United States Capitol
| United States Capitol | |
|---|---|
|
The west front of the United States Capitol in 2013, before dome restoration scaffolding was erected | |
 | |
| General information | |
| Architectural style | American Neoclassicism |
| Town or city | Capitol Hill, Washington, D.C. |
| Country | United States of America |
| Coordinates | 38°53′23.29″N 77°00′32.81″W / 38.8898028°N 77.0091139°WCoordinates: 38°53′23.29″N 77°00′32.81″W / 38.8898028°N 77.0091139°W |
| Construction started | September 18, 1793 |
| Completed | 1800 |
| Client | Washington administration |
| Technical details | |
| Floor count | 5 |
| Floor area | 16.5 acres (6.7 ha)[1] |
| Design and construction | |
| Architect |
William Thornton, designer (See Architect of the Capitol) |
| Website | |
|
www www | |
The United States Capitol, often called the Capitol Building or Capitol Hill, is the home of the United States Congress, and the seat of the legislative branch of the U.S. federal government. It sits atop Capitol Hill at the eastern end of the National Mall in Washington, D.C. Though not at the geographic center of the Federal District, the Capitol forms the origin point for the District's street-numbering system and the District's four quadrants.
The original building was completed in 1800 and was subsequently expanded, particularly with the addition of the massive dome. Like the principal buildings of the executive and judicial branches, the Capitol is built in a distinctive neoclassical style and has a white exterior. Both its east and west elevations are formally referred to as fronts, though only the east front was intended for the reception of visitors and dignitaries.
In 2014, scaffolding was erected around the dome for a restoration project scheduled to be completed by early 2017. All exterior scaffolding was removed by the end of summer 2016.[2]
History

Background
Prior to establishing the nation's capital in Washington, D.C., the United States Congress and its predecessors had met in Philadelphia (Independence Hall and Congress Hall), New York City (Federal Hall), and a number of other locations (York, Pennsylvania, Lancaster, Pennsylvania, Maryland State House in Annapolis, Maryland, Nassau Hall in Princeton, New Jersey).[3] In September 1774, the First Continental Congress brought together delegates from the colonies in Philadelphia, followed by the Second Continental Congress, which met from May 1775 to March 1781.
After adopting the Articles of Confederation in York, Pennsylvania, the Congress of the Confederation was formed and convened in Philadelphia from March 1781 until June 1783, when a mob of angry soldiers converged upon Independence Hall, demanding payment for their service during the American Revolutionary War. Congress requested that John Dickinson, the Governor of Pennsylvania, call up the militia to defend Congress from attacks by the protesters. In what became known as the Pennsylvania Mutiny of 1783, Dickinson sympathized with the protesters and refused to remove them from Philadelphia. As a result, Congress was forced to flee to Princeton, New Jersey, on June 21, 1783,[4] and met in Annapolis, Maryland, and Trenton, New Jersey, before ending up in New York City.
The United States Congress was established upon ratification of the United States Constitution and formally began on March 4, 1789. New York City remained home to Congress until July 1790,[5] when the Residence Act was passed to pave the way for a permanent capital. The decision to locate the capital was contentious, but Alexander Hamilton helped broker a compromise in which the federal government would take on war debt incurred during the American Revolutionary War, in exchange for support from northern states for locating the capital along the Potomac River. As part of the legislation, Philadelphia was chosen as a temporary capital for ten years (until December 1800), until the nation's capital in Washington, D.C., would be ready.[6]
Pierre (Peter) Charles L'Enfant was given the task of creating the city plan for the new capital city.[7] L'Enfant chose "Jenkin's Hill" as the site for the "Congress House", with a "grand avenue" (now Pennsylvania Avenue, NW) connecting it with the President's House, and a public space containing a broader "grand avenue" (now the National Mall) stretching westward to the Potomac River (see: L'Enfant Plan).[8][9]
Name
In reviewing L'Enfant's plan, Thomas Jefferson insisted the legislative building be called the "Capitol" rather than "Congress House".[8] The word "Capitol" comes from Latin and is associated with the Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus on Capitoline Hill, one of the seven hills of Rome.[10][11] The connection between the two is not, however, crystal clear.[12] In addition to coming up with a city plan, L'Enfant had been tasked with designing the Capitol and President's House, however he was dismissed in February 1792 over disagreements with President George Washington and the commissioners, and there were no plans at that point for the Capitol.[13]
Design competition
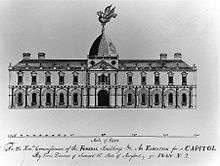
In spring 1792, United States Secretary of State Thomas Jefferson proposed a design competition to solicit designs for the Capitol and the "President's House", and set a four-month deadline. The prize for the competition was $500 and a lot in the Federal City. At least ten individuals submitted designs for the Capitol; however the drawings were regarded as crude and amateurish, reflecting the level of architectural skill present in the United States at the time.[14] The most promising of the submissions was by Stephen Hallet, a trained French architect.[15] However, Hallet's designs were overly fancy, with too much French influence, and were deemed too costly.[16]
A late entry by amateur architect William Thornton was submitted on January 31, 1793, to much praise for its "Grandeur, Simplicity, and Beauty" by Washington, along with praise from Thomas Jefferson. Thornton was inspired by the east front of the Louvre, as well as the Paris Pantheon for the center portion of the design.[17][18] Thornton's design was officially approved in a letter dated April 5, 1793, from Washington, and Thornton served as the first Architect of the Capitol (and later first Superintendent of the United States Patent Office).[19] In an effort to console Hallet, the commissioners appointed him to review Thornton's plans, develop cost estimates, and serve as superintendent of construction. Hallet proceeded to pick apart and make drastic changes to Thornton's design, which he saw as costly to build and problematic.[20] In July 1793, Jefferson convened a five-member commission, bringing Hallet and Thornton together, along with James Hoban (winning architect of the "President's Palace") to address problems with and revise Thornton's plan. Hallet suggested changes to the floor plan, which could be fitted within the exterior design by Thornton.[21][22] The revised plan was accepted, except that Secretary Jefferson and President Washington insisted on an open recess in the center of the East front, which was part of Thornton's original plan.[23]
The original design by Thornton was later modified by the famous British-American architects Benjamin Henry Latrobe, Sr., and then Charles Bulfinch.[24] The current cast-iron dome and the House's new southern extension and Senate new northern wing were designed by Thomas U. Walter and August Schoenborn, a German immigrant, in the 1850s,[25] and were completed under the supervision of Edward Clark.[26]
Construction

