Provence

Provence (/prəˈvɒns/; French pronunciation: [pʁɔ.vɑ̃s]; Provençal: Provença in classical norm or Prouvènço in Mistralian norm, pronounced [pʀuˈvɛⁿsɔ]) is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which extends from the left bank of the lower Rhône River to the west to the Italian border to the east, and is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the south.[1] It largely corresponds with the modern administrative région of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur, and includes the départements of Var, Bouches-du-Rhône, Alpes-de-Haute-Provence and parts of Alpes-Maritimes and Vaucluse.[2] The largest city of the region is Marseille.
The Romans made the region into the first Roman province beyond the Alps and called it Provincia Romana, which evolved into the present name. It was ruled by the Counts of Provence from their capital in Aix-en-Provence until 1481, when it became a province of the Kings of France.[2] While it has been part of France for more than five hundred years, it still retains a distinct cultural and linguistic identity, particularly in the interior of the region.[3]
Gallery of Provence
 Mont Ventoux and a field of lavender
Mont Ventoux and a field of lavender The old port of Marseille.
The old port of Marseille.- Place Republique in Arles
 Moustiers-Sainte-Marie, in Upper Provence
Moustiers-Sainte-Marie, in Upper Provence Provençal country road lined with plane trees
Provençal country road lined with plane trees

 Pont Saint-Bénézet at sunset
Pont Saint-Bénézet at sunset Croix de Provence on Mount Sainte-Victoire
Croix de Provence on Mount Sainte-Victoire
History
Prehistoric Provence

The coast of Provence has some of the earliest known sites of human habitation in Europe. Primitive stone tools dated to 1 to 1.05 million years BC were found in the Grotte du Vallonnet near Roquebrune-Cap-Martin, between Monaco and Menton.[4] More sophisticated tools, worked on both sides of the stone and dating to 600,000 BC, were found in the Cave of Escale at Saint Estėve-Janson, and tools from 400,000 BC and some of the first fireplaces in Europe were found at Terra Amata in Nice.[5] Tools dating to the Middle Paleolithic (300,000 BC) and Upper Paleolithic (30,000–10,000 BC) were discovered in the Observatory Cave, in the Jardin Exotique of Monaco.[6]
The Paleolithic period in Provence saw great changes in the climate, with the arrival and departure of two ice ages, and dramatic changes in the sea level. At the beginning of the Paleolithic period, the sea level in western Provence was 150 meters higher than it is today. By the end of the Paleolithic, it had dropped 100 to 150 metres lower than today's sea level. The cave dwellings of the early inhabitants of Provence were regularly inundated by the rising sea or left far from the sea and swept away by erosion.[7]
The changes in the sea level led to one of the most remarkable discoveries of signs of early man in Provence. In 1985, a diver named Henri Cosquer discovered the mouth of a submarine cave 37 metres below the surface of the Calanque de Morgiou near Marseille. The entrance led to a cave above sea level. Inside, the walls of the Cosquer Cave are decorated with drawings of bison, seals, auks, horses and outlines of human hands, dating to between 27,000 and 19,000 BC.[8]
The end of the Paleolithic and beginning of the Neolithic period saw the sea settle at its present level, a warming of the climate and the retreat of the forests. The disappearance of the forests and the deer and other easily hunted game meant that the inhabitants of Provence had to survive on rabbits, snails and wild sheep. In about 6000 BC, the Castelnovian people, living around Châteauneuf-les-Martigues, were among the first people in Europe to domesticate wild sheep, and to cease moving constantly from place to place. Since they were settled in one place they were able to develop new industries. Inspired by the imported pottery from the eastern Mediterranean, in about 6000 BC they created the first pottery to be made in France.[7]
Around 6000 BC, a wave of new settlers from the east, the Chasseens, arrived in Provence. They were farmers and warriors, and gradually displaced the earlier pastoral people from their lands. They were followed in about 2500 BC by another wave of people, also farmers, known as the Courronniens, who arrived by sea and settled along the coast of what is now the Bouches-du-Rhône department.[7] Traces of these early civilisations can be found in many parts of Provence. A Neolithic site dating to about 6,000 BC was discovered in Marseille near the Saint-Charles railway station. and a dolmen from the Bronze Age (2500–900 BC) can be found near Draguignan.
Ligures and Celts in Provence
Between the 10th and 4th century BC the Ligures were found in Provence from Massilia as far as modern day Liguria. They were of uncertain origin; they may have been the descendants of the indigenous neolithic peoples.[9] Strabo distinctly states they were not of Celtic origin and a different race from the Gauls.[10] They did not have their own alphabet, but their language remains in place names in Provence ending in the suffixes -asc, -osc. -inc, -ates, and -auni.[9] The ancient geographer Posidonios wrote of them: "Their country is savage and dry. The soil is so rocky that you cannot plant anything without striking stones. The men compensate for the lack of wheat by hunting... They climb the mountains like goats."[11] They were also warlike; they invaded Italy and went as far as Rome in the 4th century BC, and they later aided the passage of Hannibal, on his way to attack Rome (218 BC). Traces of the Ligures remain today in the dolmens and other megaliths found in eastern Provence, in the primitive stone shelters called 'Bories' found in the Luberon and Comtat, and in the rock carvings in the Valley of Marvels near Mont Bégo in the Alpes-Maritimes, at an altitude of 2,000 meters.[12]
Between the 8th and 5th centuries BC, tribes of Celtic peoples, probably coming from Central Europe, also began moving into Provence. They had weapons made of iron, which allowed them to easily defeat the local tribes, who were still armed with bronze weapons. One tribe, called the Segobriga, settled near modern-day Marseille. The Caturiges, Tricastins, and Cavares settled to the west of the Durance river.[13]
Celts and Ligurians spread throughout the area and the Celto-Ligures eventually shared the territory of Provence, each tribe in its own alpine valley or settlement along a river, each with its own king and dynasty. They built hilltop forts and settlements, later given the Latin name oppida. Today the traces 165 oppida are found in the Var, and as many as 285 in the Alpes-Maritimes.[12] They worshipped various aspects of nature, establishing sacred woods at Sainte-Baume and Gemenos, and healing springs at Glanum and Vernègues. Later, in the 5th and 4th centuries BC, the different tribes formed confederations; the Voconces in the area from the Isère to the Vaucluse; the Cavares in the Comtat; and the Salyens, from the Rhône river to the Var. The tribes began to trade their local products, iron, silver, alabaster, marble, gold, resin, wax, honey and cheese; with their neighbours, first by trading routes along the Rhône river, and later Etruscan traders visited the coast. Etruscan amphorae from the 7th and 6th centuries BC have been found in Marseille, Cassis, and in hilltop oppida in the region.[12]
Greeks in Provence
Traders from the island of Rhodes were visiting the coast of Provence in the 7th century BC. Rhodes pottery from that century has been found in Marseille, near Martigues and Istres, and at Mont Garou and Evenos near Toulon. The traders from Rhodes gave their names to the ancient town of Rhodanousia (now Trinquetaille, across the Rhône river from Arles), and to the main river of Provence, the Rhodanos, today known as the Rhône.[14]
The first permanent Greek settlement was Massalia, established at modern-day Marseille in about 600 BC by colonists coming from Phocaea (now Foça, on the Aegean coast of Asia Minor). A second wave of colonists arrived in about 540 BC, when Phocaea was destroyed by the Persians.[15]
Massalia became one of the major trading ports of the ancient world. At its height, in the 4th century BC, it had a population of about 6,000 inhabitants, living on about fifty hectares surrounded by a wall. It was governed as an aristocratic republic, by an assembly of the 600 wealthiest citizens. It had a large temple of the cult of Apollo of Delphi on a hilltop overlooking the port, and a temple of the cult of Artemis of Ephesus at the other end of the city. The Drachma coins minted in Massalia were found in all parts of Ligurian-Celtic Gaul. Traders from Massalia ventured inland deep into France on the Rivers Durance and Rhône, and established overland trade routes deep into Gaul, and to Switzerland and Burgundy, and as far north as the Baltic Sea. They exported their own products; local wine, salted pork and fish, aromatic and medicinal plants, coral and cork.[15]
The Massalians also established a series of small colonies and trading posts along the coast; which later became towns; they founded Citharista (La Ciotat); Tauroeis (Le Brusc); Olbia (near Hyères); Pergantion (Breganson); Caccabaria (Cavalaire); Athenopolis (Saint-Tropez); Antipolis (Antibes); Nikaia (Nice), and Monoicos (Monaco). They established inland towns at Glanum (Saint-Remy) and Mastrabala (Saint-Blaise.)
The most famous citizen of Massalia was the mathematician, astronomer and navigator Pytheas. Pytheas made mathematical instruments which allowed him to establish almost exactly the latitude of Marseille, and he was the first scientist to observe that the tides were connected with the phases of the moon. Between 330 and 320 BC he organised an expedition by ship into the Atlantic and as far north as England, and to visit Iceland, Shetland, and Norway. He was the first scientist to describe drift ice and the midnight sun. Though he hoped to establish a sea trading route for tin from Cornwall, his trip was not a commercial success, and it was not repeated. The Massalians found it cheaper and simpler to trade with Northern Europe over land routes.[16]
Roman Provence (2nd century BC to 5th century AD)



