1975). Society in Crisis: France in the Sixteenth Century. University paperbacks, v. 681. London: Methuen. ISBN 0-416-73050-7.
- Schaeper, T.J. The Economy of France in the Second Half of the Reign of Louis XIV (Montreal, 1980).
- Spencer, Samia I., ed. French Women and the Age of Enlightenment. 1984.
- Sutherland, D. M. G. "Peasants, Lords, and Leviathan: Winners and Losers from the Abolition of French Feudalism, 1780-1820," Journal of Economic History (2002) 62#1 pp. 1–24 in JSTOR
- Tocqueville, Alexis de. Ancien Regime and the French Revolution (1856; 2008 edition) excerpt and text search
- Wolf, John B. Louis XIV (1968), the standard scholarly biography online edition
Religion
- Aston, Nigel. Religion and Revolution in France, 1780-1804 (2000) comprehensive overview
- McManners, John. Church and Society in Eighteenth-Century France. Vol. 1: The Clerical Establishment and Its Social Ramifications; Vol. 2: The Religion of the People and the Politics of Religion(1999)
- Palmer, R.R. Catholics and Unbelievers in Eighteenth-Century France (Princeton U.P. 1939)
- Van Kley, Dale. The Religious Origins of the French Revolution: From Calvin to the Civil Constitution, 1560–1791 (1996)
- Ward, W. R. Christianity under the Ancien Régime, 1648–1789 (1999).
Other
- Important persons mentioned in this article put on a timeline
- Henry, Lucien Edward (1882). The Royal Family of France : twelve lectures on current French history. Europe in 1882: Out of the shadow. Paris: Librairie Galignani.
In French
- Bély, Lucien (1994). La France moderne: 1498–1789. Collection: Premier Cycle (in French). Paris: PUF. ISBN 2-13-047406-3.
- (French) Bluche, François. L'Ancien Régime: Institutions et société. Collection: Livre de poche. Paris: Fallois, 1993. ISBN 2-253-06423-8
- (French) Jouanna, Arlette and Philippe Hamon, Dominique Biloghi, Guy Thiec. La France de la Renaissance; Histoire et dictionnaire. Collection: Bouquins. Paris: Laffont, 2001. ISBN 2-221-07426-2
- (French) Jouanna, Arlette and Jacqueline Boucher, Dominique Biloghi, Guy Thiec. Histoire et dictionnaire des Guerres de religion. Collection: Bouquins. Paris: Laffont, 1998. ISBN 2-221-07425-4
- (French) Pillorget, René and Suzanne Pillorget. France Baroque, France Classique 1589–1715. Collection: Bouquins. Paris: Laffont, 1995. ISBN 2-221-08110-2
- Viguerie, Jean de (1995). Histoire et dictionnaire du temps des Lumières 1715–1789. Collection: Bouquins (in French). Paris: Laffont. ISBN 2-221-04810-5.
| Preceded by Hundred Years War |
French history 1453–1789 |
Succeeded by Revolutionary Period |