L'Enfant secured the lease of quarries at Wigginton Island and along Aquia Creek in Virginia for use in the foundations and outer walls of the Capitol in November 1791.[27] Surveying was under way soon after the Jefferson conference plan for the Capitol was accepted.[21] On September 18, 1793, first President George Washington, along with eight other Freemasons dressed in masonic regalia, laid the cornerstone, which was made by silversmith Caleb Bentley.[28][29]
Construction proceeded with Hallet working under supervision of James Hoban, who was also busy working on construction of the "President's House" (also later known as the "Executive Mansion"). Despite the wishes of Jefferson and the President, Hallet went ahead anyway and modified Thornton's design for the East Front and created a square central court that projected from the center, with flanking wings which would house the legislative bodies. Hallet was dismissed by Secretary of State Jefferson on November 15, 1794.[30] George Hadfield was hired on October 15, 1795, as Superintendent of Construction, but resigned three years later in May 1798, because of his dissatisfaction with Thornton's plan and quality of work done thus far.[31]
The Senate north wing was completed in 1800. The Senate and House shared quarters in the north wing until a temporary wooden pavilion was erected on the future site of the southern House wing which served for a few years for the Representatives to meet in, until the House of Representatives south wing was finally completed in 1811, with a covered wooden temporary walkway connecting the two wings with the Congressional chambers where the future center section with rotunda and dome would someday rise. However, the House of Representatives moved early into their House wing in 1807. Though the North Senate wing building was incomplete, the Capitol held its first session of the United States Congress with both chambers in session on November 17, 1800. The National Legislature was moved to Washington prematurely, at the urging of second President John Adams, in hopes of securing enough Southern votes in the Electoral College to be re-elected for a second term as President.[32]
Early religious use
For several decades, beginning when the federal government moved to Washington in the fall of 1800, the Capitol building was used for Sunday religious services as well as for governmental functions. The first services were conducted in the "hall" of the House in the north wing of the building. In 1801 the House moved to temporary quarters in the south wing, called the "Oven," which it vacated in 1804, returning to the north wing for three years. Then, from 1807 to 1857, they were held in what is now called Statuary Hall. When held in the House chamber, the Speaker's podium was used as the preacher's pulpit. According to the U.S. Library of Congress exhibit Religion and the Founding of the American Republic:
It is no exaggeration to say that on Sundays in Washington during the administrations of Thomas Jefferson (1801-1809) and of James Madison (1809-1817) the state became the church. Within a year of his inauguration, Jefferson began attending church services in the chamber of the House of Representatives. Madison followed Jefferson's example, although unlike Jefferson, who rode on horseback to church in the Capitol, Madison came in a coach and four. Worship services in the House—a practice that continued until after the Civil War—were acceptable to Jefferson because they were nondiscriminatory and voluntary. Preachers of every Protestant denomination appeared. (Catholic priests began officiating in 1826.) As early as January 1806 a female evangelist, Dorothy Ripley, delivered a camp meeting-style exhortation in the House to Jefferson, Vice President Aaron Burr, and a "crowded audience."[33]
War of 1812

Not long after the completion of both wings, the Capitol was partially burned by the British on August 24, 1814, during the War of 1812. George Bomford, and Joseph Gardner Swift, both military engineers, were called upon to help rebuild the Capitol. Reconstruction began in 1815 and included redesigned chambers for both Senate and House wings/now sides, which were completed by 1819. During the reconstruction, Congress met in the Old Brick Capitol, a temporary structure financed by local investors. Construction continued through to 1826, with the addition of the center section with front steps and columned portico, an interior Rotunda, rising above, the first low dome of the Capitol. Latrobe is principally connected with the original construction and many innovative interior features; his successor, Bulfinch, also played a major role, such as the design of the first low dome covered in copper.
The House and Senate Wings

By 1850, it became clear that the Capitol could not accommodate the growing number of legislators arriving from newly admitted states. A new design competition was held, and 13th President Millard Fillmore appointed Philadelphia architect Thomas U. Walter to carry out the expansion. Two new wings were added – a new chamber for the House of Representatives on the south side, and a new chamber for the Senate on the north.[34]
When the Capitol was expanded in the 1850s, some of the construction labor was carried out by slaves "who cut the logs, laid the stones and baked the bricks".[35] The original plan was to use workers brought in from Europe; however, there was a poor response to recruitment efforts, and African Americans, some free and some enslaved, composed the majority of the work force.[36]
Capitol dome