In the 2nd century BC the people of Massalia appealed to Rome for help against the Ligures. Roman legions entered Provence three times; first in 181 BC the Romans suppressed Ligurian uprisings near Genoa; in 154 BC the Roman Consul Optimus defeated the Oxybii and the Deciates, who were attacking Antibes; and in 125 BC, the Romans put down an uprising of a confederation of Celtic tribes.[17] After this battle, the Romans decided to establish permanent settlements in Provence. In 122 BC, next to the Celtic town of Entremont, the Romans built a new town, Aquae Sextiae, later called Aix-en-Provence. In 118 BC they founded Narbo (Narbonne).
The Roman general Gaius Marius crushed the last serious resistance in 102 BC by defeating the Cimbri and the Teutons. He then began building roads to facilitate troop movements and commerce between Rome, Spain and Northern Europe; one from the coast inland to Apt and Tarascon, and the other along the coast from Italy to Spain, passing through Fréjus and Aix-en-Provence.
In 49 BC, Massalia had the misfortune to choose the wrong side in the power struggle between Pompey and Julius Caesar. Pompey was defeated, and Massalia lost its territories and political influence. Roman veterans, in the meantime, populated two new towns, Arles and Fréjus, at the sites of older Greek settlements.
In 8 BC the Emperor Augustus built a triumphal monument at La Turbie to commemorate the pacification of the region, and he began to Romanize Provence politically and culturally. Roman engineers and architects built monuments, theatres, baths, villas, fora, arenas and aqueducts, many of which still exist. (See Architecture of Provence.) Roman towns were built at Cavaillon; Orange; Arles; Fréjus; Glanum (outside Saint-Rémy-de-Provence); Carpentras; Vaison-la-Romaine; Nîmes; Vernègues; Saint-Chamas and Cimiez (above Nice). The Roman province, which was called Gallia Narbonensis, for its capital, Narbo (modern Narbonne), extended from Italy to Spain, from the Alps to the Pyrenees.
The Pax Romana in Provence lasted until the middle of the 3rd century. Germanic tribes invaded Provence in 257 and 275. At the beginning the 4th century, the court of Roman Emperor Constantine (280–337) was forced to take refuge in Arles. By the end of the 5th century, Roman power in Provence had vanished, and an age of invasions, wars, and chaos began.
Arrival of Christianity (3rd–6th centuries)
There are many legends about the earliest Christians in Provence, but they are difficult to verify. It is documented that there were organised churches and bishops in the Roman towns of Provence as early as the 3rd and 4th centuries; in Arles in 254; Marseille in 314; Orange, Vaison and Apt in 314; Cavaillon, Digne, Embrun, Gap, and Fréjus at the end of the 4th century; Aix-en-Provence in 408; Carpentras, Avignon, Riez, Cimiez (today part of Nice) and Vence in 439; Antibes in 442; Toulon in 451; Senez in 406, Saint-Paul-Trois-Châteaux in 517; and Glandèves in 541.[18] The oldest Christian structure still surviving in Provence is the baptistery of the cathedral in Fréjus, dating from the 5th century. At about the same time, in the 5th century, the first two monasteries in Provence were founded; Lérins, on an island near Cannes; and Saint-Victor in Marseille.
Germanic invasions, Merovingians and Carolingians (5th–9th centuries)
Beginning in the second half of the 5th century, as Roman power waned, successive waves of Germanic tribes entered Provence; first the Visigoths (480); then the Ostrogoths; then the Burgundians; finally, the Franks in the 6th century. Arab invaders and Berber pirates came from North Africa to the Coast of Provence in the beginning of the 7th century.
During the late 7th and early 8th century, Provence was formally subject to the Frankish kings of the Merovingian dynasty, but it was in fact ruled by its own regional nobility of Gallo-Roman stock, who ruled themselves according to Roman, not Frankish law. Actually, the region enjoyed a prestige that the northern Franks hadn't, but the local aristocracy feared Charles Martel's expansionist ambitions.[19] In 737 Charles Martel headed down the Rhône Valley after subduing Burgundy. Charles attacked Avignon and Arles, garrisoned by the Umayyads. He came back in 739 to capture for a second time Avignon and chase the duke Maurontus to his stronghold of Marseille.[20] The city was brought to heel and the duke had to flee to an island. The region was thereafter under the rule of Carolingian Kings, descended from Charles Martel; and then was part of the empire of Charlemagne (742–814).
In 879, after the death of the Carolingian ruler Charles the Bald, Boso of Provence, (also known as Boson), his brother-in-law, broke away from the Carolingian kingdom of Louis III and was elected the first ruler of an independent state of Provence.
The Counts of Provence (9th–13th centuries)



Three different dynasties of Counts ruled Provence during the Middle Ages, and Provence became a prize in the complex rivalries between the Catalan rulers of Barcelona, the Kings of Burgundy, the German rulers of the Holy Roman Empire, and the Angevin Kings of France.
The Bosonids (879–1112) were the descendants of the first King of Provence, Boson. His son, Louis the Blind (890–928) lost his sight trying to win the throne of Italy, after which his cousin, Hugh of Italy (died 947) became the Duke of Provence and the Count of Vienne. Hugh moved the capital of Provence from Vienne to Arles and made Provence a fief of Rudolph II of Burgundy.
In the 9th century, Arab pirates (called Saracens by the French) and then the Normans invaded Provence. The Normans pillaged the region and then left, but the Saracens built castles and began raiding towns and holding local residents for ransom. Early in 973, the Saracens captured Maieul, the Abbot of the Monastery at Cluny, and held him for ransom. The ransom was paid and the abbot was released, but the people of Provence, led by Count William I rose up and defeated the Saracens near their most powerful fortress Fraxinet (La Garde-Freinet) at the Battle of Tourtour. The Saracens who were not killed at the battle were baptised and made into slaves, and the remaining Saracens in Provence fled the region. Meanwhile, the dynastic quarrels continued. A war between Rudolph III of Burgundy and his rival, the German Emperor Conrad the Salic in 1032 led to Provence becoming a fiefdom of the Holy Roman Empire, which it remained until 1246.
In 1112, the last descendant of Boson, Douce I, Countess of Provence, married the Catalan Ramon Berenguer III, Count of Barcelona, who as a result became Raymond Berenguer I, Count of Provence. He ruled Provence from 1112 until 1131, and his descendants, the Catalan Dynasty ruled Provence until 1246. In 1125, Provence was divided; the part of Provence north and west of the Durance river went to the Count of Toulouse, while the lands between the Durance and the Mediterranean, and from the Rhône river to the Alps, belonged to the Counts of Provence. The capital of Provence was moved from Arles to Aix-en-Provence, and later to Brignoles.[21]

Under the Catalan dynasty, the 12th century saw the construction of important cathedrals and abbeys in Provence, in a harmonious new style, the romanesque, which united the Gallo-Roman style of the Rhône Valley with the Lombard style of the Alps. Aix Cathedral was built on the site of the old Roman forum, and then rebuilt in the gothic style in the 13th and 14th centuries. The Church of St. Trophime in Arles was a landmark of Romanesque architecture, built between the 12th and the 15th centuries. A vast fortress-like monastery, Montmajour Abbey, was built on an island just north of Arles, and became a major destination for medieval pilgrims.
In the 12th century three Cistercian monasteries were built in remote parts of Provence, far from the political intrigues of the cities. Sénanque Abbey was the first, established in the Luberon 1148 and 1178. Le Thoronet Abbey was founded in a remote valley near Draguignan in 1160. Silvacane Abbey, on the Durance river at La Roque-d'Anthéron, was founded in 1175.
In the 13th century, the French kings started to use marriage to extend their influence into the south of France. One son of King Louis VIII of France "the Lion", Alphonse, Count of Poitou, married the heiress of the Count of Toulouse, Joan. Another, Louis IX "the Saint" of France or Saint Louis (1214–1270), married Marguerite of Provence. Then, in 1246, Charles, Count of Anjou, the youngest son of Louis VIII, married the heiress of Provence, Beatrice. Provence's fortunes became tied to the Angevin Dynasty and the Kingdom of Naples.[22]
The Popes in Avignon (14th century)

In 1309, Pope Clement V, who was originally from Bordeaux, moved the Roman Catholic Papacy to Avignon.[23] From 1309 until 1377, seven Popes reigned in Avignon before the Schism between the Roman and Avignon churches, which led to the creation of rival popes in both places. After that three Antipopes reigned in Avignon until 1423, when the Papacy finally returned to Rome. Between 1334 and 1363 the old and new Papal Palaces of Avignon were built by Popes Benedict XII and Clement VI respectively; together the Palais des Papes was the largest gothic palace in Europe.[24]
The 14th century was a terrible time in Provence, and all of Europe: the population of Provence had been about 400,000 people; the Black Plague (1348–1350) killed fifteen thousand people in Arles, half the population of the city, and greatly reduced the population of the whole region. The defeat of the French Army during the Hundred Years' War forced the cities of Provence to build walls and towers to defend themselves against armies of former soldiers who ravaged the countryside.
The Angevin rulers of Provence also had a difficult time. An assembly of nobles, religious leaders, and town leaders of Provence was organised to resist the authority of Queen Joan I of Naples (1343–1382). She was murdered in 1382 by her cousin and heir, Charles of Durazzo, who started a new war, leading to the separation of Nice, Puget-Théniers and Barcelonnette from Provence in 1388, and their attachment to the County of Savoy. From 1388 up to 1526, the area acquired by the Savoy was known as Terres Neuves de Provence; after 1526 it officially took on the name County of Nice.
Good King René, the last ruler of Provence


The 15th century saw a series of wars between the Kings of Aragon and the Counts of Provence. In 1423 the army of Alphonse of Aragon captured Marseille, and in 1443 they captured Naples, and forced its ruler, King René I of Naples, to flee. He eventually settled in one of his remaining territories, Provence.
History and legend has given René the title "Good King René of Provence", though he only lived in Provence in the last ten years of his life, from 1470 to 1480, and his political policies of territorial expansion were costly and unsuccessful. Provence benefitted from population growth and economic expansion, and René was a generous patron of the arts, sponsoring painters Nicolas Froment, Louis Bréa, and other masters. He also completed one of the finest castles in Provence at Tarascon, on the Rhône river.
When René died in 1480, his title passed to his nephew Charles du Maine. One year later, in 1481, when Charles died, the title passed to Louis XI of France. Provence was legally incorporated into the French royal domain in 1486.
1486 to 1789
Soon after Provence became part of France, it became involved in the Wars of Religion that swept the country in the 16th century. Between 1493 and 1501, many Jews were expelled from their homes and sought sanctuary in the region of Avignon, which was still under the direct rule of the Pope. In 1545, the Parliament of Aix ordered the destruction of the villages of Lourmarin, Mérindol, Cabriéres in the Luberon, because their inhabitants were Vaudois, of Italian Piedmontese origin, and were not considered sufficiently orthodox Catholics. Most of Provence remained strongly Catholic, with only one enclave of Protestants, the principality of Orange, Vaucluse, an enclave ruled by Prince William of the House of Orange-Nassau of the Netherlands, which was created in 1544 and was not incorporated into France until 1673. An army of the Catholic League laid siege to the Protestant city of Mėnerbes in the Vaucluse between 1573 and 1578. The wars did not stop until the end of the 16th century, with the consolidation of power in Provence by the House of Bourbon kings.

