Carotid artery stenosis
| Carotid artery stenosis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | cardiology |
| ICD-10 | I65.2 |
| ICD-9-CM | 433.1 |
| DiseasesDB | 31178 |
| MedlinePlus | 007427 |
| MeSH | D016893 |
Carotid stenosis is a narrowing or constriction of the inner surface (lumen) of the carotid artery, usually caused by atherosclerosis.
Signs and symptoms
The carotid artery is the large artery whose pulse can be felt on both sides of the neck under the jaw. On the right side it starts from the brachiocephalic trunk (a branch of the aorta) as the common carotid artery, and on the left side the common carotid artery comes directly off the aortic arch. At the throat it forks into the internal and external carotid arteries. The internal carotid artery supplies the brain, and the external carotid artery supplies the face. This fork is a common site for atherosclerosis, an inflammatory buildup of atheromatous plaque that can narrow the lumen of the common or internal carotid arteries.
The plaque can be stable and asymptomatic, or it can be a source of embolization. Emboli break off from the plaque and travel through the circulation to blood vessels in the brain. As the vessel gets smaller, they can lodge in the vessel wall and restrict blood flow to parts of the brain which that vessel supplies. This ischemia can either be temporary, yielding a transient ischemic attack, or permanent resulting in a thromboembolic stroke.
Clinically, risk of stroke from carotid stenosis is evaluated by the presence or absence of symptoms and the degree of stenosis on imaging.
Transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) are a warning sign, and are often followed by severe permanent strokes, particularly within the first two days. TIAs by definition last less than 24 hours and frequently take the form of a weakness or loss of sensation of a limb or the trunk on one side of the body, or the loss of sight (amaurosis fugax) in one eye. Less common symptoms are artery sounds (bruits), or ringing in the ears (tinnitus).
Pathophysiology
The carotid artery is the large vertical artery in red. The blood supply to the carotid artery starts at the arch of the aorta (bottom). The carotid artery divides into the internal carotid artery and the external carotid artery. The internal carotid artery supplies the brain. Plaque often builds up at that division, and causes a narrowing (stenosis). Pieces of plaque can break off and block the small arteries above in the brain, which causes a stroke. Plaque can also build up at the origin of the carotid artery at the aorta.
-

Section of carotid artery with plaque. Blood flows from the common carotid artery(bottom), and divides into the internal carotid artery (left) and external carotid artery (right). The atherosclerotic plaque is the dark mass on the left
Diagnosis
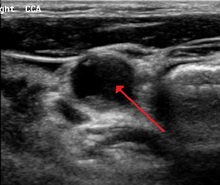

Carotid stenosis is usually diagnosed by color flow duplex ultrasound scan of the carotid arteries in the neck. This involves no radiation, no needles and no contrast agents that may cause allergic reactions. This test has moderate sensitivity and specificity, and yields many false-positive results.
Typically duplex ultrasound scan is the only investigation required for decision making in carotid stenosis as it is widely available and rapidly performed. However, further imaging can be required if the stenosis is not near the bifurcation of the carotid artery.
One of several different imaging modalities, such as angiogram, computed tomography angiogram (CTA)[1][2][3] or magnetic resonance imaging angiogram (MRA) may be useful. Each imaging modality has its advantages and disadvantages - Magnetic resonance angiography and CT angiography with contrast is contraindicated in patients with renal insufficiency, catheter angioigraphy has a 0.5% to 1.0% risk of stroke, MI, arterial injury or retoperitoneal bleeding. The investigation chosen will depend on the clinical question and the imaging expertise, experience and equipment available.[4]
Screening
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends against screening for carotid artery stenosis in those without symptoms.[5]
Management
Options include:
- Medications alone (an antiplatelet drug (or drugs) and control of risk factors for atherosclerosis).
- Medical management plus carotid endarterectomy or carotid stenting, which is preferred in patients at high surgical risk and in younger patients.
- Control of smoking, high blood pressure, and high levels of lipids in the blood.
The goal of treatment is to reduce the risk of stroke (cerebrovascular accident). Intervention (carotid endarterectomy or carotid stenting) can cause stroke; however, where the risk of stroke from medical management alone is high, intervention may be beneficial. In selected trial participants with asymptomatic severe carotid artery stenosis, carotid endarterectomy reduces the risk of stroke in the next 5 years by 50%, though this represents a reduction in absolute incidence of all strokes or perioperative death of approximately 6%. In most centres, carotid endarterectomy is associated with a 30-day stroke or mortality rate of < 3%; some areas have higher rates.[6]
Clinical guidelines (such as those of National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE) ) recommend that all patients with carotid stenosis be given medication, usually blood pressure lowering medications, anti-clotting medications, anti-platelet medications (such as aspirin or clopidogrel), and especially statins (which were originally prescribed for their cholesterol-lowering effects but were also found to reduce inflammation and stabilize plaque).
NICE and other guidelines also recommend that patients with symptomatic carotid stenosis be given carotid endarterectomy urgently, since the greatest risk of stroke is within days. Carotid endarterectomy reduces the risk of stroke or death from carotid emboli by about half.