The 1850 expansion more than doubled the length of the Capitol, dwarfing the original, timber-framed, copper-sheeted, low dome of 1818, designed by Charles Bulfinch and no longer in proportion with the increased size of the building. In 1855, the decision was made to tear it down and replace it with the "wedding-cake style" cast-iron dome that stands today. Also designed by Thomas U. Walter, the new dome would stand three times the height of the original dome and 100 feet (30 m) in diameter, yet had to be supported on the existing masonry piers. Like Mansart's dome at "Les Invalides" (which he had visited in 1838), Walter's dome is double, with a large oculus in the inner dome, through which is seen "The Apotheosis of Washington" painted on a shell suspended from the supporting ribs, which also support the visible exterior structure and the tholos that supports "Freedom", a colossal statue that was raised to the top of the dome in 1863. This statue was cast by a slave named Philip Reid. The weight of the cast iron for the dome has been published as 8,909,200 pounds (4,041,100 kg).
Later expansion

When the Capitol's new dome was finally completed, its massive visual weight, in turn, overpowered the proportions of the columns of the East Portico, built in 1828. The East Front of the Capitol building was rebuilt in 1904, following a design of the architects Carrère and Hastings, who also designed the Russell Senate and Cannon House office buildings.
The next major expansion to the Capitol started in 1958, with a 33.5 feet (10.2 m) extension of the East Portico. During this project, in 1960 the dome underwent its last restoration.[37] A marble duplicate of the sandstone East Front was built 33.5 feet (10.2 m) from the old Front. (In 1962, a connecting extension incorporated what had been an outside wall as an inside wall.) In the process, the Corinthian columns were removed. It was not until 1984 that landscape designer Russell Page created a suitable setting for them in a large meadow at the U.S. National Arboretum in northeast Washington as the National Capitol Columns, where they are combined with a reflecting pool in an ensemble that reminds some visitors of the ruins of Persepolis, in Persia. Besides the columns, hundreds of blocks of the original stone were removed and are stored behind a National Park Service maintenance yard in Rock Creek Park.[38]


On December 19, 1960, the Capitol was declared a National Historic Landmark by the National Park Service.[39] The building was ranked #6 in a 2007 survey conducted for the American Institute of Architects' "America's Favorite Architecture" list.[40] The Capitol draws heavily from other notable buildings, especially churches and landmarks in Europe, including the dome of St. Peter's Basilica in the Vatican and St. Paul's Cathedral in London.[41] On the roofs of the Senate and House Chambers are flagpoles that fly the U.S. flag when either is in session. On September 18, 1993, to commemorate the Capitol's bicentennial, the Masonic ritual cornerstone laying with George Washington was reenacted. U.S. Senator Strom Thurmond was one of the Freemason politicians who took part in the ceremony.
On June 20, 2000, ground was broken for the Capitol Visitor Center, which opened on December 2, 2008.[42] From 2001 through 2008, the East Front of the Capitol (site of most presidential inaugurations until Ronald Reagan began a new tradition in 1981) was the site of construction for this massive underground complex, designed to facilitate a more orderly entrance for visitors to the Capitol. Prior to the center being built, visitors to the Capitol had to queue on the parking lot and ascend the stairs, whereupon entry was made through the massive sculpted Columbus Doors, through a small narthex cramped with security, and thence directly into the Rotunda. The new underground facility provides a grand entrance hall, a visitors theater, room for exhibits, and dining and restroom facilities, in addition to space for building necessities such as an underground service tunnel.
A large-scale Capitol dome restoration project, the first extensive such work since 1959–1960, began in 2014, with completion scheduled before the 2017 presidential inauguration.[43] As of 2012, $20 million in work around the skirt of the dome had been completed, but other deterioration, including at least 1,300 cracks in the brittle iron that have led to rusting and seepage inside, needed to be addressed. Before the August 2012 recess, the Senate Appropriations Committee voted to spend $61 million to repair the exterior of the dome. The House wanted to spend less on government operations,[37] but in late 2013, it was announced that renovations would take place over two years, starting in spring 2014.[44] Extensive scaffolding was erected in 2014, enclosing and obscuring the dome.[43] All exterior scaffolding was removed by mid-September 2016.[2]
Interior
The Capitol's building is marked by its central dome above a rotunda in the central section of the structure (which also includes, the older original smaller center flanked by the two original (designed 1793, occupied 1800) smaller two wings (inner north) and inner south) containing the two original smaller meeting chambers for the Senate and the House of Representatives (between 1800 and late 1850s) and then flanked by two further extended (newer) wings, one also for each chamber of the larger, more populous Congress: the new north wing is the Senate chamber and the new south wing is the House of Representatives chamber. Above these newer chambers are galleries where visitors can watch the Senate and House of Representatives. It is an example of the neoclassical architecture style. The statue on top of the dome is the "Statue of Freedom".[45]
Underground tunnels and a private subway connect the main Capitol building with each of the Congressional office buildings in the surrounding complex. All rooms in the Capitol are designated as either S (for Senate) or H (for House), depending on whether they are north (Senate) or south (House) of the Rotunda. Additionally, all addresses in Washington, D.C., are designated N.E., N.W., S.E., or S.W., in relation to the Rotunda. Since the Capitol Rotunda is not precisely located in the center of the District of Columbia(it is slightly farther east and to the south), the four District quadrants on the old territories of Maryland and Virginia, north and south of the Potomac River are not the same shape and size.
Art