The semi-independent Parliament of Provence in Aix and some of the cities of Provence, particularly Marseille, continued to rebel against the authority of the Bourbon king. After uprisings in 1630–31 and 1648–1652, the young King Louis XIV had two large forts, fort St. Jean and Fort St. Nicholas, built at the harbour entrance to control the city's unruly population.
At the beginning of the 16th century, Cardinal Richelieu began to build a naval arsenal and dockyard at Toulon to serve as a base for a new French Mediterranean fleet. The base was greatly enlarged by Jean-Baptiste Colbert, the minister of Louis XIV, who also commissioned his chief military engineer Vauban to strengthen the fortifications around the city.
At the beginning of the 17th century Provence had a population of about 450,000 people.[25] It was predominantly rural, devoted to raising wheat, wine, and olives, with small industries for tanning, pottery, perfume-making, and ship and boat building. Provençal quilts, made from the mid-17th century onwards, were successfully exported to England, Spain, Italy, Germany and Holland.[26] There was considerable commerce along the coast, and up and down the Rhône river. The cities: Marseille, Toulon, Avignon and Aix-en-Provence, saw the construction of boulevards and richly-decorated private houses.

At the beginning of the 18th century Provence suffered from the economic malaise of the end of the reign of Louis XIV. The plague struck the region between 1720 and 1722, beginning in Marseille, killing some 40,000 people. Still, by the end of the century, many artisanal industries began to flourish; making perfumes in Grasse; olive oil in Aix and the Alpilles; textiles in Orange, Avignon and Tarascon; and faience pottery in Marseille, Apt, Aubagne, and Moustiers-Sainte-Marie. Many immigrants arrived from Liguria and the Piedmont in Italy. By the end of the 18th century, Marseille had a population of 120,000 people, making it the third largest city in France.[25]
During the French Revolution
Though most of Provence, with the exception of Marseille, Aix and Avignon, was rural, conservative and largely royalist, it did produce some memorable figures in the French Revolution; Honoré Gabriel Riqueti, comte de Mirabeau from Aix, who tried to moderate the Revolution, and turn France into a constitutional monarchy like England; the Marquis de Sade from Lacoste in the Luberon, who was a Deputy from the far left in the National Assembly; Charles Barbaroux from Marseille, who sent a battalion of volunteers to Paris to fight in the French Revolutionary Army; and Emmanuel-Joseph Sieyès (1748–1836), an abbé, essayist and political leader, who was one of the chief theorists of the French Revolution, French Consulate, and First French Empire, and who, in 1799, was the instigator of the coup d'état of 18 Brumaire, which brought Napoleon to power.

Provence also produced the most memorable song of the period, the La Marseillaise. Though the song was originally written by a citizen of Strasbourg, Claude Joseph Rouget de Lisle in 1792, and it was originally a war song for the revolutionary Army of the Rhine, it became famous when it sung on the streets of Paris by the volunteers from Marseille, who had heard it when it was sung in Marseille by a young volunteer from Montpellier named François Mireur. It became the most popular song of the Revolution, and in 1879 became the national anthem of France.
The Revolution was as violent and bloody in Provence as it was in other parts of France. On 30 April 1790, Fort Saint-Nicolas in Marseille was besieged, and many of the soldiers inside were massacred. On 17 October 1791 a massacre of royalists and religious figures took place in the ice storage rooms (glaciere) of the prison of the Palace of the Popes in Avignon.
When the radical Montagnards seized power from the Girondins in May 1793, a real counter-revolution broke out in Avignon, Marseille and Toulon. A revolutionary army under General Carteaux recaptured Marseille in August 1793 and renamed it "City without a Name" (Ville sans Nom.) In Toulon, the opponents of the Revolution handed the city to a British and Spanish fleet on 28 August 1793. A Revolutionary Army laid siege to the British positions for four months (see the Siege of Toulon), and finally, thanks to the enterprise of the young commander of artillery, Napoleon Bonaparte, defeated the British and drove them out in December 1793. About 15,000 royalists escaped with the British fleet, but five to eight hundred of the 7,000 who remained were shot on the Champ de Mars, and Toulon was renamed "Port la Montagne".
The fall of the Montagnards in July 1794 was followed by a new White Terror aimed at the revolutionaries. Calm was only restored by the rise of Napoleon to power in 1795.
Under Napoleon
Napoleon restored the belongings and power of the families of the old regime in Provence. The British fleet of Admiral Horatio Nelson blockaded Toulon, and almost all maritime commerce was stopped, causing hardship and poverty. When Napoleon was defeated, his fall was celebrated in Provence. When he escaped from Elba on 1 March 1815, and landed at Golfe-Juan, he detoured to avoid the cities of Provence, which were hostile to him, and therefore directed his small force directly to the northeast of it.[27]
19th century

Provence enjoyed prosperity in the 19th century; the ports of Marseille and Toulon connected Provence with the expanding French Empire in North Africa and the Orient, especially after the opening of the Suez Canal in 1869.
In April–July 1859, Napoleon III made a secret agreement with Cavour, Prime Minister of Piedmont, for France to assist in expelling Austria from the Italian Peninsula and bringing about a united Italy, in exchange for Piedmont ceding Savoy and the Nice region to France. He went to war with Austria in 1859 and won a victory at Solferino, which resulted in Austria ceding Lombardy to France. France immediately ceded Lombardy to Piedmont, and, in return, Napoleon received Savoy and Nice in 1860, and Roquebrune-Cap-Martin and Menton in 1861.
The railroad connected Paris with Marseille (1848) and then with Toulon and Nice (1864). Nice, Antibes and Hyères became popular winter resorts for European royalty, including Queen Victoria. Under Napoleon III, Marseille grew to a population of 250,000, including a very large Italian community. Toulon had a population of 80,000. The large cities like Marseille and Toulon saw the building of churches, opera houses, grand boulevards, and parks.
After the fall of Louis Napoleon following the defeat in the Franco-Prussian War barricades went up in the streets of Marseille (23 March 1871) and the Communards, led by Gaston Cremieux and following the lead of the Paris Commune, took control of the city. The Commune was crushed by the army and Cremieux was executed on 30 November 1871. Though Provence was generally conservative, it often elected reformist leaders; Prime Minister Léon Gambetta was the son of a Marseille grocer, and future prime minister Georges Clemenceau was elected deputy from the Var in 1885.
The second half of the 19th century saw a revival of the Provençal language and culture, particularly traditional rural values. driven by a movement of writers and poets called the Felibrige, led by poet Frédéric Mistral. Mistral achieved literary success with his novel Miréio (Mireille in French); he was awarded the Nobel Prize for literature in 1904.
20th century
Between World War I and World War II, Provence was bitterly divided between the more conservative rural areas and the more radical big cities. There were widespread strikes in Marseille in 1919, and riots in Toulon in 1935.
After the defeat of France by Germany in June 1940, France was divided into an occupied zone and unoccupied zone, with Provence in the unoccupied zone. Parts of eastern Provence were occupied by Italian soldiers. Collaboration and passive resistance gradually gave way to more active resistance, particularly after Nazi Germany invaded the Soviet Union in June 1941 and the Communist Party became active in the resistance. Jean Moulin, the deputy of Charles de Gaulle, the leader of the Free France resistance movement, was parachuted into Eygalières, in the Bouches-du-Rhône on 2 January 1942 to unite the diverse resistance movements in all of France against the Germans.
In November 1942, following Allied landings in North Africa (Operation Torch), the Germans occupied all of Provence (Operation Attila) and then headed for Toulon (Case Anton). The French fleet at Toulon sabotaged its own ships to keep them from falling into German hands.

The Germans began a systematic rounding-up of French Jews and refugees from Nice and Marseille. Many thousands were taken to concentration camps, and few survived. A large quarter around the port of Marseille was emptied of inhabitants and dynamited, so it would not serve as a base for the resistance. Nonetheless, the resistance grew stronger; the leader of the pro-German militia, the Milice, in Marseille was assassinated in April 1943.
On 15 August 1944, two months after the Allied landings in Normandy (Operation Overlord), the Seventh United States Army under General Alexander Patch, with a Free French corps under General Jean de Lattre de Tassigny, landed on the coast of the Var between St. Raphael and Cavalaire (Operation Dragoon). The American forces moved north toward Manosque, Sisteron and Gap, while the French First Armored Division under General Vigier liberated Brignoles, Salon, Arles, and Avignon. The Germans in Toulon resisted until 27 August, and Marseille was not liberated until 25 August.
After the end of the War, Provence faced an enormous task of repair and reconstruction, particularly of the ports and railroads destroyed during the war. As part of this effort, the first modern concrete apartment block, the Unité d'Habitation of Corbusier, was built in Marseille in 1947–52. In 1962, Provence absorbed a large number of French citizens who left Algeria after its independence. Since that time, large North African communities settled in and around the big cities, particularly Marseille and Toulon.
In the 1940s, Provence underwent a cultural renewal, with the founding of the Avignon Festival of theatre (1947), the reopening of the Cannes Film Festival (begun in 1939), and many other major events. With the building of new highways, particularly the Paris Marseille autoroute which opened in 1970, Provence became destination for mass tourism from all over Europe. Many Europeans, particularly from Britain, bought summer houses in Provence. The arrival of the TGV high-speed trains shortened the trip from Paris to Marseille to less than four hours.
At the end of the 20th century and the beginning of the 21st century, the residents of Provence were struggling to reconcile economic development and population growth with their desire to preserve the landscape and culture that make Provence unique.
Extent and geography
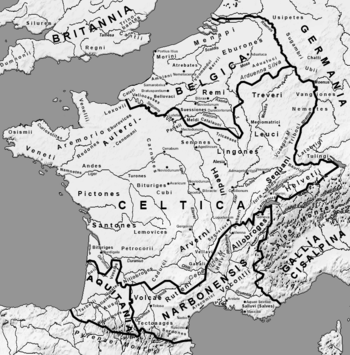

