Art Deco
Left to right, top to bottom: Grand Rex movie theater in Paris (1932), Cassandre poster for ocean liner SS Normandie (1935), salon of Paul Reynaud in Paris (1934), Chrysler Building in New York City (1930) and hood ornament "Victoire" by René Lalique (1928) | |||||||
| Years active | 1913-1939 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Art Deco (/ˌɑːrt ˈdɛkoʊ/), or Deco, is a style of visual arts, architecture and design that first appeared in France just before World War I.[1] It became popular in the 1920s and 1930s, and influenced the design of buildings, furniture, jewellery, fashion, cars, movie theaters, trains, ocean liners, and everyday objects such as radios and vacuum cleaners.[2] It took its name, short for Arts Décoratifs, from the Exposition Internationale des Arts Décoratifs et Industriels Modernes (International Exhibition of Modern Decorative and Industrial Arts) held in Paris in 1925.[3] It combined modernist styles with fine craftsmanship and rich materials. During its heyday, Art Deco represented luxury, glamour, exuberance, and faith in social and technological progress.
Art Deco was a pastiche of many different styles, sometimes contradictory, united by a desire to be modern. From its outset, Art Deco was influenced by the bold geometric forms of Cubism; the bright colors of Fauvism and of the Ballets Russes; and the updated craftsmanship of the furniture of the eras of Louis Philippe and Louis XVI; by the exotic styles of China and Japan, India, Persia, ancient Egypt and Maya art. It featured rare and expensive materials such as ebony and ivory and exquisite craftsmanship. The Chrysler Building and other skyscrapers of New York were the most visible monuments of the new style. In the 1930s, after the Great Depression, the style became more subdued. New materials arrived, including chrome plating, stainless steel and plastic. A more sleek form of the style, called Streamline Moderne, appeared in the 1930s; it featured curving forms and smooth, polished surfaces.[4] Art Deco became one of the first truly international architectural styles, with examples found in European cities, the United States, Russia, Latin America, Africa and Asia. The style came to an end with the beginning World War II. Deco was replaced as the dominant global style by the strictly functional and unadorned styles of modernism and the International Style of architecture.[5]
Naming

Art Deco took its name, short for Arts Décoratifs, from the Exposition Internationale des Arts Décoratifs et Industriels Modernes held in Paris in 1925,[3] though the diverse styles that characterize Art Deco had already appeared in Paris and Brussels before World War I.
The term arts décoratifs was first used in France in 1858; published in the Bulletin de la Société française de photographie.[6]
In 1868, Le Figaro newspaper used the term art décoratifs with respect to objects for stage scenery created for the Théâtre de l'Opéra.[7][8][9]
In 1875, furniture designers, textile, jewelry and glass designers and other craftsmen were officially given the status of artists by the French government. In response to this, the École royale gratuite de dessin (Royal Free School of Design) originally founded in 1766 under King Louis XVI to train artists and artisans in crafts relating to the fine arts, was renamed the National School of Decorative Arts (l'École nationale des arts décoratifs). It took its present name of ENSAD (École nationale supérieure des arts décoratifs) in 1927.
During the 1925 Exposition the architect Le Corbusier wrote a series of articles about the exhibition for his magazine L'Esprit Nouveau under the title, "1925 Expo: Arts Déco" which were combined into a book, "L'art décoratif d'aujourd'hui" (Decorative Art Today). The book was a spirited attack on the excesses of the colorful and lavish objects at the Exposition; and on the idea that practical objects such as furniture should have any decoration at all; his conclusion was that "Modern decoration has no decoration".[10]
The shorthand title "Arts Deco" that Le Corbusier used in the articles and book was adapted in 1966 for title of the first modern exhibit on the subject, called Les Années 25 : Art déco, Bauhaus, Stijl, Esprit nouveau, which covered the variety of major styles in the 1920s and 1930s. The term Art déco was then used in a 1966 newspaper article by Hillary Gelson in the Times (London, 12 November), describing the different styles at the exhibit.[11][12]
Art Deco gained currency as a broadly applied stylistic label in 1968 when historian Bevis Hillier published the first major academic book on the style: Art Deco of the 20s and 30s.[2] Hillier noted that the term was already being used by art dealers and cites The Times (2 November 1966) and an essay named "Les Arts Déco" in Elle magazine (November 1967) as examples of prior usage.[13] In 1971, Hillier organized an exhibition at the Minneapolis Institute of Arts, which he details in his book about it, The World of Art Deco.[14][15]
Origins
The Society of Decorative Artists (1901-1913)

