Corinthian order
The Corinthian order is the last developed of the three principal classical orders of ancient Greek and Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric order which was the earliest, followed by the Ionic order. When classical architecture was revived during the Renaissance, two more orders were added to the canon, the Tuscan order and the Composite order. The Corinthian, with its offshoot the Composite, is the most ornate of the orders, characterized by slender fluted columns and elaborate capitals decorated with acanthus leaves and scrolls. There are many variations.
The name "Corinthian" is derived from the ancient Greek city of Corinth, although the style had its own model in Roman practice, following precedents set by the Temple of Mars Ultor in the Forum of Augustus (c. 2 AD).[1] It was employed in southern Gaul at the Maison Carrée, Nîmes (illustration, below) and at the comparable podium temple at Vienne. Other prime examples noted by Mark Wilson Jones are the lower order of the Basilica Ulpia and the arch at Ancona (both of the reign of Trajan, 98–117 AD) the "column of Phocas" (re-erected in Late Antiquity but 2nd century in origin), and the "Temple of Bacchus" at Baalbek (c. 150 AD).[2]
Description
Greek Corinthian order
The Corinthian order is named for the Greek city-state of Corinth, to which it was connected in the period. However, according to the architectural historian Vitruvius, the column was created by the sculptor Callimachus, probably an Athenian, who drew acanthus leaves growing around a votive basket. Its earliest use can be traced back to the Late Classical Period (430-323 BC). The earliest Corinthian capital was found in Bassae, dated at 427 BC.
Roman Corinthian order

Proportion is a defining characteristic of the Corinthian order: the "coherent integration of dimensions and ratios in accordance with the principles of symmetria" are noted by Mark Wilson Jones, who finds that the ratio of total column height to column-shaft height is in a 6:5 ratio, so that, secondarily, the full height of column with capital is often a multiple of 6 Roman feet while the column height itself is a multiple of 5. In its proportions, the Corinthian column is similar to the Ionic column, though it is more slender, and stands apart by its distinctive carved capital. The abacus upon the capital has concave sides to conform to the outscrolling corners of the capital, and it may have a rosette at the center of each side. Corinthian columns were erected on the top level of the Roman Colosseum, holding up the least weight, and also having the slenderest ratio of thickness to height. Their height to width ratio is about 10:1.[3]
One variant is the Tivoli Order, found at the Temple of Vesta, Tivoli. The Tivoli Order's Corintinan Capital has two rows of Acanthus (ornament) and its abacus is decorated with oversize fleuron (architectural) in the form of hibiscus flowers with pronounced spiral pistils. The column flutes have flat tops. The frieze exhibits fruit swag (motif) suspended between bucrania. Above each swag is a rosette (design). The cornice does not have modillions.
Gandharan capitals
Indo-Corinthian capitals are capitals crowning columns or pilasters, which can be found in the northwestern Indian subcontinent, and usually combine Hellenistic and Indian elements. These capitals are typically dated to the 1st centuries of our era, and constitute important elements of Greco-Buddhist art of Gandhara.
The classical design was often adapted, usually taking a more elongated form, and sometimes being combined with scrolls, generally within the context of Buddhist stupas and temples. Indo-Corinthian capitals also incorporated figures of the Buddha or Bodhisattvas, usually as central figures surrounded, and often in the shade, of the luxurious foliage of Corinthian designs.