The original Roman province was called Gallia Transalpina, then Gallia Narbonensis, or simply Provincia Nostra ('Our Province') or Provincia. It extended from the Alps to the Pyrenees and north to the Vaucluse, with its capital in Narbo Martius (present-day Narbonne).
Borders
In the 15th century the Conté of Provence was bounded by the Var river on the east, the Rhône river to the west, with the Mediterranean to the south, and a northern border that roughly followed the Durance river.
The Comtat Venaissin, a territory which included Avignon, and the principality of Orange were both papal states, ruled by the Pope from the 13th century until the French Revolution. At the end of the 14th century another piece of Provence along the Italian border, including Nice and the lower Alps, was detached from Provence and attached to the lands of the Duke of Savoy. The lower Alps were re-attached to France after the Treaty of Utrecht in 1713, but Nice did not return to France until 1860, during the reign of Napoleon III.[28]
The administrative region of Provence-Alpes-Cote d'Azur was created in 1982. It included Provence, plus the territory of the Comtat Venaissin around Avignon, the eastern portion of the Dauphiné, and the former county of Nice.
Rivers

The Rhône river, on the western border of Provence, is one of the major rivers of France, and has been a highway of commerce and communications between inland France and the Mediterranean for centuries. It rises as the effluent of the Rhône Glacier in Valais, Switzerland, in the Saint-Gotthard massif, at an altitude of 1753 m. It is joined by the river Saône at Lyon. Along the Rhône Valley, it is joined on the right bank by Cévennes rivers Eyrieux, Ardèche, Cèze and Gardon or Gard, on the left Alps bank by rivers Isère, Drôme, Ouvèze and Durance. At Arles, the Rhône divides itself in two arms, forming the Camargue delta, with all branches flowing into the Mediterranean Sea. One arm is called the "Grand Rhône"; the other one is the "Petit Rhône".
The Durance river, a tributary of the Rhône, has its source in the Alps near Briançon. It flows south-west through Embrun, Sisteron, Manosque, Cavaillon, and Avignon, where it meets the Rhône.
The Verdon River is a tributary of the Durance, rising at an altitude of 2,400 metres in the southwestern Alps near Barcelonette, and flowing southwest for 175 kilometres through the Alpes-de-Haute-Provence and Var (départements) before it reaches the Durance at near Vinon-sur-Verdon, south of Manosque. The Verdon is best known for its canyon, the Verdon Gorge. This limestone canyon, also called the 'Grand Canyon of Verdon', 20 kilometres in length and more than 300 metres deep, is a popular climbing and sight-seeing area.
The Var River rises near the Col de la Cayolle (2,326 m/7,631 ft) in the Maritime Alps and flows generally southeast for 120 kilometres (75 mi) into the Mediterranean between Nice and Saint-Laurent-du-Var. Before Nice was returned to France in 1860, the Var marked the eastern border of France along the Mediterranean. The Var is the unique case in France of a river giving a name to a department, but not flowing through that department (due to subsequent adjustments to the department's boundaries).
The Camargue
With an area of over 930 km2 (360 mi2), the Camargue is Western Europe's largest river delta (technically an island, as it is wholly surrounded by water). It is a vast plain comprising large brine lagoons or étangs, cut off from the sea by sandbars and encircled by reed-covered marshes which are in turn surrounded by a large cultivated area.
The Camargue is home to more than 400 species of birds, the brine ponds providing one of the few European habitats for the greater flamingo. The marshes are also a prime habitat for many species of insects, notably (and notoriously) some of the most ferocious mosquitoes to be found anywhere in France. It is also famous for bulls and the Camargue horse.
Mountains


By considering the Maritime Alps, along the border with Italy, as a part of the cultural Provence, they constitute the highest elevations of the region (the Punta dell'Argentera has an elevation of 3,297 m). They form the border between the French département Alpes-Maritimes and the Italian province of Cuneo. Mercantour National Park is located in the Maritime Alps. On the other hand, if the département Hautes Alpes is also considered as part of the modern Provence, then the alpin Écrins mountains represent the highest elevations of the region with the Barre des Écrins culminating at 4102m.

Outside of the Maritime Alps, Mont Ventoux (Occitan: Ventor in classical norm or Ventour in Mistralian norm), at 1,909 metres (6,263 ft), is the highest peak in Provence. It is located some 20 km north-east of Carpentras, Vaucluse. On the north side, the mountain borders the Drôme département. It is nicknamed the "Giant of Provence", or "The Bald Mountain". Although geologically part of the Alps, is often considered to be separate from them, due to the lack of mountains of a similar height nearby. It stands alone to the west of the Luberon range, and just to the east of the Dentelles de Montmirail, its foothills. The top of the mountain is bare limestone without vegetation or trees. The white limestone on the mountain's barren peak means it appears from a distance to be snow-capped all year round (its snow cover actually lasts from December to April).
The Alpilles are a chain of small mountains located about 20 kilometres (12 mi) south of Avignon. Although they are not particularly high – only some 387 metres (1,270 ft) at their highest point – the Alpilles stand out since they rise abruptly from the plain of the Rhône valley. The range is about 25 km long by about 8 to 10 km wide, running in an east–west direction between the Rhône and Durance rivers. The landscape of the Alpilles is one of arid limestone peaks separated by dry valleys.

Montagne Sainte-Victoire is probably the best-known mountain in Provence, thanks to the painter Paul Cézanne, who could see it from his home, and painted it frequently. It is a limestone mountain ridge which extends over 18 kilometres between the départements of Bouches-du-Rhône and Var. Its highest point is the Pic des mouches at 1,011 m.
The Massif des Maures (Mountains of the Moors) is a small chain of mountains that lies along the coast of the Mediterranean in the Var Department between Hyères et Fréjus. Its highest point is the signal de la Sauvette, 780 metres high. The name is a souvenir of the Moors (Maures in Old French), Arabs and Berbers from North Africa, who settled on the coast of Provence in the 9th and 10th centuries.
The massif des Maures extends about sixty kilometres along the coast, and reaches inland about thirty kilometres. On the north it is bordered by a depression which is followed by the routes nationales 97 and 7 and the railroad line between Toulon and Nice. On the south it ends abruptly at the Mediterranean, forming a broken and abrupt coastline.
The peninsula of Saint-Tropez is part of the Massif des Maures, along with the peninsula of Giens and the islands offshore of Hyères; Porquerolles, Port-Cros, and île du Levant. Cape Sicié, west of Toulon, as well as the massif of Tanneron, belong geologically to the massif des Maures.
The Calanques

The Calanques, also known as the Massif des Calanques, are a dramatic feature of the Provence coast, a 20-km long series of narrow inlets in the cliffs of the coastline between Marseille on the west and Cassis on the east. The highest peak in the massif is Mont Puget, 565 metres high.
The best known calanques of the Massif des Calanques include the Calanque de Sormiou, the Calanque de Morgiou, the Calanque d'En-Vau, the Calanque de Port-Pin and the Calanque de Sugiton.
Calanques are remains of ancient river mouths formed mostly during Tertiary. Later, during quaternary glaciations, as glaciers swept by, they further deepened those valleys which would eventually (at the end of the last glaciation) be invaded with sea and become calanques.
The Cosquer cave is an underwater grotto in the Calanque de Morgiou, 37 metres (121 ft) underwater, that was inhabited during Paleolithic era, when the sea level was much lower than today. Its walls are covered with paintings and engravings dating back to between 27,000 and 19,000 BC, depicting animals such as bison, ibex, and horses, as well as sea mammals such as seals, and at least one bird, the auk.
Landscapes
The Garrigue is the typical landscape of Provence; it is a type of low, soft-leaved scrubland or chaparral found on limestone soils around the Mediterranean Basin, generally near the seacoast, where the climate is moderate, but where there are annual summer drought conditions.[29] Juniper and stunted holm oaks are the typical trees; aromatic lime-tolerant shrubs such as lavender, sage, rosemary, wild thyme and Artemisia are common garrigue plants. The open landscape of the garrigue is punctuated by dense thickets of Kermes oak.
Climate