The emergence of Art Deco was closely connected with the rise in status of decorative artists, who in the 19th century had been considered simply as artisans. The term "arts décoratifs" had been invented in 1875, giving the designers of furniture, textiles, and other decoration official status. The Société des artistes décorateurs (Society of decorative artists), or SAD, was founded in 1901, and decorative artists were given the same rights of authorship as painters and sculptors. A similar movement developed in Italy. The first international exhibition devoted entirely to the decorative arts, the Esposizione international d'Arte decorative moderna , was held in Turin in 1902. Several new magazines devoted to decorative arts were founded in Paris, including Arts et décoration and L'Art décoratif moderne. Decorative arts sections were introduced into the annual salons of the Sociéte des artistes français, and later in the Salon d'automne. French nationalism also played a part in the resurgence of decorative arts; French designers felt challenged by the increasing exports of less expensive German furnishings. In 1911 the SAD proposed the holding of a major new international exposition of decorative arts in 1912. No copies of old styles were to be permitted; only modern works. The exhibit was postponed until 1914, then, because of the war, postponed until 1925, when it gave its name to the whole family of styles known as Déco.[16]
Some avant-garde painters began to cross the traditional line between fine arts and decorative arts. In 1908 the Symbolist painter Odilon Redon created a fireplace screen and other decorative objects.
The Paris department stores and fashion designers also played an important part in the rise of Art Déco. Established firms including the luggage maker Louis Vuitton silverware firm Christofle, glass designer René Lalique, and the jewelers Louis Cartier and Boucheron, who all began designing products in more modern styles. Beginning in 1900, the Department stores had recruited decorative artists to work in their design studios. The decoration of the 1912 Salon d'Automne had been entrusted to the department store Printemps.[17] During the same year Printemps created its own workshop called "Primavera". By 1920 Primavera employed more than three hundred artists. The styles ranged from the updated versions of Louis XIV, Louis XVI and especially Louis Philippe furniture made by Louis Süe and the Primavera workshop to more modern forms from the workshop of the Au Louvre department store. Other designers, including Émile-Jacques Ruhlmann and Paul Foliot refused to use mass production, and insisted that each piece be made individually by hand. The early art deco style featured luxurious and exotic materials such as ebony, and ivory and silk, very bright colors and stylized motifs, particularly baskets and bouquets of flowers of all colors, giving a modernist look.[18]
The Théâtre des Champs-Élysées (1910-1913)
-
_(3713880263).jpg)
Antoine Bourdelle, La Danse, facade of the Théâtre des Champs-Elysées, Paris (1912)
-

Théâtre des Champs-Élysées, by Auguste Perret, 15 avenue Montaigne, Paris, (1910–13). Reinforced concrete gave architects the ability to create new forms and bigger spaces.
-

Interior of the Théâtre des Champs-Élysées, with Bourdelle bas-reliefs over the stage
-