Renaissance Corinthian order

During the first flush of the Italian Renaissance, the Florentine architectural theorist Francesco di Giorgio expressed the human analogies that writers who followed Vitruvius often associated with the human form, in squared drawings he made of the Corinthian capital overlaid with human heads, to show the proportions common to both.[4]
The Corinthian architrave is divided in two or three sections, which may be equal, or they may bear interesting proportional relationships, one with another. Above the plain, unadorned architrave lies the frieze, which may be richly carved with a continuous design or left plain, as at the U.S. Capitol extension (illustration, right). At the Capitol the proportions of architrave to frieze are exactly 1:1. Above that, the profiles of the cornice moldings are like those of the Ionic order. If the cornice is very deep, it may be supported by brackets or modillions, which are ornamental brackets used in a series under a cornice.
The Corinthian column is almost always fluted. If it is not, it is often worth pausing to unravel the reason why (sometimes simply a tight budget). Even the flutes of a Corinthian column may be enriched. They may be filleted, with rods nestled within the hollow flutes, or stop-fluted, with the rods rising a third of the way, to where the entasis begins. The French like to call these chandelles and sometimes they end them literally with carved wisps of flame, or with bellflowers. Alternatively, beading or chains of husks may take the place of the fillets in the fluting, for Corinthian is the most playful and flexible of the orders. Its atmosphere is rich and festive, with more opportunities for variation than the other orders.
Elaborating upon an offhand remark when Vitruvius accounted for the origin of its acanthus capital, it became a commonplace to identify the Corinthian column with the slender figure of a young girl; in this mode the classicizing French painter Nicolas Poussin wrote to his friend Fréart de Chantelou in 1642
The beautiful girls whom you will have seen in Nîmes will not, I am sure, have delighted your spirit any less than the beautiful columns of Maison Carrée for the one is no more than an old copy of the other.[5]
Sir William Chambers expressed the conventional comparison with the Doric order:
The proportions of the orders were by the ancients formed on those of the human body, and consequently, it could not be their intention to make a Corithian column, which, as Vitruvius observes, is to represent the delicacy of a young girl, as thick and much taller than a Doric one, which is designed to represent the bulk and vigour of a muscular full grown man.[6]
History

The oldest known example of a Corinthian column is in the Temple of Apollo Epicurius at Bassae in Arcadia, c. 450–420 BC. It is not part of the order of the temple itself, which has a Doric colonnade surrounding the temple and an Ionic order within the cella enclosure. A single Corinthian column stands free, centered within the cella. This is a mysterious feature, and archaeologists debate what this shows: some state that it is simply an example of a votive column. A few examples of Corinthian columns in Greece during the next century are all used inside temples. A more famous example, and the first documented use of the Corinthian order on the exterior of a structure, is the circular Choragic Monument of Lysicrates in Athens, erected c. 334 BC.


Right image: Corinthian anta capital at the Niha Bekaa Roman Temple, 1st century AD.
A Corinthian capital carefully buried in antiquity in the foundations of the circular tholos at Epidaurus was recovered during modern archaeological campaigns. Its enigmatic presence and preservation have been explained as a sculptor's model for stonemasons to follow[7] in erecting the temple dedicated to Asclepius. The architectural design of the building was credited in antiquity to the sculptor Polykleitos the Younger, son of the Classical Greek sculptor Polykleitos the Elder. The temple was erected in the 4th century BC. These capitals, in one of the most-visited sacred sites of Greece, influenced later Hellenistic and Roman designs for the Corinthian order. The concave sides of the abacus meet at a sharp keel edge, easily damaged, which in later and post-Renaissance practice has generally been replaced by a canted corner. Behind the scrolls the spreading cylindrical form of the central shaft is plainly visible.
Much later, the Roman writer Vitruvius (c. 75 BC – c. 15 BC) related that the Corinthian order had been invented by Callimachus, a Greek architect and sculptor who was inspired by the sight of a votive basket that had been left on the grave of a young girl. A few of her toys were in it, and a square tile had been placed over the basket, to protect them from the weather. An acanthus plant had grown through the woven basket, mixing its spiny, deeply cut leaves with the weave of the basket.[8]
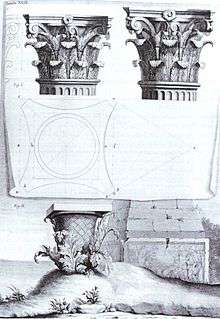
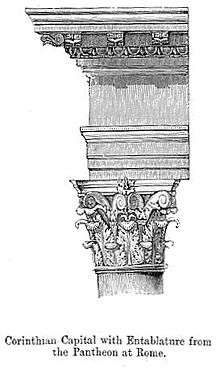
Claude Perrault incorporated a vignette epitomizing the Callimachus tale in his illustration of the Corinthian order for his translation of Vitruvius, published in Paris, 1684 (illustration, left). Perrault demonstrates in his engraving how the proportions of the carved capital could be adjusted according to demands of the design, without offending. The texture and outline of Perrault's leaves is dry and tight compared to their 19th-century naturalism at the U.S. Capitol (below, left). A Corinthian capital may be seen as an enriched development of the Ionic capital, though one may have to look closely at a Corinthian capital (illustration, right) to see the Ionic volutes ("helices"), at the corners, perhaps reduced in size and importance, scrolling out above the two ranks of stylized acanthus leaves and stalks ("cauliculi" or caulicoles), eight in all, and to notice that smaller volutes scroll inwards to meet each other on each side. The leaves may be quite stiff, schematic and dry, or they may be extravagantly drilled and undercut, naturalistic and spiky. In Late Antique and Byzantine practice, the leaves may be blown sideways, as if by the wind of Faith. Unlike the Doric and Ionic column capitals, a Corinthian capital has no neck beneath it, just a ring-like astragal molding or a banding that forms the base of the capital, recalling the base of the legendary basket.
Most buildings (and most clients) are satisfied with just two orders. When orders are superposed one above another, as they are at the Flavian Amphitheater— the Colosseum— the natural progression is from sturdiest and plainest (Doric) at the bottom, to slenderest and richest (Corinthian) at the top. The Colosseum's topmost tier has an unusual order that came to be known as the Composite order during the 16th century. The mid-16th-century Italians, especially Sebastiano Serlio and Jacopo Barozzi da Vignola, who established a canonic version of the orders, thought they detected a "Composite order", combining the volutes of the Ionic with the foliage of the Corinthian, but in Roman practice volutes were almost always present.