Most of Provence has a Mediterranean climate, characterised by hot, dry summers, mild winters, little snow, and abundant sunshine. Within Provence there are micro-climates and local variations, ranging from the Alpine climate inland from Nice to the continental climate in the northern Vaucluse. The winds of Provence are an important feature of the climate, particularly the mistral, a cold, dry wind which, especially in the winter, blows down the Rhône Valley to the Bouches-du-Rhône and the Var Departments, and often reaches over one hundred kilometres an hour.
Bouches-du-Rhône
Marseille, in the Bouches-du-Rhône, has an average of 59 days of rain a year, though when it does rain the rain is often torrential; the average annual rainfall is 544.4 mm. It snows an average of 2.3 days a year, and the snow rarely remains long. Marseille has an average of 2835.5 hours of sunshine a year. The average minimum temperature in January is 2.3 °C., and the average maximum temperature in July is 29.3 °C. The mistral blows an average of one hundred days a year.[30]
The Var
Toulon and the Department of the Var (which includes St. Tropez and Hyères) have a climate slightly warmer, dryer and sunnier than Nice and the Alpes-Maritime, but also less sheltered from the wind. Toulon has an average of 2899.3 hours of sunshine a year, making it the sunniest city in metropolitan France,[31] The average maximum daily temperature in August is 29.1 °C., and the average daily minimum temperature in January is 5.8 °C. The average annual rainfall is 665 mm, with the most rain from October to November. Strong winds blow an average of 118 days a year in Toulon, compared with 76 days at Fréjus further east. The strongest Mistral wind recorded in Toulon was 130 kilometres an hour.[32]
Alpes-Maritimes
Nice and the Alpes-Maritimes Department are sheltered by the Alps, and are the most protected part of the Mediterranean coast. The winds in this department are usually gentle, blowing from the sea to the land, though sometimes the Mistral blows strongly from the northwest, or, turned by the mountains, from the east. In 1956 a mistral wind from the northwest reached the speed of 180 kilometres an hour at Nice airport. Sometimes in summer the scirocco brings high temperatures and reddish desert sand from Africa. (See Winds of Provence.)
Rainfall is infrequent – 63 days a year, but can be torrential, particularly in September, when storms and rain are caused by the difference between the colder air inland and the warm Mediterranean water temperature (20–24 degrees C.). The average annual rainfall in Nice is 767 mm, more than in Paris, but concentrated in fewer days.
Snow is extremely rare, usually falling once every ten years. 1956 was a very exceptional year, when 20 centimetres of snow blanketed the coast. In January 1985 the coast between Cannes and Menton received 30 to 40 centimetres of snow. In the mountains, the snow is present from November to May
Nice has an annual average of 2694 hours of sunshine. The average maximum daily temperature in Nice in August is 28 °C., and the average minimum daily temperature in January is 6 °C.[33]
Alpes-de-Haute-Provence
The Department of Alpes-de-Haute-Provence has a Mediterranean climate in the lower valleys under one thousand metres in altitude and an alpine climate in the high valleys, such as the valleys of the Blanche, the Haut Verdon and the Ubaye, which are over 2500 metres high. The alpine climate in the higher mountains is moderated by the warmer air from the Mediterranean.
Haute-Provence has unusually high summer temperatures for its altitude and latitude (44 degrees north). The average summer temperature is 22 to 23 °C. at an altitude of 400 metres, and 18 to 19 °C. at the altitude of 1000 metres; and the winter average temperature is 4 to 5 °C. at 400 metres and 0 C. at 1000 metres. The lower valleys have 50 days of freezing temperatures a year, more in the higher valleys. Sometimes the temperatures in the high valleys can reach −30 °C. Because of this combination of high mountains and Mediterranean air, it is not unusual that the region frequently has some of the lowest winter temperatures and some of the hottest summer temperatures in France.
Rainfall in Haute-Provence is infrequent – 60 to 80 days a year – but can be torrential; 650 to 900 mm. a year in the foothills and plateaus of the southwest, and in the valley of the Ubaye; and 900 to 1500 mm. in the mountains. Most rainfall comes in the autumn, in brief and intense storms; from mid-June to mid-August, rain falls during brief but violent thunderstorms. Thunder can be heard 30 to 40 days a year.
Snow falls in the mountains from November to May, and in midwinter can be found down to altitude of 1000–1200 metres on the shady side of the mountains and 1300 to 1600 metres on the sunny side. Snowfalls are usually fairly light, and melt rapidly.
The Mistral (wind) is a feature of the climate in the western part of the Department, blowing from the north and the northwest, bringing clear and dry weather. The eastern part of the department is more protected from the Mistral. The Marin (wind) comes from the south, bringing warm air, clouds and rain.
Haute-Provence is one of the sunniest regions of France, with an average of between 2550 and 2650 hours of sunshine annually in the north of the department, and 2700 to 2800 hours in the southwest. The clear nights and sunny days cause a sharp difference between nighttime and daytime temperatures. Because of the clear nights, the region is home of important observatories, such as the Observatory of Haute-Provence in Saint-Michel-Observatoire near of Forcalquier.[34]
The Vaucluse
The Vaucluse is the meeting point of three of the four different climatic zones of France; it has a Mediterranean climate in the south, an alpine climate in the northeast, around the mountains of Vaucluse and the massif of the Baronnies; and a continental climate in the northwest. The close proximity of these three different climates tends to moderate all of them, and the Mediterranean climate usually prevails.
Orange in the Vaucluse has 2595 hours of sunshine a year. It rains an average of 80 days a year, for a total of 693.4 mm a year. The maximum average temperature in July is 29.6 °C., and the average minimum temperature in January is 1.3 °C. There are an average of 110 days of strong winds a year.[35]
Language and literature
Scientists, scholars and prophets
- Pytheas (4th century BCE) was a geographer and mathematician who lived in the Greek colony of Massalia, which became Marseille. He conducted an expedition by sea north around England to Iceland, and was the first to describe the midnight sun and polar regions.
- Petrarch (1304–1374) was an Italian poet and scholar, considered the father of humanism and one of the first great figures of Italian literature. He spent much of his early life in Avignon and Carpentras as an official at the Papal court in Avignon, and wrote a famous account of his ascent of Mount Ventoux near Aix-en-Provence.
- Nostradamus (1503–1566), a Renaissance apothecary and reputed clairvoyant best known for his alleged prophecies of great world events, was born in Saint-Remy-de-Provence and lived and died in Salon-de-Provence.
Occitan literature

Historically the language spoken in Provence was Provençal, a dialect of the Occitan language, also known as langue d'oc, and closely related to Catalan. There are several regional variations: vivaro-alpin, spoken in the Alps; and the provençal variations of south, including the maritime, the rhoadanien (in the Rhône Valley) and the niçois (in Nice). Niçois is the archaic form of provençal closest to the original language of the troubadours, and is sometimes to said to be literary language of its own.[36]
Provençal was widely spoken in Provence until the beginning of the 20th century, when the French government launched an intensive and largely successful effort to replace regional languages with French. Today Provençal is taught in schools and universities in the region, but is spoken regularly by a small number of people, probably less than five hundred thousand, mostly elderly.
Writers and poets in the Occitan language

The golden age of Provençal literature, more correctly called Occitan literature, was the 11th century and the 12th century, when the troubadours broke away from classical Latin literature and composed romances and love songs in their own vernacular language. Among the most famous troubadours was Folquet de Marselha, whose love songs became famous all over Europe, and who was praised by Dante in his Divine Comedy. In his later years, Folquet gave up poetry to become the Abbot of Le Thoronet Abbey, and then Bishop of Toulouse, where he fiercely persecuted the Cathars.
In the middle of the 19th century there was a literary movement to revive the language, called the Félibrige, led by the poet Frédéric Mistral (1830–1914), who shared the Nobel Prize for Literature in 1904.
Provençal writers and poets who wrote in Occitan include:
- Raimbaut de Vaqueiras (1180–1207)
- Louis Bellaud (1543–1588)
- Théodore Aubanel (1829–1886)
- Joseph d'Arbaud (1874–1950)
- Robert Lafont (1923–2009)
French authors
- Alphonse Daudet (1840–1897) was the best-known French writer from Provence in the 19th century, though he lived mostly in Paris and Champrosay. He was best known for his Lettres de mon moulin (eng: Letters from my Mill) (1869) and the Tartarin de Tarascon trilogy (1872, 1885, 1890). His story L'Arlésienne (1872) was made into a three-act play with music by Bizet.[37]
- Marcel Pagnol (1895–1970), born in Aubagne, is known both as a filmmaker and for his stories of his childhood, Le Château de la Mere, La Gloire de mon Pere, and Le Temps des secrets. He was the first filmmaker to become a member of the Académie française in 1946.
- Colette (Sidonie-Gabrielle Colette) (1873–1954), although she was not from Provence, became particularly attached to Saint-Tropez. After World War II, she headed a committee which saw that the village, badly-damaged by the war, was restored to its original beauty and character
- Jean Giono (1895–1970), born in Manosque, wrote about peasant life in Provence, inspired by his imagination and by his vision of Ancient Greece.
- Paul Arène (1843–1896), born in Sisteron, wrote about life and the countryside around his home town.
Emigrés, exiles, and expatriates
In the 19th and 20th centuries, the climate and lifestyle of Provence attracted writers almost as much as it attracted painters. It was particularly popular among British, American and Russian writers in the 1920s and 1930s.
- Edith Wharton (1862–1937), bought Castel Sainte-Claire in 1927, on the site of a former convent in the hills above Hyères, where she lived during the winters and springs until her death in 1937.
- F. Scott Fitzgerald (1896–1940) and his wife Zelda first visited the Riviera in 1924, stopping at Hyères, Cannes and Monte Carlo, eventually staying at St. Raphaël, where he wrote much of The Great Gatsby and began Tender is the Night.
- Ivan Bunin (1870–1953), the first Russian writer to win the Nobel Prize for Literature, went to France after the Russian Revolution, set several of his short stories on the Côte d'Azur, and had a house in Grasse.
- Somerset Maugham (1874–1965) bought a house, the Villa Mauresque, in Saint-Jean-Cap-Ferrat in 1928, and, except for the years of World War II, spent much of his time there until his death.
Other English-speaking writers who live in or have written about Provence include:
- Peter Mayle
- Carol Drinkwater
- John Lanchester
- Willa Cather
- Charles Spurgeon (who spent long periods in Menton)
- Katherine Mansfield
- Lawrence Durrell
Music
Music written about Provence includes:
- The saxophone concerto Tableaux de Provence (Pictures of Provence) composed by Paule Maurice.
- The opera Mireille by Charles Gounod after Frédéric Mistral's poem Mireio.
- Georges Bizet, 'L'Arlésienne' incidental music to play by Alphonse Daudet.
- Darius Milhaud, 'Suite Provençale'
- Two song settings of Vladimir Nabokov's poem "Provence" in Russian and English versions by composers Ivan Barbotin and James DeMars on the 2011 contemporary classical album Troika.[38]
- The piece "Suite Provencale", written for symphonic band by Jan Van der Roost.
Painters