Dome of the Theater, with Art-Deco rose design by Maurice Denis
The Théâtre des Champs-Élysées (1910-1913), by Auguste Perret was the first landmark Art Deco building completed in Paris. Previously reinforced had been used only for industrial and apartment buildings, Perret had built the first modern reinforced concrete apartment building in Paris on rue Benjamin Franklin in 1903-04. Henri Sauvage, another important future Art Deco architect, built another in 1904 at 7 rue Trétaigne (1904). From 1908 to 1910, the 21-year old Le Corbusier worked as a draftsman in Perret's office, learning the techniques of concrete construction. Perret's building had clean rectangular form, geometric decoration and straight lines, the future trademarks of Art Deco. The decor of the theater was also revolutionary; the facade was decorated with plaques of Art Deco sculpture by Antoine Bourdelle, a dome by Maurice Denis, paintings by Édouard Vuillard, and an Art Deco curtain Ker-Xavier Roussel. The theater became famous as the venue for many of the first performances of the Ballets Russes. Perret and Sauvage became the leading Art Deco architects in Paris in the 1920s.[19][20]
The Salon d'Automne (1912-13)
-
_02_by_L._Bakst_2.jpg)
Set design for Sheherazade (1910) by Leon Bakst
-

Table and chairs by Maurice Dufrene and carpet by Paul Follot at the 1912 Salon des artistes décorateurs
-

Art Deco armchair made for art collector Jacques Doucet (1912–13)
-
.jpg)
Display of early Art Deco furnishings by the Atelier Français at the 1913 Salon d'Automne from Art et décoration magazine (1914)
At its birth between 1910 and 1914, Art Deco was an explosion of colors, featuring bright and often clashing hues, frequently in floral designs, presented in furniture upholstery, carpets, screens, wallpaper and fabrics. Many colorful works, including chairs and a table by Maurice Dufrene and a bright Gobelin carpet by Paul Follot were presented at the 1912 Salon des artistes décorateurs. In 1912-1913 designer Alfred Karbowsky made a floral chair with a parrot design for the hunting lodge of art collector Jacques Doucet.[21] The furniture designers Louis Süe and André Mare made their first appearance at the 1912 exhibit, under the name of the Atelier Française, combining colorful fabrics with exotic and expensive materials, including ebony and ivory. After World War I they became one of the most prominent French interior design firms, producing the furniture for the first-class salons and cabins of the French transatlantic ocean liners.[22]
The vivid colors of Art Deco came many sources, including the exotic set designs by Leon Bakst for the Ballets Russes, which caused a sensation in Paris just before World War I. Some of the colors were inspired by the earlier Fauvism movement led by Henri Matisse; others by the Orphism of painters such as Sonia Delaunay; others by the movement known as the Nabis, and in the work of symbolist painter Odilon Redon, who designed fireplace screens and other decorative objects. Bright colors were a feature of the work of fashion designer Paul Poiret, whose work influenced both Art Deco fashion and interior design.[22]
The Cubist House (1912)
-

Design for the facade of La Maison Cubiste (Cubist House) by Raymond Duchamp-Villon (1912)
-
_at_the_Salon_d'Automne%2C_1912%2C_detail_of_the_entrance._Photograph_by_Duchamp-Villon.jpg)
Raymond Duchamp-Villon, 1912, La Maison Cubiste (Cubist House) at the Salon d'Automne, 1912, detail of the entrance
-

Le Salon Bourgeois, designed by André Mare inside La Maison Cubiste, in the decorative arts section of the Salon d'Automne, 1912, Paris. Metzinger's Femme à l'Éventail on the left wall