In Romanesque and Gothic architecture, where the Classical system had been replaced by a new esthetic composed of arched vaults springing from columns, the Corinthian capital was still retained. It might be severely plain, as in the typical Cistercian architecture (illustration left), which encouraged no distraction from liturgy and ascetic contemplation, or in other contexts it could be treated to numerous fanciful variations, even on the capitals of a series of columns or colonettes within the same system.
During the 16th century, a sequence of engravings of the orders in architectural treatises helped standardize their details within rigid limits. Sebastiano Serlio; the Regola delli cinque ordini of Giacomo Barozzi da Vignola (1507–1573); the Quattro libri di Architettura of Andrea Palladio, and Vincenzo Scamozzi's Idea della Architettura Universale, were followed in the 17th century by French treatises with further refined engraved models, such as Perrault's.
Notable examples




- Greece
- Israel
- Italy
- Pantheon, Rome (illustration)
- Temple of Mars Ultor
- Temple of Vesta, Tivoli
- France
- Maison Carrée, Nimes
- The July Column, Paris
- Portugal
- Renaissance and Baroque
- Neoclassical and Beaux-Arts
- United States Capitol (illustration)
- St. La Salle Hall, Manila
- Don Enrique T. Yuchengco Hall, Manila
- Enrique M. Razon Sports Center, Manila
- Syria
- Ukraine
- Great Lavra Belltower (fourth tier – 8 columns)
- United Kingdom
- United States of America
- Germany
- The Reichstag, Berlin
- Jordan
See also
Notes
- ↑ Mark Wilson Jones, "Designing the Roman Corinthian order", Journal of Roman Archaeology 2:35-69 (1989).
- ↑ Jones 1989.
- ↑ Peter D'Epiro; Mary Desmond Pinkowish (22 December 2010). What are the Seven Wonders of the World?: And 100 Other Great Cultural Lists--Fully Explicated. Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group. p. 133. ISBN 978-0-307-49107-7.
- ↑ Francesco di Giorgio's sheet with the drawings, from the Turin codex Saluzziano of his Trattati di architettura ingegneria e arte militare, c. 1480–1500, is illustrated by Rudolf Wittkower, Architectural Principles in the Age of Humanism (1962) 1965, pl. ic
- ↑ Quoted by Sir Kenneth Clark, The Nude: A Study in Ideal Form, 1956, p. 45.
- ↑ Chambers, A Treatise on the Decorative Part of Civil Architecture (Joseph Gwilt ed, 1825:pp 159–61).
- ↑ Alison Burford (The Greek Temple Builders at Epidauros, Liverpool, 1969, p. 65) suggests instead that it was spoilt in the carving, one volute being incorrectly detached from its field; Hugh Plommer, reviewing it for The Classical Review (New Series, 21.2 [June 1971], pp 269–272), remarks that the error involved an excess of work and remains convinced that the capital was a model.
- ↑ Vitr. 4.1.9-10
External links
![]() Media related to Corinthian columns at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Corinthian columns at Wikimedia Commons