Artists have been painting in Provence since prehistoric times; paintings of bisons, seals, auks and horses dating to between 27,000 and 19,000 BC were found in the Cosquer Cave near Marseille.[39]
The 14th-century wooden ceiling of the cloister of Fréjus Cathedral has a remarkable series of paintings of biblical scenes, fantastic animals, and scenes from daily life, painted between 1350 and 1360. They include paintings of a fallen angel with the wings of a bat, a demon with the tail of a serpent, angels playing instruments, a tiger, an elephant, an ostrich, domestic and wild animals, a mermaid, a dragon, a centaur, a butcher, a knight, and a juggler.[40]
Nicolas Froment (1435–1486) was the most important painter of Provence during the Renaissance, best known for his triptych of the Burning Bush (c. 1476), commissioned by King René I of Naples. The painting shows the Annunciation to the shepherds, with the Virgin Mary and Christ above the burning bush. The wings of the triptych show King Rene with Mary Magdalene, St. Anthony and St. Maurice on one side, and Queen Jeanne de Laval, with Saint Catherine, John the Evangelist, and Saint Nicholas on the other.[41]
Louis Bréa (1450–1523) was a 15th-century painter, born in Nice, whose work is found in churches from Genoa to Antibes. His Retable of Saint-Nicholas (1500) is found in Monaco, and his Retable de Notre-Dame-de-Rosaire (1515) is found in Antibes.
Pierre Paul Puget (1620–1694), born in Marseille, was a painter of portraits and religious scenes, but was better known for his sculptures, found in Toulon Cathedral, outside the city hall of Toulon, and in the Louvre. There is a mountain named for him near Marseille, and a square in Toulon.

.jpg)

In the 19th and 20th centuries, many of the most famous painters in the world converged on Provence, drawn by the climate and the clarity of the light. The special quality of the light is partly a result of the Mistral wind, which removes dust from the atmosphere, greatly increasing visibility.
- Adolphe Monticelli (1824–1886) was born in Marseille, moved to Paris in 1846 and returned to Marseille in 1870. His work influenced Vincent van Gogh who greatly admired him.[42]
- Paul Cézanne (1839–1906) was born in Aix-en-Provence, and lived and worked there most of his life. The local landscapes, particularly Montagne Sainte-Victoire, featured often in his work. He also painted frequently at L'Estaque.
- Vincent van Gogh (1853–1890) lived little more than two years in Provence, but his fame as a painter is largely a result of what he painted there. He lived in Arles from February 1888 to May 1889, and then in Saint-Remy from May 1889 until May 1890.
- Auguste Renoir (1841–1919) visited Beaulieu, Grasse, Saint Raphael and Cannes, before finally settling in Cagnes-sur-Mer in 1907, where he bought a farm in the hills and built a new house and workshop on the grounds. He continued to paint there until his death in 1919. His house is now a museum.
- Henri Matisse (1869–1954) first visited St. Tropez in 1904. In 1917 he settled in Nice, first at the Hotel Beau Rivage, then the Hotel de la Mediterranée, then la Villa des Allies in Cimiez. In 1921 he lived in an apartment at 1 place Felix Faure in Nice, next to the flower market and overlooking the sea, where he lived until 1938. He then moved to the Hotel Regina in the hills of Cimiez, above Nice. During World War II he lived in Vence, then returned to Cimiez, where he died and is buried.
- Pablo Picasso (1881–1973) spent each summer from 1919 to 1939 on the Côte d'Azur, and moved there permanently in 1946, first at Vallauris, then at Mougins, where he spent his last years.
- Pierre Bonnard (1867–1947) retired to and died at Le Cannet.
- Georges Braque (1882–1963) painted frequently at L'Estaque between 1907 and 1910.
- Henri-Edmond Cross (1856–1910) discovered the Côte d'Azur in 1883 and painted at Monaco and Hyères.
- Maurice Denis (1870–1943) painted at St. Tropez and Bandol.
- André Derain (1880–1954) painted at L'Estaque and Martigues.
- Raoul Dufy (1877–1953), whose wife was from Nice, painted in Forcalquier, Marseille and Martigues.
- Albert Marquet (1873–1947) painted at Marseille, St. Tropez and L'Estaque.
- Claude Monet (1840–1927) visited Menton, Bordighera, Juan-les-Pins, Monte-Carlo, Nice, Cannes, Beaulieu and Villefranche, and painted a number of seascapes of Cap Martin, near Menton, and at Cap d'Antibes.
- Edvard Munch (1863–1944) visited and painted in Nice and Monte-Carlo (where he developed a passion for gambling), and rented a villa at Saint-Jean-Cap-Ferrat in 1891.
- Paul Signac (1863–1935) visited St. Tropez in 1892, and bought a villa, La Hune, at the foot of citadel in 1897. It was at his villa that his friend, Henri Matisse, painted his famous Luxe, Calme et Volupté" in 1904. Signac made numerous paintings along the coast.
- Pierre Deval (1897–1993), a French modernist and figurist painter, lived and worked at the Domaine d'Orvès in La Valette-du-Var from 1925 until his death in 1993.
- Nicolas de Staël (1914–1955) lived in Nice and Antibes.
- Yves Klein (1928–1962), a native of Nice, is considered an important figure in post-war European art.
- Sacha Sosno (b. 1937) is a French painter and sculptor living and working in Nice.
Source and Bibliography about artists on the Mediterranean
- Méditerranée de Courbet á Matisse, catalogue of the exhibit at the Grand Palais, Paris from September 2000 to January 2001. Published by the Réunion des musées nationaux, 2000.
Film
Provence has a special place in the history of the motion picture – one of the first projected motion pictures, L'Arrivée d'un train en gare de La Ciotat (The Entry of a Train Into the Station of Ciotat), a fifty-second silent film, was made by Auguste and Louis Lumière at the train station of the coastal town of La Ciotat. It was shown to an audience in Paris on 28 December 1895, causing a sensation.[43]
Before its commercial premiere in Paris, the film was shown to invited audiences in several French cities, including La Ciotat. It was shown at the Eden Theater in September 1895, making that theatre one of the first motion picture theatres, and the only of the first theatres still showing movies in 2009.[44]
Three other of the earliest Lumiere films, Partie de cartes, l'Arroseur arrosé (the first known filmed comedy), and Repas de bébé, were also filmed in La Ciotat in 1895, at the Villa du Clos des Plages, the summer residence of the Lumière Brothers.
Two modern French film classics particularly capture the idyllic qualities of Provence: Jean de Florette and its sequel Manon des Sources.
A modern day British film, "A Good Year", shows off the true beauty of Provence and its vineyards.
Parks and gardens in Provence
Cuisine

 A traditional Bouillabaisse from Marseille, soup and fish served separately
A traditional Bouillabaisse from Marseille, soup and fish served separately Brandade de Morue is a dish of salt cod and olive oil, served with potatoes or bread in winter
Brandade de Morue is a dish of salt cod and olive oil, served with potatoes or bread in winter- A Daube, or Provençal beef stew, cooked in wine

 A bowl of ratatouille with bread
A bowl of ratatouille with bread
 The Calissons from Aix
The Calissons from Aix
The cuisine of Provence is the result of the warm, dry Mediterranean climate; the rugged landscape, good for grazing sheep and goats but, outside of the Rhône Valley, with poor soil for large-scale agriculture; and the abundant seafood on the coast. The basic ingredients are olives and olive oil; garlic; sardines, rockfish, sea urchins and octopus; lamb and goat; chickpeas; local fruits, such as grapes, peaches, apricots, strawberries, cherries, and the famous melons of Cavaillon.
The fish frequently found on menus in Provence are the rouget, a small red fish usually eaten grilled, and the loup, (known elsewhere in France as the bar), often grilled with fennel over the wood of grapevines.
- Aïoli is a thick emulsion sauce made from olive oil flavoured with crushed garlic. It often accompanies a bourride, a fish soup, or is served with potatoes and cod (fr. Morue). There are as many recipes as there are families in Provence.
- Bouillabaisse is the classic seafood dish of Marseille. The traditional version is made with three fish: scorpionfish, sea robin, and European conger, plus an assortment of other fish and shellfish, such as John Dory, monkfish, sea urchins, crabs and sea spiders included for flavour. The seasoning is as important as the fish, including salt, pepper, onion, tomato, saffron, fennel, sage, thyme, bay laurel, sometimes orange peel, and a cup of white wine or cognac. In Marseille the fish and the broth are served separately – the broth is served over thick slices of bread with rouille (see below.)[45]
- Brandade de Morue is a thick purée of salt cod, olive oil, milk, and garlic, usually spread on toast.[46]
- Daube provençale is a stew made with cubed beef braised in wine, vegetables, garlic, and herbes de provence. Variations also call for olives, prunes, and flavouring with duck fat, vinegar, brandy, lavender, nutmeg, cinnamon, cloves, juniper berries, or orange peel. For best flavour, it is cooked in several stages, and cooled for a day between each stage to allow the flavours to meld together. In the Camargue area of France, bulls killed in the bullfighting festivals are sometimes used for daube.
- Escabeche is another popular seafood dish; the fish (usually sardines) are either poached or fried after being marinated overnight in vinegar or citrus juice.
- Fougasse is the traditional bread of Provence, round and flat with holes cut out by the baker. Modern versions are baked with olives or nuts inside.
- Oursinade a sauce made from sea urchins, often applied to fish. Its name refers to a "tasting" of sea urchins.
- La pissaladière is another speciality of Nice. Though it resembles a pizza, it is made with bread dough and the traditional variety never has a tomato topping. It is usually sold in bakeries, and is topped with a bed of onions, lightly browned, and a kind of paste, called pissalat, made from sardines and anchovies, and the small black olives of Nice, called caillettes.[47]
- Ratatouille is a traditional dish of stewed vegetables, which originated in Nice.[48]
- Rouille is a mayonnaise with red pimentos, often spread onto bread and added to fish soups.
- Socca is a speciality of Nice – it is a round flat cake made of chickpea flour and olive oil, like the Italian farinata. It is baked in the oven in a large pan more than a meter in diameter, then seasoned with pepper and eaten with the fingers while hot. In Toulon socca is known as La Cade.
- Soupe au pistou, either cold or hot, usually made with fresh basil ground and mixed with olive oil, along with summer vegetables, such as white beans, green beans, tomatoes, summer squash, and potatoes.[49]
- Tapenade is a relish consisting of pureed or finely chopped olives, capers, and olive oil, usually spread onto bread and served as an hors d'œuvre.
- The calisson is the traditional confection of Aix-en-Provence, made from a base of almond paste flavoured with confit of melon and orange. They have been made in Aix-en-Provence since the 17th century.
- The gâteau des Rois is a type of epiphany cake found all over France; the Provençal version is different because it is made of brioche in a ring, flavoured with the essence of orange flowers and covered with sugar and fruit confit.
- Tarte Tropézienne is a tart of pastry cream (crème pâtissière) invented by a St. Tropez pastry chef named Alexandre Micka in the 1950s, based on a recipe he brought from his native Poland. In 1955, he was chef on the set of the film And God Created Woman when actress Brigitte Bardot suggested he name the cake La Tropézienne. It is now found in bakeries throughout the Var.
- The Thirteen desserts is a Christmas tradition in Provence, when thirteen different dishes, representing Jesus and the twelve apostles, and each with a different significance, are served after the large Christmas meal.
- Herbes de Provence (or Provençal herbs) are a mixture of dried herbs from Provence which are commonly used in Provençal cooking. And wine.
Wines
The wines of Provence were probably introduced into Provence around 600 BC by the Greek Phoceans who founded Marseille and Nice. After the Roman occupation, in 120 BC the Roman Senate forbade the growing of vines and olives in Provence, to protect the profitable trade in exporting Italian wines, but in the late Roman empire retired soldiers from Roman Legions settled in Provence and were allowed to grow grapes.[50]
The Romans complained about the competition from and poor quality of the wines of Provence. In the 1st century AD the Roman poet Martial condemned the wines of Marseille as "terrible poisons, and never sold at a good price."[51]