The art style known as Cubism appeared in France between 1907 and 1912, influencing the development of Art Deco. The Cubists, themselves under the influence of Paul Cézanne, were interested in the simplification of forms to their geometric essentials: the cylinder, the sphere, the cone.[23]
In 1912, the artists of the Section d'Or exhibited works considerably more accessible to the general public than the analytical Cubism of Picasso and Braque. The Cubist vocabulary was poised to attract fashion, furniture and interior designers.[24][25]
In the 1912 writings of André Vera. Le Nouveau style, published in the journal L'Art décoratif, he expressed the rejection of Art Nouveau forms (asymmetric, polychrome and picturesque) and called for simplicité volontaire, symétrie manifeste, l'ordre et l'harmonie, themes that would eventually become common within Art Deco; though with time the Deco style was often extremely colorful and anything but simple.[26]
In the Art Décoratif section of the 1912 Salon d'Automne, an architectural installation was exhibited known as the La Maison Cubiste .[27][28] The facade was designed by Raymond Duchamp-Villon. The decor of the house was by the firm of Louis Süe and André Mare, who had formed a company called the Atlelier Français in 1912.[29] La Maison Cubiste was a furnished installation with a facade, a staircase, wrought iron banisters, a bedroom, a living room—the Salon Bourgeois, where paintings by Albert Gleizes, Jean Metzinger, Marie Laurencin, Marcel Duchamp, Fernand Léger and Roger de La Fresnaye were hung.[30][31][32] Thousands of spectators at the salon passed through the full-scale model.[33]

The facade of the house, designed by Raymond Duchamp-Villon, was not very radical by modern standards; the lintels and pediments had prismatic shapes, but otherwise the facade resembled an ordinary house of the period. The rooms were furnished by Mare with neo-Louis XVI and Louis-Philippe style chairs and sofas that were updated with more angular features to make hem go with the Cubist paintings. The critic Emile Sedeyn described Mare's work in the magazine Art et Décoration: "He does not embarrass himself with simplicity, for he multiplies flowers wherever they can be put. The effect he seeks is obviously one of picturesqueness and gaiety. He achieves it."[34] The Cubist element was provided by the paintings. Despite its tameness, the installation was attacked by some critics as extremely radical, which helped make for its success.[35] This architectural installation was subsequently exhibited at the 1913 Armory Show, New York, Chicago and Boston.[25][36][37][38][39] Thanks largely to the exhibition, the term "Cubist" began to be applied to anything modern, from women's haircuts to clothing to theater performances.[35]
The Cubist style continued within Art Deco, even as Deco branched out in many other directions. In 1927, Cubists Joseph Csaky, Jacques Lipchitz, Louis Marcoussis, Henri Laurens, the sculptor Gustave Miklos, and others collaborated in the decoration of a Studio House, rue Saint-James, Neuilly-sur-Seine, designed by the architect Paul Ruaud and owned by the French fashion designer Jacques Doucet, also a collector of Post-Impressionist art by Henri Matisse and Cubist paintings (including Les Demoiselles d'Avignon, which he bought directly from Picasso's studio). Laurens designed the fountain, Csaky designed Doucet's staircase,[40] Lipchitz made the fireplace mantel, and Marcoussis made a Cubist rug.[41][42][43]
Besides the Cubist artists, Doucet brought in other Deco interior designers to help in decorating the house, including Pierre Legrain, who was in charge of organizing the decoration, and Paul Iribe, Marcel Coard, André Groult, Eileen Gray and Rose Adler to provide furniture. The decor included massive pieces made of macassar ebony, inspired by African art, and furniture covered with Morocco leather, crocodile skin and snakeskin, and patterns taken from African designs.[44]
Influences
-
%2C_Vaslav_Nijinsky_(1890-1950)%2C_1913_1.jpg)
The exoticism of the Ballets Russes had a strong influence on early Deco. A drawing of the dancer Vaslav Nijinsky by Paris fashion artist Georges Barbier (1913)
-

Illustration by Georges Barbier of a gown by Paquin (1914). Stylized floral designs and bright colors were a feature of early Art Deco.
-

Stairway in the hôtel particulier of fashion designer-art collector Jacques Doucet (1927). Design by Joseph Csaky. The geometric forms of Cubism had an important influence on Art Deco
-
Lobby of 450 Sutter Street in San Francisco by Timothy Pflueger, (1929) inspired by ancient Maya art
-
The gilded bronze Prometheus at Rockefeller Center by Paul Manship (1934), a stylized Art Deco update of classical sculpture (1936)
-