The Capitol has a long history in art of the United States, beginning in 1856 with Italian/Greek American artist Constantino Brumidi and his murals in the hallways of the first floor of the Senate side of the Capitol. The murals, known as the Brumidi Corridors,[46] reflect great moments and people in United States history. Among the original works are those depicting Benjamin Franklin, John Fitch, Robert Fulton, and events such as the Cession of Louisiana. Also decorating the walls are animals, insects and natural flora indigenous to the United States. Brumidi's design left many spaces open so that future events in United States history could be added. Among those added are the Spirit of St. Louis, the Moon landing, and the Space Shuttle Challenger shuttle crew.
Brumidi also worked within the Rotunda. He is responsible for the painting of "The Apotheosis of Washington" beneath the top of the dome, and also the famous "Frieze of American History".[47] "The Apotheosis of Washington" was completed in 11 months and painted by Brumidi while suspended nearly 180 feet (55 m) in the air. It is said to be the first attempt by the United States to deify a founding father. Washington is depicted surrounded by 13 maidens in an inner ring with many Greek and Roman gods and goddesses below him in a second ring. The frieze is located around the inside of the base of the dome and is a chronological, pictorial history of the United States from the landing of Christopher Columbus to the Wright Brothers's flight in Kitty Hawk, North Carolina. The frieze was started in 1878 and was not completed until 1953. The frieze was therefore painted by four different artists: Brumidi, Filippo Costaggini, Charles Ayer Whipple, and Allyn Cox. The final scenes depicted in the fresco had not yet occurred when Brumidi began his "Frieze of the United States History".
Within the Rotunda there are eight large paintings about the development of the United States as a nation. On the east side are four paintings depicting major events in the discovery of America. On the west are four paintings depicting the founding of the United States. The east side paintings include The Baptism of Pocahontas by John Gadsby Chapman, The Embarkation of the Pilgrims by Robert Walter Weir, The Discovery of the Mississippi by William Henry Powell, and The Landing of Columbus by John Vanderlyn. The paintings on the west side are by John Trumbull: Declaration of Independence, Surrender of General Burgoyne, Surrender of Lord Cornwallis, and General George Washington Resigning His Commission. Trumbull was a contemporary of the United States' founding fathers and a participant in the American Revolutionary War; he painted a self-portrait into Surrender of Lord Cornwallis.
First Reading of the Emancipation Proclamation of President Lincoln hangs over the west staircase in the Senate wing.[48]

The Capitol also houses the National Statuary Hall Collection, comprising two statues donated by each of the fifty states to honor persons notable in their histories. One of the most notable statues in the National Statuary Hall is a bronze statue of King Kamehameha donated by the state of Hawaii upon its accession to the union in 1959. The statue's extraordinary weight of 15,000 pounds (6,804 kg) raised concerns that it might come crashing through the floor, so it was moved to Emancipation Hall of the new Capitol Visitor Center. The 100th, and last statue for the collection, that of Po'pay from the state of New Mexico, was added on September 22, 2005. It was the first statue moved into the Emancipation Hall.
Crypt
On the ground floor is an area known as the Crypt. It was intended to be the burial place of George Washington, with a ringed balustrade at the center of the Rotunda above looking down to his tomb. However, under the stipulations of his last will, Washington was buried at Mount Vernon. The Crypt houses exhibits on the history of the Capitol. A compass star inlaid in the floor marks the point at which Washington, D.C. is divided into its four quadrants; however, the geographic center of the city lies near the White House.
Within the Crypt is Gutzon Borglum's massive Head of Abraham Lincoln. The sculptor had a fascination with large-scale art and themes of heroic nationalism, and carved the piece from a six-ton block of marble. It was exhibited in Theodore Roosevelt's White House. Borglum was a patriot; believing that the "monuments we have built are not our own," he looked to create art that was "American, drawn from American sources, memorializing American achievement", according to a 1908 interview article. Supposedly, according to legend, the marble head remains unfinished (missing a left ear) to symbolize Lincoln's unfinished life.
Features
At one end of the room near the Old Supreme Court Chamber is a statue of John C. Calhoun. On the right leg of the statue, a mark from a bullet fired during the 1998 shooting incident is clearly visible. The bullet also left a mark on the cape, located on the back right side of the statue.
Eleven presidents have lain in state in the Rotunda for public viewing, most recently Gerald Ford. The tomb meant for Washington stored the catafalque which is used to support coffins lying in state or honor in the Capitol. The catafalque is now on display in the Capitol Visitors Center for the general public to see when not in use.
The Hall of Columns is located on the House side of the Capitol, home to twenty-eight fluted columns and statues from the National Statuary Hall Collection. In the basement of the Capitol building in a utility room are two marble bathtubs, which are all that remain of the once elaborate Senate baths. These baths were a spa-like facility designed for members of Congress and their guests before many buildings in the city had modern plumbing. The facilities included several bathtubs, a barbershop, and a massage parlor.
A steep, metal staircase, totaling 365 steps, leads from the basement to an outdoor walkway on top of the Capitol's dome.[49] The number of steps represents each day of the year.[50]
Height
Contrary to a popular myth, D.C. building height laws have never referred to the height of the Capitol building, which rises to 289 feet (88 m).[51] Indeed, the Capitol is only the fifth-tallest structure in Washington.
House Chamber
The House of Representatives Chamber has 448 permanent seats. Unlike Senators, Representatives do not have assigned seats.[52] It is adorned with relief portraits of famous lawmakers and lawgivers throughout history. Of the twenty-three relief portraits only Moses is sculpted from a full front view and is located across from the dais where the Speaker of the House ceremonially sits.