As recently as the 1970s the wines of Provence had the reputation of being rather ordinary: In 1971 wine critic Hugh Johnson wrote: "The whites are dry and can lack the acidity to be refreshing; the reds are straightforward, strong and a trifle dull; it is usually the rosés, often orange-tinted, which have most appeal." He added, "Cassis and Bandol distinguish themselves for their white and red wines respectively. Cassis (no relation of the blackcurrant syrup) is livelier than the run of Provençal white wine, and Bandol leads the red in much the same way."[52]
Since that time, cultivation of poorer varieties has been reduced and new technologies and methods have improved the quality considerably.
The wines of Provence are grown under demanding conditions; hot weather and abundant sunshine (Toulon, near Bandol, has the most sunshine of any city in France) which ripens the grapes quickly; little rain, and the mistral.
The great majority of the wines produced in Provence are rosés. The most characteristic grape is mourvèdre, used most famously in the red wines of Bandol. Cassis is the only area in Provence known for its white wines.
There are three regional classifications (Appellation d'origine contrôlée (AOC)) in Provence:
- AOC Côtes de Provence. This AOC classification dates to 1997, though these wines were recognised in the 17th and 18th century, notably by Madame de Sévigné, who reported the habits and preferred wines of the Court of Louis XIV. The title Côtes de Provence was already in use in 1848, but production was nearly destroyed by phylloxera later in that century, and took decades to recover. The appellation today covers 84 communes in the Var and Bouches-du-Rhône departments, and one in Alpes-Maritimes. The principal grapes used in the red wines are the grenache, mourvèdre, cinsault, tibouren, and syrah. For the white wines, clairette, vermentino, sémillon, and ugni blanc.
The appellation covers 20,300 hectares. 80 percent of the production is rosé wine, fifteen percent is red wine, and 5 percent white wine.
- AOC Coteaux d'Aix-en-Provence was classified as an AOC in 1985. The wines of Aix were originally planted by veterans of the Roman legions in the 1st century BC, and were promoted in the 15th century by René I of Naples, the last ruler of Provence. Most vineyards were destroyed by phylloxera in the 19th century, and very slowly were reconstituted. The principal grapes for the red wines and rosés are the grenache, mourvèdre, cinsault, syrah, counoise, carignan, and cabernet sauvignon. White wines are made mainly with bourboulenc, clairette, grenache blanc, and vermentino. There are 4000 hectares in production. 70 percent of the wines are rosés, 25 percent red wines, and 5 percent white wines.
- AOC Coteaux varois en Provence is a recent AOC in Provence. The name Coteaux Varois was first used in 1945, and became an AOC in 1993. the name was changed to Couteaux Varois en Provence in 2005. The red wines principally use the grenache, cinsaut, mourvèdre, and syrah grapes. White wines use the clairette, grenache blanc, rolle blanc, Sémillon Blanc, and Ugni Blanc. There are 2200 hectares in this AOL. It produces 80 percent rosés, 17 percent red wines, and 3 percent white wines.
In addition, there are five local classifications: (Les appellations locales):
- Bandol AOC, grown in the Var on the coast west of Toulon, mostly around the villages of La Cadiere d'Azur and Castellet. Wines of this appellation must have at least fifty percent Mourvèdre grapes, though most have considerably more. Other grapes used are grenache, cinsault, syrah, and carignan.
- AOC Cassis, made near the coastal town of Cassis, between Toulon and Marseille, was the first wine in Provence to be classified as an AOC in 1936, and is best known for its white wines. Wines from Cassis are described in French literature as early as the 12th century. The grapes most commonly used are the marsanne, the clairette, the ugni blanc, sauvignon blanc, and the Bourboulenc. Rosé wines use the grenache, carignan, and mourvèdre.
- AOC Bellet; at the time of the French Revolution, the little town of Saint Roman de Bellet (now part of Nice) was the center of an important wine region. Production was nearly destroyed by the phylloxera and by the two wars, and only in 1946 was the region again producing fully. It was classified as an AOC in 1941. Today the region is one of the smallest in France; just 47 hectares. The grapes are grown on terraces along the left bank of the Var River, east of the town. The major grapes grown for red wines and rosés are the braquet, Folle, and Cinsault, blended sometimes with grenache. For white wines, the major grapes grown are rolle blanc, roussane, spagnol, and mayorquin; the secondary grapes are clairette, bourboulenc, chardonnay, pignerol, and muscat.
- Palette AOC; the little village of Palete, four kilometres east of Aix-en-Provence, has long been famous for the production of a vin cuit, or fortified wine, used in the traditional Provence Christmas dessert, the Thirteen desserts, and the Christmas cake called pompo à l'oli, or the olive-oil pump. This production was nearly abandoned, but is now being recreated. The main grapes for red wine are grenache, mourvèdre, and cinsaut; for the white wines clairette.
- AOC Les Baux de Provence; was established as an AOC for red and rosé wines in 1995.
South of Avignon, it occupies the north and south slopes of the Alpilles, up to an altitude of 400 metres, and extends about thirty kilometres from east to west. The principal grapes for the red wines are the grenache, mourvèdre, and syrah. For the rosés, the main grapes are the syrah and cinsault.
Pastis