A ceramic vase inspired by motifs of traditional African carved wood sculpture, by Emile Lenoble (1937), Museum of Decorative Arts, Paris
Art Deco was not a single style, but a collection of different and sometimes contradictory styles. In architecture, Art Deco was the successor to and reaction against Art Nouveau, a style which flourished in Europe between 1895 and 1900, and also gradually replaced the Beaux-Arts and neoclassical that were predominant in European and American architecture. In 1905 Eugène Grasset wrote and published Méthode de Composition Ornementale, Éléments Rectilignes,[45] in which he systematically explored the decorative (ornamental) aspects of geometric elements, forms, motifs and their variations, in contrast with (and as a departure from) the undulating Art Nouveau style of Hector Guimard, so popular in Paris a few years earlier. Grasset stressed the principle that various simple geometric shapes like triangles and squares are the basis of all compositional arrangements. The reinforced concrete buildings of Auguste Perret and Henri Sauvage, and particularly the Theatre des Champs-Elysees, offered a new form of construction and decoration which was copied worldwide.[46]
In decoration, many different styles were borrowed and used by Art Deco. They included pre-modern art from around the world and observable at the Musée du Louvre, Musée de l'Homme and the Musée national des Arts d'Afrique et d'Océanie. There was also popular interest in archeology due to excavations at Pompeii, Troy, the tomb of Tutankhamun, etc. Artists and designers integrated motifs from ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, Greece, Rome, Asia, Mesoamerica and Oceania with Machine Age elements.[47][48][49][50][51][52]
Other styles borrowed included Russian Constructivism and Italian Futurism, as well as Orphism, Functionalism, and Modernism in general.[25][53][47][54] Art Deco also used the clashing colors and designs of Fauvism, notably in the work of Henri Matisse and André Derain, inspired the designs of art deco textiles, wallpaper, and painted ceramics.[25] It took ideas from the high fashion vocabulary of the period, which featured geometric designs, chevrons, zigzags, and stylized bouquets of flowers. It was influenced by discoveries in From 1925 onwards, it was often inspired by a passion for new machines (airships, automobiles and ocean liners). and, after 1930, by aerodynamic forms, the streamline style.[55]
The style of luxury and modernity
-

The boudoir of fashion designer Jeanne Lanvin (1922–25) now in the Museum of Decorative Arts, Paris
-

Bath of Jeanne Lanvin, of Sienna marble, with decoration of carved stucco and bronze (1922–25)
-

An Art Deco study by the Paris design firm of Alavoine, now in the Brooklyn Museum (1928–30)
-

The Glass Salon, designed for Suzanne Talbot by Paul Ruaud, with furniture by Eileen Gray (1932)
Art Deco was associated with both luxury and modernity; it combined very expensive materials and exquisite craftsmanship put into modernistic forms. Nothing was cheap about Art Deco: pieces of furniture included ivory and silver inlays, and pieces of Art Deco jewellry combined diamonds with platinum, jade, and other precious materials. The style was used to decorate the first-class salons of ocean liners, deluxe trains, and skyscrapers. It was used around the world to decorate the great movie palaces of the late 1920s and 1930s. Later, after the Great Depression, the style changed and became more sober.
A good example of the luxury style of Art Deco is the boudoir of the fashion designer Jeanne Lanvin, designed by Armand-Albert Rateau (1882-1938) made between 1922-25. It was located in her house at 16 rue Barbet de Jouy, in Paris, which was demolished in 1965. The room was reconstructed in the Museum of Decorative Arts in Paris. The walls are covered with molded lambris below sculpted bas-reliefs in stucco. The alcove is framed with columns of marble on with bases and a plinth of sculpted wood. The floor is of white and black marble, and in the cabinets decorative objects are displayed against a background of blue silk. Her bathroom had a tub and washstand made of sienna marble, with a wall of carved stucco and bronze fittings.[56]
By 1928 the style had become more comfortable, with deep leather club chairs. The study designed by the Paris firm of Alavoine for an American businessman in 1928-30, now in the Brooklyn Museum, had a unique American feature. Since it was constructed during Prohibition, when serving alcohol was prohibited, it included a secret bar hidden behind the panels.[57]
By the 1930s, the style had been somewhat simplified, but it was still extravagant. In 1932 the decorator Paul Ruoud made the Glass Salon for Suzanne Talbot. It featured a serpentine armchair and two tubular armchairs by Eileen Gray, a floor of mat silvered glass slabs, a panel of abstract patterns in silver and black lacquer, and an assortment of animal skins.[58]
The International Exhibition of Modern Decorative and Industrial Arts (1925)
-