In order clockwise around the chamber:
- George Mason
- Robert Joseph Pothier
- Jean Baptiste Colbert
- Edward I of England
- Alfonso X of Castile
- Pope Gregory IX
- Louis IX of France
- Justinian I
- Tribonian
- Lycurgus of Sparta
- Hammurabi
- Moses
- Solon
- Aemilius Papinianus
- Gaius
- Maimonides
- Suleiman the Magnificent
- Pope Innocent III
- Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester
- Hugo Grotius
- William Blackstone
- Napoleon[53]
- Thomas Jefferson
There is also a quote etched in the marble of the chamber, as stated by venerable statesman Daniel Webster: "Let us develop the resources of our land, call forth its powers, build up its institutions, promote all its great interests, and see whether we also, in our day and generation, may not perform something worthy to be remembered."[54]
Old Supreme Court Chamber
From 1800 to 1806, this room served as the Senate Chamber and from 1806 until 1860, the room was used as the Supreme Court Chamber. In 1860, the Supreme Court began using the newly vacated Old Senate Chamber. Since 1935, the Supreme Court has met in the United States Supreme Court Building.
Senate Chamber
The current Senate Chamber opened in 1859[55] and is adorned with white marble busts of the former Presidents of the Senate (Vice Presidents).[56]
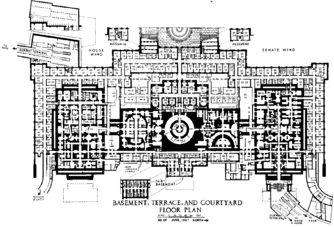
Floor plans



Exterior

Grounds

The Capitol Grounds cover approximately 274 acres (1.11 km²), with the grounds proper consisting mostly of lawns, walkways, streets, drives, and planting areas. Several monumental sculptures used to be located on the east facade and lawn of the Capitol including The Rescue and George Washington. The current grounds were designed by noted American landscape architect Frederick Law Olmsted, who planned the expansion and landscaping performed from 1874 to 1892. In 1875, as one of his first recommendations, Olmsted proposed the construction of the marble terraces on the north, west, and south sides of the building that exist today.
Olmsted also designed the Summer House, the open-air brick building that sits just north of the Capitol. Three arches open into the hexagonal structure, which encloses a fountain and twenty-two brick chairs. A fourth wall holds a small window that looks onto an artificial grotto. Built between 1879 and 1881, the Summer House was intended to answer complaints that visitors to the Capitol had no place to sit and no place to obtain water for their horses and themselves. Modern drinking fountains have since replaced Olmsted's fountain for the latter purpose. Olmsted intended to build a second, matching Summer House on the southern side of the Capitol, but congressional objections led to the project's cancellation.
Flags
Up to four U.S. flags can be seen flying over the Capitol. Two flagpoles are located at the base of the dome on the East and West sides. These flagpoles have flown the flag day and night since World War I. The other two flagpoles are above the North (Senate) and South (House of Representatives) wings of the building, and fly only when the chamber below is in session. The flag above the House of Representatives is raised and lowered by House pages. The flag above the United States Senate is raised and lowered by Senate Doorkeepers. To raise the flag, Doorkeepers access the roof of the Capitol from the Senate Sergeant at Arms's office. Several auxiliary flagpoles, to the west of the dome and not visible from the ground, are used to meet congressional requests for flags flown over the Capitol. Constituents pay for U.S. flags flown over the Capitol to commemorate a variety of events such as the death of a veteran family member.
Major events

The Capitol, as well as the grounds of Capitol Hill, have played host to major events, including presidential inaugurations held every four years. During an inauguration, the front of the Capitol is outfitted with a platform and a grand staircase. Annual events at the Capitol include Independence Day celebrations, and the National Memorial Day Concert.
The general public has paid respect to a number of individuals lying in state at the Capitol, including numerous former presidents, senators, and other officials. Other Americans lying in honor include Officers Jacob Chestnut and John Gibson, the two officers killed in the 1998 shooting incident. Chestnut was the first African American ever to lie in honor in the Capitol. The public also paid respect to civil rights icon Rosa Parks at the Capitol in 2005. She was the first woman and second African American to lie in honor in the Capitol. On September 24, 2015, Pope Francis gave a joint address to Congress, the first Pope to do so.[57]
Security

On January 30, 1835, what is believed to be the first attempt to kill a sitting President of the United States occurred just outside the United States Capitol. When President Andrew Jackson was leaving the Capitol out of the East Portico after the funeral of South Carolina Representative Warren R. Davis, Richard Lawrence, an unemployed and deranged housepainter from England, either burst from a crowd or stepped out from hiding behind a column and aimed a pistol at Jackson which misfired. Lawrence then pulled out a second pistol which also misfired. It has since been postulated that the moisture from the humid weather of the day contributed to the double misfiring.[58] Lawrence was then restrained, with legend saying that Jackson attacked Lawrence with his cane, prompting his aides to restrain him. Others present, including Davy Crockett, restrained and disarmed Lawrence.
On July 2, 1915, prior to the United States' entry into World War I, Eric Muenter (aka Frank Holt), a German professor who wanted to stop American support of the Allies of World War I, exploded a bomb in the reception room of the U.S. Senate. The next morning he tried to assassinate J. P. Morgan, Jr., son of the financier, at his home on Long Island, New York. In a letter to the Washington Evening Star published after the explosion, Muenter writing under an assumed name, said he hoped that the detonation would "make enough noise to be heard above the voices that clamor for war." J.P. Morgan's company served as Great Britain's principal U.S. purchasing agent for munitions and other war supplies.