For people with stenosis but no symptoms, the interventional recommendations are less clear. Such patients have a historical risk of stroke of about 1-2% per year. Carotid endarterectomy has a surgical risk of stroke or death of about 2-4% in most institutions. In the large Asymptomatic Carotid Surgery Trial (ACST) endarterectomy reduced major stroke and death by about half, even after surgical death and stroke was taken into account.[7] According to the Cochrane Collaboration the absolute benefit of surgery is small. For intervention using stents, there is insufficient evidence to support stenting rather than open surgery, and several trials, including the ACST-2, are comparing these 2 procedures.
Surgery and stenting
The largest clinical trial performed, CREST, randomized patients at risk for a stroke from carotid artery blockage to either open surgery (carotid endarterectomy) or carotid stent placement with embolic protection. This trial followed patients for 4 years and found no overall difference in the primary end point of both treatment arms (myocardial infarctions, any perioperative strokes or ipsilateral strokes within 4 years, or death during procedure). Patients assigned to the surgical arm experienced more perioperative myocardial infarctions compared to the stenting group; however, the difference was not statistically significant (6.8% vs or 7.2% HR for stenting is 1.1 CI 0.81-1.51 P value 0.51) whereas patients assigned to the carotid stent arm experienced more periprocedural strokes compared to endarteretomy (6.4% vs 4.7% HR for stenting 1.5 P-0.03). There was no mortality difference and no difference for major (disabling) strokes between surgery and stenting. It was noted that there did seem to exist an age cutoff where below 75 years old endarterectomy provided more positive outcomes and over 75 stenting offered a better risk profile. However, it should be noted that the CREST trial was not designed for subgroup analysis and thus not powered enough to draw any statistically significant conclusions.[8] A later study published in 2013 evaluated how these perioperative complications affect long-term survival. This study showed that experiencing a stroke within the first year conferred a two-fold lower survival rate (Hazard Ratio(HR) 6.6 [CI 3.7-12]) than those who experienced a perioperative myocardial infarction at two years post intervention (HR 3.6 [CI 2-6.8]). This difference in mortality, however, converges and becomes negligible at 5 years (HR 2.7 [CI 1.7-4.3] vs HR 2.8 [CI 1.8-4.3]).[9] A 2010 study found benefits (reduced strokes) from carotid endarterectomy in those without symptoms who are under 75.[10]
See also
References
- ↑ Bartlett ES, Walters TD, Symons SP, Fox AJ. Quantification of carotid stenosis on CT angiography. American Journal of Neuroradiology. 2006 January; 27(1):13-19.
- ↑ White JH, Bartlett ES, Bharatha A, Aviv RI, Fox AJ, Thompson AL, Bitar R, Symons SP. Reproducibility of semi-automated measurement of carotid stenosis on CTA. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences. 2010 July; 37(4):498-503.
- ↑ Lian K, White JH, Bartlett ES, Bharatha A, Aviv RI, Fox AJ, Symons SP. NASCET percent stenosis semi-automated versus manual measurement on CTA. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences. 2012 May; 39(3):343-346.
- ↑ Solomon, Caren G.; Grotta, James C. (19 September 2013). "Carotid Stenosis". New England Journal of Medicine. 369 (12): 1143–1150. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1214999.
- ↑ Jonas, DE; Feltner, C; Amick, HR; Sheridan, S; Zheng, ZJ; Watford, DJ; Carter, JL; Rowe, CJ; Harris, R (Jul 8, 2014). "Screening for Asymptomatic Carotid Artery Stenosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force". Annals of Internal Medicine. 161 (5): 336–46. doi:10.7326/M14-0530. PMID 25004169.
- ↑ Screening for Carotid Artery Stenosis. December 2007. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD.
- ↑ Naylor AR (July 2004). "The Asymptomatic Carotid Surgery Trial: bigger study, better evidence". Br J Surg. 91 (7): 787–9. doi:10.1002/bjs.4552. PMID 15227684.
- ↑ Brott TG, Hobson RW, Howard G, et al. (July 2010). "Stenting versus endarterectomy for treatment of carotid-artery stenosis". N. Engl. J. Med. 363 (1): 11–23. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0912321. PMC 2932446
 . PMID 20505173.
. PMID 20505173. - ↑ Simons, JP; et. al (8 Feb 2013). "The Effect of Postoperative Stroke and Myocardial Infarction on long-term Survival after carotid revascularization.". Journal of Vascular Surgery. 12 (6): 1581–8. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2012.11.118. PMID 23402875. Retrieved 20 March 2013.
- ↑ Halliday A, Harrison M, Hayter E, et al. (September 2010). "10-year stroke prevention after successful carotid endarterectomy for asymptomatic stenosis (ACST-1): a multicentre randomised trial". Lancet. 376 (9746): 1074–84. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61197-X. PMC 2956884
 . PMID 20870099.
. PMID 20870099.