Postcard of the International Exhibition of Modern Decorative and Industrial Arts in Paris (1925)
-

Pavilion of the Galeries Lafayette Department Store at the 1925 Exposition
-
.jpg)
The Hotel du Riche Collectioneur, pavilion of the furniture manufacturer Emile-Jacques Ruhlmann
-
.jpg)
Salon of the Hôtel du Riche Collectionneur from the 1925 International Exposition of Decorative Arts, furnished by Emile-Jacques Ruhlmann, painting by Jean Dupas
The event that marked the zenith of the style and gave it its name was the International Exhibition of Modern Decorative and Industrial Arts which took place in Paris from April to October in 1925. This was officially sponsored by the French government, and covered a site in Paris of 55 acres, running from the Grand Palais on the right bank to Les Invalides on the left bank, and along the banks of the Seine. The Grand Palais, the largest hall in the city, was filled with exhibits of decorative arts from the participating countries. There were 15,000 exhibitors from twenty different countries, including England, Italy, Spain, Poland, Czechoslovakia, Belgium, Japan, and the new Soviet Union, though Germany was not invited because of tensions after the war and the United States, misunderstanding the purpose of the exhibit, declined to participate. It was visited by sixteen million people during its seven-month run. The rules of the exhibition required that all work be modern; no historical styles were allowed. The main purpose of the Exhibit was to promote the French manufacturers of luxury furniture, porcelain, glass, metal work, textiles and other decorative products. To further promote the products, all the major Paris department stores and major designers had their own pavilions. The Exposition had a secondary purpose in promoting products from French colonies in Africa and Asia, including ivory and exotic woods.
The Hôtel du Riche Collectionneur was a popular attraction at the Exposition; it displayed the new furniture designs of Emile-Jacques Ruhlmann, as well as Art Deco fabrics, carpets, and a painting by Jean Dupas. The interior design followed the same principles of symmetry and geometric forms which set it apart from Art Nouveau, and bright colors, fine craftsmanship rare and expensive materials which set it apart from the strict functionality of the Modernist style. While most of the pavilions were lavishly decorated and filled with hand-made luxury furniture, two pavilions, those of the Soviet Union and Pavilion du Nouveau Esprit, built by the magazine of that name run by Le Corbusier, were built in an austere style with plain white walls and no decoration; they were among the earliest examples of modernist architecture.[59]
The New York skyscrapers
-

The American Radiator Building in New York City by Raymond Hood (1924)
-
.jpg)
Chrysler Building in New York City, by William Van Alen (1928–30)
-