In 1954, Puerto Rican nationalists opened fire on members of Congress from the visitors' gallery, injuring 5 representatives. On March 1, 1971, a bomb exploded on the ground floor of the Capitol, placed by the radical left domestic terrorist group, the Weather Underground. They placed the bomb as a demonstration against U.S. involvement in Laos. On November 7, 1983, a group called the Armed Resistance Unit claimed responsibility for a bomb that detonated in the lobby outside the office of Senate Minority Leader Robert Byrd.[59] Six people associated with the John Brown Anti-Klan Committee were later found in contempt of court for refusing to testify about the bombing.[60] In 1990, three members of the Armed Resistance Unit were convicted of the bombing, which they claimed was in response to the invasion of Grenada.[61] On July 24, 1998, Russell Eugene Weston Jr. burst into the Capitol and opened fire, killing two Capitol Police officers. The Capitol is believed to have been the intended target of the hijacked United Airlines Flight 93 on September 11, 2001, before it crashed near Shanksville in Somerset County, Pennsylvania, after passengers tried to take over control of the plane from hijackers.[62][63]
Since the September 11 attacks, the roads and grounds around the Capitol have undergone dramatic changes. The United States Capitol Police have also installed checkpoints to inspect vehicles at specific locations around Capitol Hill,[64][65] and have closed a section of one street indefinitely.[65] The level of screening employed varies. On the main east-west thoroughfares of Constitution and Independence Avenues, barricades are implanted in the roads that can be raised in the event of an emergency. Trucks larger than pickups are interdicted by the Capitol Police and are instructed to use other routes. On the checkpoints at the shorter cross streets, the barriers are typically kept in a permanent "emergency" position, and only vehicles with special permits are allowed to pass. All Capitol visitors are screened by a magnetometer, and all items that visitors may bring inside the building are screened by an x-ray device. In both chambers, gas masks are located underneath the chairs in each chamber for members to use in case of emergency. Structures ranging from scores of Jersey barriers to hundreds of ornamental bollards have been erected to obstruct the path of any vehicles that might stray from the designated roadways.[66]
In 2004 the capitol was briefly evacuated after a plane carrying the then governor of Kentucky strayed into restricted airspace over the district. A shooting incident occurred in March 2016. One female bystander was wounded by police but not seriously injured; a man pointing a gun was shot and arrested, in critical but stable condition.[67] The city police of Washington D.C. described the shooting incident as "isolated".[68]
Capitol Visitor Center