Pastis is the traditional liqueur of Provence, flavoured with anise and typically containing 40–45% alcohol by volume. When absinthe was banned in France in 1915, the major absinthe producers (then Pernod Fils and Ricard, who have since merged as Pernod Ricard) reformulated their drink without the banned wormwood and with more aniseed flavour, coming from star anise, sugar and a lower alcohol content, creating pastis. It is usually drunk diluted with water, which it turns a cloudy color. It is especially popular in and around Marseille.
Pétanque or boules
Pétanque, a form of boules, is a popular sport played in towns and villages all over Provence. The origins of the game are said to be ancient, going back to the Egyptians, ancient Greeks, and Ancient Romans, who are said to have introduced it to Provence first. The sport was very popular during the Middle Ages throughout Europe, known as bowls or lawn bowling in England, and as boules in France.
A more athletic version of the sport called jeu provençal was popular throughout Provence in the 19th century – this version is featured in the novels and memoires of Marcel Pagnol; players ran three steps before throwing the ball, and it resembled at times a form of ballet. The modern version of the game was created in 1907 at the town of La Ciotat by a former champion of jeu provençal named Jules Hugues, who was unable to play because of his rheumatism. He devised a new set of rules where the field was much smaller, and players did not run before throwing the ball, but remained inside a small circle with their feet together. This gave the game its name, lei peds tancats, in the Provençal dialect of occitan, 'feet together.' The first tournament was played in La Ciotat in 1910. The first steel boules were introduced in 1927.
The object is to throw a ball (boule) as close as possible to a smaller ball, called the cochonnet, (this kind of throw is called to faire le point or pointer); or to knock away a boules of the opponent that is close to the cochonnet (this is called to tirer). Players compete one-on-one (tête-à-tête), in teams of two (doublettes) or teams of three (triplettes). The object is to accumulate thirteen points. The point belongs to the ball the closest to the cochonnet. A player pitches balls until he can regain the point (reprenne le point) by having his ball closest to the cochonnet. Each ball from a single team, if there are no other balls from the other team closer to the cochonnet, counts as a point. The points are counted when all of the balls have been tossed by both teams.[53]
Genetics
A recent genetic study in 2011 analysed 51 southern French individuals from Provence and 89 Anatolian Greek subjects whose paternal ancestry derives from Smyrna (modern-day Izmir in Turkey) and Asia Minor Phokaia (modern-day Foça in Turkey), the ancestral embarkation port to the 6th century BCE ancient Greek colonies of Massalia (Marseilles) and Alalie (Aleria, Corsica). The study found that 17% of the Y-chromosomes of Provence may be attributed to Greek colonisation. The study also concluded that "estimates of colonial Greek vs indigenous Celto-Ligurian demography predict a maximum of a 10% Greek contribution, suggesting a Greek male elite-dominant input into the Iron Age Provence population."[54] This evidence supports the persistence of the gene pool of the Ancient Greeks among the modern southern French.
See also
Sources and references
- ↑ See article on Provence in the French-language Wikipedia.
- 1 2 Le Petit Robert, Dictionnaire Universel des Noms Propres (1988).
- ↑ Eduouard Baratier (editor), Histoire de la Provence, Editions Privat, Toulouse, 1990, Introduction.
- ↑ Max Escalon de Fonton, L'Homme avant l'histoire, article in Histoire de la Provence, edited by Edouard Baratier, Editions Privat, Toulouse, 1990. Pg. 14 See also Henry de Lumley, La Grand Histoire des premiers hommes européens, Odile Jacob, Paris, 2010
- ↑ Max Escalon de Fonton, L'Homme avant l'histoire, pg. 15
- ↑ "Site of the Exotic Garden of Monaco, and the Museum of Archeology". Jardin-exotique.mc. Retrieved 11 June 2011.
- 1 2 3 Escalon de Fonton, L'Homme avant l'histoire, pg. 16–17
- ↑ Aldo Bastié, Histoire de la Provence, Editions Ouest-France, 2001
- 1 2 J.R. Palanque, Ligures, Celts et Grecs, in Histoire de la Provence. Pg. 33.
- ↑ "Herakles in the West – Frater L". Jwmt.org. Retrieved 18 August 2010.
- ↑ J. Cited by R. Palanque, Ligures, Celts et Grecs, in Histoire de la Provence. Pg. 34.
- 1 2 3 J. R. Palanque, Ligures, Celts et Grecs, in Histoire de la Provence. Pg. 34.
- ↑ J. R. Palanque, Ligures, Celts et Grecs, in Histoire de la Provence. Pg. 34
- ↑ J.R. Palanque, Ligures, Celtes et Grecs, in Histoire de la Provence, pg. 39.
- 1 2 R. Palanque, Ligures, Celtes et Grecs, in Histoire de la Provence, pg. 41.
- ↑ R. Palanque, Ligures, Celtes et Grecs, in Histoire de la Provence, pg. 44.
- ↑ Bastié, Histoire de la Provence, pg. 9
- ↑ Aldo Bastié, Histoire de la Provence, (pg. 13.)
- ↑ Collins, Roger (1989). The Arab Conquest of Spain 710–797. Oxford, UK / Cambridge, USA: Blackwell. p. 92. ISBN 0-631-19405-3.
- ↑ Collins, Roger (1989). p. 92. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Histoire de la Provence, pg. 16
- ↑ Bastiė, Histoire de la Provence
- ↑ Noble; et al. (2013). Cengage Advantage Books: Western Civilization: Beyond Boundaries (7 ed.). Cengage Learning. p. 304. ISBN 9781285661537.
- ↑ Bastiė, Histoire de la Provence, pg. 20.
- 1 2 Bastié, Histoire de la Provence, (pg. 35)
- ↑ Etienne-Bugnot, Isabelle, Quilting in France: The French Traditions, retrieved 2 May 2010
- ↑ Mark Jarrett. The Congress of Vienna: War and Great Power Diplomacy after Napoleon I.B.Tauris, 30 jun. 2013. ISBN 0857735705 p 158
- ↑ Edward Baratier, Histoire de la Provence, 6–7.
- ↑ See Mediterranean climate.
- ↑ "Précipitations à Marseille" (in French). Infoclimat.fr. Retrieved 18 August 2010.
- ↑ (French) Precipitations a Toulon.
- ↑ Météo-France. site
- ↑ (French) "Infoclimat – Météo en temps réel – observations previsions climatologie forum" (in French). Infoclimat.fr. Retrieved 18 August 2010.
- ↑ "Infoclimat – Météo en temps réel – observations previsions climatologie forum" (in French). Infoclimat.fr. Retrieved 18 August 2010.
- ↑ "source: infoclimat.fr précipitations à Orange" (in French). Infoclimat.fr. Retrieved 18 August 2010.
- ↑ from the article "Provence" in the French-language Wikipedia.
- ↑ Atlantic Brief Lives, A Biographical Companion to the Arts, pg. 204, Atlantic Monthly Press, 1971.
- ↑ "Troika: Russia’s westerly poetry in three orchestral song cycles", Rideau Rouge Records, ASIN: B005USB24A, 2011.
- ↑ Aldo Bastié, Histoire de la Provence, Editions Ouest-France, 2001.
- ↑ Fixot, Michel, and Sauze, Elisabeth, 2004: La cathédrale Saint-Léonce et le groupe épiscopale de Fréjus. Monum, Éditions du patrimoine.
- ↑ The cult of Mary Magdalene was very important in medieval Provence; What was believed to be her sarcophagus had been found in a Gallo-Roman crypt in Saint-Maximin-la-Sainte-Baume in 1279, and the construction of a large church, the Basilica Sainte Marie-Madeleine, was begun on the spot in 1295.
- ↑ See exhibition "Van Gogh – Monticelli" in Marseille's Centre de la Vieille Charité, Sep 2008 – Jan 2009
- ↑
- Complete film on YouTube
- The Lumiere Institute, Lyon, France
- ↑ "...Onze autres projections en France (Paris, Lyon, La Ciotat, Grenoble) et en Belgique (Bruxelles, Louvain) auront lieu avec un programme de films plus étoffé durant l'année 1895, avant la première commerciale du 28 décembre, remportant à chaque fois le même succès." From the site of the Institut Lumiere in Lyon. see Site of the Institut Lumiere
- ↑ See the Michelin Guide Vert, Côte d'Azur, pg.31 (in French), for this classic version. There are countless others.
- ↑ Olney, Richard (1994). Lulu's Provenc̜al Table : the exuberant food and wine from Domaine Tempier Vineyard. New York: HarperCollins Publishers. pp. 83–85. ISBN 0-06-016922-2.
- ↑ "Link to the traditional recipe for pissaladiëre(in French)". Nice-cooking.com. Retrieved 18 August 2010.
- ↑ Ratatouille. Oxford English Dictionary. 2nd edition.
- ↑ Vanel, Lucy (23 April 2006). "Lucy's Kitchen Notebook. L'Ail est Arrivé! – Soupe au Pistou". Kitchen-notebook.blogspot.com. Retrieved 18 August 2010.
- ↑ Cicero, Book III Chapter 9 of De Republica, quoted in Histore sociale et culturelle du Vin, Gilbert Garrier, Larousse, 1998.
- ↑ Martial, Epigrams X-36, cited by Garrier, op.cit.
- ↑ Hugh Johnson, The World Atlas of Wine, Mitchell Beazley Publishers, 1971
- ↑ Marco Foyot, Alain Dupuy, Louis Dalmas, Pétanque – Technique,Tactique, Entrainement Robert Laffont, Paris 1984. This seems to be the definitive book on the subject, co-written by pétanque champion Marco Foyot.
- ↑ Chiaroni, Jacques (2011). The coming of the Greeks to Provence and Corsica: Y-chromosome models of archaic Greek colonization of the western Mediterranean. BMC Evolutionary Biology. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-11-69.
The process of Greek colonization of the central and western Mediterranean during the Archaic and Classical Eras has been understudied from the perspective of population genetics. To investigate the Y chromosomal demography of Greek colonization in the western Mediterranean, Y-chromosome data consisting of 29 YSNPs and 37 YSTRs were compared from 51 subjects from Provence, 58 subjects from Smyrna and 31 subjects whose paternal ancestry derives from Asia Minor Phokaia, the ancestral embarkation port to the 6th century BCE Greek colonies of Massalia (Marseilles) and Alalie (Aleria, Corsica). Results 19% of the Phokaian and 12% of the Smyrnian representatives were derived for haplogroup E-V13, characteristic of the Greek and Balkan mainland, while 4% of the Provençal, 4.6% of East Corsican and 1.6% of West Corsican samples were derived for E-V13. An admixture analysis estimated that 17% of the Y-chromosomes of Provence may be attributed to Greek colonization. Using the following putative Neolithic Anatolian lineages: J2a-DYS445 = 6, G2a-M406 and J2a1b1-M92, the data predict a 0% Neolithic contribution to Provence from Anatolia. Estimates of colonial Greek vs. indigenous Celto-Ligurian demography predict a maximum of a 10% Greek contribution, suggesting a Greek male elite-dominant input into the Iron Age Provence population.
Bibliography
- Edouard Baratier (editor), Histoire de la Provence, Editions Privat, Toulouse, 1990 (ISBN 2-7089-1649-1)
- Aldo Bastié, Histoire de la Provence, Editions Ouest-France, 2001.
- Michel Vergé-Franceschi, Toulon – Port Royal (1481–1789). Tallandier: Paris, 2002.
- Cyrille Roumagnac, L'Arsenal de Toulon et la Royale, Editions Alan Sutton, 2001
- Jim Ring, Riviera, The Rise and Fall of the Côte d'Azur, John Murray Publishers, London 2004
- Marco Foyot, Alain Dupuy, Louis Dalmas, Pétanque – Technique, Tactique, Entrainement, Robert Laffont, Paris, 1984.
- Denizeau, Gerard, Histoire Visuelle des Monuments de France, Larousse, 2003
- LeMoine, Bertrand, Guide d'architecture, France, 20e siecle, Picard, Paris 2000
- Jean-Louis André, Jean-François Mallet, Jean daniel Sudres, Cuisines des pays de France, Éditions du Chêne, Hachette Livre, Paris 2001
- Prosper Mérimée, Notes de voyages, ed. Pierre-Marie Auzas (1971)
- Martin Garrett, Provence: a Cultural History (2006)
- James Pope-Hennessy, Aspects of Provence (1988)
- Laura Raison (ed.), The South of France: an Anthology (1985)
External links
| Look up provence in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Provence. |
- Official Provence Alpes Côte d'Azur (PACA) Tourist Board
- Official Bouches-du-Rhône Tourist Board
- Official Vaucluse Tourist Board
- Aix-en-Provence Tourist Office