Lower Manhattan in 1931
-

Crown of the General Electric Building (also known as 570 Lexington Avenue) by Cross & Cross (1933)
-
30 Rockefeller Center, now the Comcast Building, by Raymond Hood (1933)
The skyscrapers of Manhattan marked the summit of the Art Deco style; they became the tallest and most recognizable modern buildings in the world. They were designed to show the prestige of their builders through their height, their shape, their color, and their dramatic illumination at night.[60] The first New York skyscraper, the Woolworth Building, in a neoclassical style, was completed in 1913, and the American Telephone and Telegraph Building (1924) had ionic and doric columns and a classical Doric hypostyle with a frieze. The American Radiator Building by Raymond Hood (1924) combined Gothic and Deco modern elements in the design of the building. Black brick on the frontage of the building (symbolizing coal) was selected to give an idea of solidity and to give the building a solid mass. Other parts of the facade were covered in gold bricks (symbolizing fire), and the entry was decorated with marble and black mirrors.
The New York skyline was radically changed by the Chrysler Building in Manhattan (1927–30), designed by William Van Allen which became the icon of Art Deco. It was a giant seventy-seven floor tall advertisement for Chrysler automobiles. The top was crowned by a stainless steel spire, and was ornamented by deco "gargoyles" in the form stainless steel radiator cap decorations. The base of the tower, thirty-three stories above the street, was decorated with colorful art deco friezes, and the lobby was decorated with art deco symbols and images expressing modernity.[61]
The Chrysler Building was followed by Empire State Building by William F. Lamb (1931) and the RCA Building (now the Comcast Building) in Rockefeller Center, by Raymond Hood (1933) which together completely changed the skyline of New York. The tops of the buildings were decorated with Art Deco crowns and spires covered with stainless steel, and, in the case of the Chrysler building, with Art Deco gargoyles modeled after radiator ornaments, while the entrances and lobbies were lavishly decorated with Art Deco sculpture, ceramics, and design. Similar buildings, though not quite as tall, soon appeared in Chicago and other large American cities.The Chrysler Building was soon surpassed in height by the Empire State Building, in a slightly less lavish Deco style. Rockefeller Center added a new design element; several tall building grouped around an open plaza, with a fountain in the center.[62]
Late Art Deco
-

Lincoln Theater in Miami Beach , Florida by Thomas W. Lamb (1936)
-

The Palais de Chaillot by Louis-Hippolyte Boileau, Jacques Carlu and Léon Azéma from the 1937 Paris International Exposition
-
_(11872278295).jpg)
Stairway of the Economic and Social Council in Paris, originally the Museum of Public Works, built for the 1937 Paris International Exposition by Auguste Perret (1937)
-

High School in King City, California, built by Robert Stanton for the Works Progress Administration (1939)
In 1925 two different competing schools coexisted within Art Deco: the traditionalists, who had founded the Society of Decorative Artists; included the furniture designer Emile-Jacques Ruhlmann, Jean Dunard, the sculptor Antoine Bourdelle, and designer Paul Poiret; they combined modern forms with traditional craftsmanship and expensive materials. On the other side were the modernists, who increasingly rejected the past and wanted a style based upon advances in new technologies, simplicity, a lack of decoration, inexpensive materials, and mass production. The modernists founded their own organization, The French Union of Modern Artists, in 1929. Its members included architects Pierre Chareau, Francis Jourdain, Robert Mallet-Stevens, Corbusier, and, in the Soviet Union, Konstantin Melnikov; the Irish designer Eileen Gray, and French designer Sonia Delaunay, the jewelers Jean Fouquet and Jean Puiforcat. They fiercely attacked the traditional art deco style, which they said was created only for the wealthy, and insisted that well-constructed buildings should be available to everyone, and that form should follow function. The beauty of an object or building resided in whether it was perfectly fit to fulfill its function. Modern industrial methods meant that furniture and buildings could be mass-produced, not made by hand.[63][64]
The Art Deco interior designer Paul Follot defended Art Deco in this way: "We know that man is never content with the indispensable and that the superfluous is always needed...If not, we would have to get rid of music, flowers, and perfumes..!"[65] However, Le Corbusier was a brilliant publicist for modernist architecture; he stated that a house was simply "a machine to live in", and tirelessly promoted the idea that Art Deco was the past and modernism was the future. Le Corbusier's ideas were gradually adopted by architecture schools, and the aesthetics of Art Deco were abandoned. The same features that made Art Deco popular in the beginning, its craftsmanship, rich materials and ornament, led to its decline. The Great Depression that began in the United States in 1929, and reached Europe shortly afterwards, greatly reduced the number of wealthy clients who could pay for the furnishings and art objects. In the Depression economic climate, few companies were ready to build new skyscrapers.[25] Even the Ruhlmann firm was forced to produce pieces of furniture in series, rather than individual hand-made items. The last buildings built in Paris in the new style were the Museum of Public Works by Auguste Perret (now the French, Economic and Environmental Council]] and the Palais de Chaillot by Louis-Hippolyte Boileau, Jacques Carlu and Léon Azéma, and the Palais de Tokyo of the 1937 Paris International Exposition; they looked out at the grandiose pavilion of Nazi Germany, designed by Albert Speer, which faced the equally grandiose socialist-realist pavilion of Stalin's Soviet Union.
After World War II the dominant architectural style became the International Style pioneered by Le Corbusier, and Mies Van der Rohe. A handful of Art Deco hotels were built in Miami Beach after World War II, but elsewhere the style largely vanished, except in industrial design, where it continued to be used in automobile styling and products such as juke boxes. In the 1960s, it experienced a modest academic revival, thanks in part to the writings of architectural historians such as Bevis Hillier. In the 1970s efforts were made in the United States and Europe to preserve the best examples of Art Deco architecture, and many buildings were restored and repurposed. Postmodern architecture, which first appeared in the 1980s, like Art Deco, often includes purely decorative features.[25][47][66][67] Deco continues to inspire designers, and is often used in contemporary fashion, jewelry, and toiletries.[68]
Painting
-
_(11037440654).jpg)
Mural by Jean Dupas, La Vigne et le Vin, from the Bordeaux Pavilion of the Exposition internationale des arts décoratifs et industriels moderns in Paris (1925)
-