The United States Capitol Visitor Center (CVC) opened on December 2, 2008. The CVC is meant to bring all visitors in through one handicap accessible security checkpoint, with a capacity of up to 4,000 tourists,[69] and an expansion space for the US Congress.[70] It is located below the East Front of the Capitol and its plaza, between the Capitol building and 1st Street East. The complex contains 580,000 square feet (54,000 m2) of space below ground on three floors,[71] and offers visitors educational exhibits, a food court, and restrooms. There are also skylights that provide views of the Capitol dome. Long in the planning stages, construction began in the fall of 2001, following the killing of two Capitol police officers in 1998. The estimated final cost of constructing the CVC was $621 million.[72]
See also
- Apotheosis of Democracy by Paul Wayland Bartlett, a pediment on the east front of the House of Representatives Portico.
- Congressional Prayer Room
- United States fifty-dollar bill, the Capitol is pictured on the back of the US $50 bill
Citations
- ↑ "The United States Capitol: An Overview of the Building and Its Function". AOC.gov. Retrieved November 5, 2010.
- 1 2 "Dome Restoration Project Updates". Architect of the Capitol. Retrieved October 19, 2016.
- ↑ See List of capitals in the United States
- ↑ Crew, Harvey W.; William Bensing Webb; John Wooldridge (1892). Centennial History of the City of Washington, D. C. Dayton, Ohio: United Brethren Publishing House. p. 66.
- ↑ Allen (2001), p. 4
- ↑ Allen (2001), p. 4–7
- ↑ L'Enfant identified himself as "Peter Charles L'Enfant" during most of his life, while residing in the United States. He wrote this name on his "Plan of the city intended for the permanent seat of the government of t(he) United States ...." (Washington, D.C.) and on other legal documents. However, during the early 1900s, a French ambassador to the U.S., Jean Jules Jusserand, popularized the use of L'Enfant's birth name, "Pierre Charles L'Enfant". (Reference: Bowling, Kenneth R (2002). Peter Charles L'Enfant: vision, honor, and male friendship in the early American Republic. George Washington University, Washington, D.C. ISBN 978-0-9727611-0-9). The United States Code states in 40 U.S.C. § 3309: "(a) In General.—The purposes of this chapter shall be carried out in the District of Columbia as nearly as may be practicable in harmony with the plan of Peter Charles L'Enfant." The National Park Service identifies L'Enfant as "Major Peter Charles L'Enfant" and as "Major Pierre (Peter) Charles L'Enfant" on its website.
- 1 2 Kornwolf, James D; Kornwolf, Georgiana Wallis (2002). "The Creation of the Federal City: Washington". Architecture and Town Planning in Colonial North America: Vol. 3. Baltimore, Maryland: The Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 1552. ISBN 0801859867. OCLC 45066419. Retrieved October 29, 2016.
A final legacy of Jefferson's vision of the city is found in correspondence between him and L'Enfant. Jefferson consistently called the building to house Congress, the "Capitol," whereas L'Enfant just as consistently referred to it as "Congress House."
At Google Books. - ↑ (1) L'Enfant, Peter Charles (1791). "Plan of the city intended for the permanent seat of the government of t(he) United States : projected agreeable to the direction of the President of the United States, in pursuance of an act of Congress passed the sixteenth day of July, MDCCXC, "establishing the permanent seat on the bank of the Potowmac": (Washington, D.C.)". Photocopy of annotated facsimile created by U.S. Coast and Geodetic Survey, Washington, D.C. (1887). Library of Congress. Retrieved 2016-01-26.
(2) "Enlarged image of central portion of The L'Enfant Plan for Washington" (PDF). National Park Service. Retrieved 2009-10-23.
(3) Vlach, John Michael (Spring 2004). "The Mysterious Mr. Jenkins of Jenkins Hill". Capitol History: The Capitol Dome. United States Capitol Historical Society. Archived from the original on 2008-07-05. Retrieved 2009-09-14.
(4) Allen (2001), p. 8 - ↑ Harper, Douglas. "Capitol". Online Etymology Dictionary.
- ↑ Allen (2001), p. 10
- ↑ Hodgkins, George W. (1960). "Naming the Capitol and the Capital". Records of the Columbia Historical Society, Washington, D.C. 60/62: 36–53. JSTOR 40067217.
- ↑ Allen (2001), p. 11
- ↑ Allen (2001), p. 13–15
- ↑ Frary (1969), p. 28
- ↑ Allen (2001), p. 18
- ↑ Allen (2001), p. 19
- ↑ "William Thornton (1759–1828)". Library of Congress. Retrieved July 7, 2007.
- ↑ Frary (1969), p. 33
- ↑ Frary (1969), p. 34–35
- 1 2 Allen (2001), p. 23
- ↑ Jefferson, Thomas (July 17, 1793). "Letter: Jefferson to Washington". Thomas Jefferson and the National Capital. University of Virginia. Retrieved December 11, 2008.
- ↑ Frary (1969), p. 36
- ↑ "United States Capitol, Washington, D.C.: East Front Elevation, Rendering". World Digital Library. Retrieved February 13, 2013.
- ↑ Woods, Robert O. (June 2003). "Under the Capitol Dome". Mechanical Engineering Magazine. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers. Retrieved December 11, 2008.
- ↑ "A Brief Construction History of the Capitol". Architect of the Capitol. Retrieved December 11, 2008.
- ↑ Morgan, J.D. (1899). "Maj. Pierre Charles L'Enfant". Records of the Columbia Historical Society. 2: 120.
- ↑ Hazelton (1907), p. 84
- ↑ Allen, William C. (1995). In the Greatest Solemn Dignity: The Capitol's Four Cornerstones. Government Printing Office. p. 7.
- ↑ Frary (1969), p. 37–39
- ↑ Frary (1969), p. 44–45
- ↑ Carter II, Edward C. (1971–1972). "Benjamin Henry Latrobe and the Growth and Development of Washington, 1798–1818". Records of the Columbia Historical Society: 139.
- ↑ "Religion and the Founding of the American Republic". U.S. Library of Congress. July 23, 2010. Retrieved September 23, 2011.
- ↑ "The History of the United States Capitol". YouTube. Retrieved February 19, 2012.
- ↑ "Capitol slave labor studied". The Washington Times. Associated Press. June 1, 2005. Archived from the original on June 4, 2005.
- ↑ "Timeline". White House Historical Association. Retrieved June 10, 2007.
- 1 2 Steinhauer, Jennifer (August 24, 2012). "Dome Is Imperiled by 1,300 Cracks and Partisan Rift". The New York Times. Retrieved October 4, 2012.
- ↑ Jule Banville, Stone-Cold Whodunit (April 24, 2009), Washington City Paper; Stones from US Capitol in Rock Creek Park (July 25, 2011), Rock Creek Runner.
- ↑ "District of Columbia – Inventory of Historic Sites" (PDF). District of Columbia: Office of Planning. Government of the District of Columbia. September 1, 2004. Retrieved August 9, 2009.
- ↑ "America's Favorite Architecture". Harris Interactive. American Institute of Architects. 2007. Retrieved August 9, 2009.
- ↑ "World Architecture Images- U.S. Capitol". American-architecture.info. Retrieved November 5, 2010.
- ↑ "Capitol Visitors Center FAQ". Architect Of the Capitol. Retrieved December 4, 2008.
- 1 2 "Capitol Dome Restoration Project Overview". Architect of the Capitol. Retrieved November 12, 2014.
- ↑ "Capitol's historic dome set for 2-year renovation". Winston-Salem Journal. Associated Press. December 26, 2013. Retrieved December 26, 2013.
- ↑ "Frequently Asked Questions". The Architect of the Capitol.
- ↑ "AOC.gov". AOC.gov. Retrieved November 5, 2010.
- ↑ "Frieze of American History". Aoc.gov. Retrieved November 5, 2010.
- ↑ "U.S. Senate: Art & History Home, First Reading of the Emancipation Proclamation of Presid". Senate.gov. Retrieved February 19, 2012.
- ↑ "365 Steps to the Top of Capitol Hill". The New York Times. August 10, 1997. Section 1, Page 22. Retrieved August 9, 2009.
- ↑ Logan, Mrs. John A. (Mary Simmerson) (1901). Thirty Years in Washington; or, Life and Scenes in Our National Capital. Hartford, Connecticut: A. D. Worthington & Co. p. 78. OCLC 29540458. Retrieved August 9, 2009.
- ↑ Matthew Gilmore. "H-DC Discussion Network". H-net.org. Retrieved November 5, 2010.
- ↑ "The House Chamber".
- ↑ "Napoleon I". Architect of the Capitol. Retrieved April 19, 2013.
- ↑ Carrier, Thomas J. (2000). The White House, the Capitol, and the Supreme Court: historic self-guided tours. Images of America. Charleston, South Carolina: Arcadia Publishing. p. 84. ISBN 0-7385-0557-9. OCLC 44503337. Retrieved August 9, 2009.
- ↑ "The Senate Chamber 1859–2009". Retrieved January 26, 2009.
- ↑ "The Senate Chamber: Senate Vice Presidential Bust Collection". United States Senate. Retrieved December 6, 2007.
- ↑ "Apostolic Journey - United States of America: Visit to the Congress of the United States of America (Washington D.C., 24 September 2015) | Francis". w2.vatican.va. Retrieved 2016-03-19.
- ↑ Jon Grinspan. "Trying to Assassinate Andrew Jackson". Retrieved November 11, 2008.
- ↑ Kessler, Ronald (November 9, 1983). "Capitol Bombing: Group Hit Other Targets, FBI Believes". The Washington Post.
- ↑ Seppy, Tom (February 12, 1985). "Judge Finds Four in Contempt in Bombing Probe". Associated Press.
- ↑ Rowley, James (September 7, 1990). "Three Leftists Plead Guilty to Bombing the U.S. Capitol". Associated Press.
- ↑ Al-Jazeera offers accounts of 9/11 planning at the Wayback Machine (archived February 20, 2006)
- ↑ Report of the 9/11 Commission, US Govt Printing Office
- ↑ "Increased Security on Capitol Grounds" (Press release). United States Capitol Police. August 2, 2004. Retrieved September 26, 2006.
- 1 2 Lyndsey Layton and Manny Fernandez (August 3, 2004). "Street Closing Irks D.C. Leaders: Checkpoints Set Up Near World Bank, IMF and Capitol". The Washington Post. Retrieved September 26, 2006.
- ↑ Post Store (January 29, 2006). "WashingtonPost.com". The Washington Post. Retrieved November 5, 2010.
- ↑ Michael S. Schmidt (28 March 2016). "U.S. Capitol on Lockdown After Reports of Gunshots". The New York Times. Retrieved 28 March 2016.
- ↑ "US Capitol shooting: Gunman wounds Capitol police officer". BBC News Online. 28 March 2016. Retrieved 28 March 2016.
- ↑ "Capitol Visitor Center Frequently Asked Questions". Architect of the Capitol. Retrieved 2008-11-14.
- ↑ Philip Kopper "A Capitol Attraction," American Heritage, Spring 2009.
- ↑ "Capitol Visitor Center: Project Information". Architect of the Capitol. Retrieved 2008-11-10.
- ↑ "Capitol Visitor Center Fact Sheet" (PDF). Architect of the Capitol. Spring 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 31, 2008. Retrieved November 14, 2008.
References
- Allen, William C. (2001). History of the United States Capitol – A Chronicle of Design, Construction, and Politics. Government Printing Office. ISBN 0160508304. OCLC 46420177. Archived from the original on April 23, 2002. Retrieved October 29, 2016.
- Brown, Glenn (1998). Architect of the Capitol for The United States Capitol Preservation Commission, ed. History of the United States Capitol (Annotated Edition in Commemoration of The Bicentennial of the United States Capitol ed.). Government Printing Office.
- Frary, Ihna Thayer (1969). They Built the Capitol. Ayer Publishing. ISBN 0-8369-5089-5.
- Guy Gugliotta (2012). Freedom's Cap: The United States Capitol and the Coming of the Civil War. Farrar, Straus and Giroux. ISBN 978-0-8090-4681-2.
- Hazelton, George Cochrane (1907). The National Capitol. J. F. Taylor & Co.
Further reading
- Aikman, Lonnelle. We, the People: the Story of the United States Capitol, Its Past and Its Promise. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Capitol Historical Society, in cooperation with the National Geographic Society, 1964.
- Bordewich, Fergus M., "A Capitol Vision From a Self-Taught Architect", Smithsonian magazine, December 2008
- Ovason, David, The Secret Architecture of our Nation's Capital : the Masons and the building of Washington, D.C., New York City, New York: Harper Collins, 2000. ISBN 0-06-019537-1
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to United States Capitol. |
-
 Geographic data related to United States Capitol at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to United States Capitol at OpenStreetMap - Official website
- Capitol Visitors Center
- United States Capitol Historical Society
- Architect of the Capitol
- Capitol History Project — documentary and website by C-SPAN.
- Temple of Liberty: Building the Capitol for a New Nation, Library of Congress
- U.S. Capitol Police
- "Book Discussion on Freedom's Cap", C-SPAN, March 20, 2012
| Records | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Unknown |
Tallest Building in Washington, D.C. 1863–1899 88 meters |
Succeeded by Old Post Office Building (Washington, D.C.) |
| Preceded by Tenth Presbyterian Church |
Tallest building in the United States outside of New York City 1863–1888 88 meters |
Succeeded by Illinois State Capitol |