Tamara de Lempicka, 1929, La Musicienne, oil on canvas, 161 x 96 cm
-
Detail of American Progress ceiling mural in lobby of Rockefeller Center by the Catalan painter Josep Maria Sert (circa 1935)
-

Reginald Marsh, 1936, Workers sorting the mail, a mural in the U.S. Customs House in New York
-

Rockwell Kent, 1938, Art in the Tropics, mural in the William Jefferson Clinton Federal Building
There was no section set aside for painting at the 1925 Exposition. Art deco painting was by definition decorative, designed to decorate a room or work of architecture, so few painters worked exclusively in the style, but two painters are closely associated with Art Deco. Jean Dupas painted Art Deco murals for the Bordeaux Pavilion at the 1925 Decorative Arts Exposition in Paris, and also painted the picture over the fireplace in the Maison de la Collectioneur exhibit at the 1925 Exposition, which featured furniture by Ruhlmann and other prominent Art Deco designers. His murals were also prominent in the decor of the French ocean liner SS Normandie. His work was purely decorative, designed as a background or accompaniment to other elements of the decor.[69] The other painter closely associated with the style is Tamara de Lempicka. Born in Poland in an aristocratic family, she emigrated to Paris after the Russian Revolution. There she became a student of the artist Maurice Denis of the movement called Les Nabis and the Cubist André Lhote and borrowed many elements from their styles. She painted almost exclusively portraits in a realistic, dynamic and colorful Art Deco style.[70]
In the 1930s a dramatic new form of Art Deco painting appeared in the United States. During the Great Depression, the Federal Art Project of the Works Progress Administration was created to give work to unemployed artists. Many were given the task of decorating government buildings, hospitals and schools. There was no specific art deco style used in the murals; artists engaged to paint murals in government buildings came from many different schools, from American regionalism to social realism; they included Reginald Marsh, Rockwell Kent and the Mexican painter Diego Rivera. The murals were Art Deco because they were all decorative and related to the activities in the building or city where they were painted: Reginald Marsh and Rockwell Kent both decorated U.S. postal buildings, and showed postal employees at work while Diego Rivera depicted automobile factory workers for the Detroit Institute of Arts. Diego Rivera's mural "American Progress" for Rockefeller Center featured an unauthorized portrait of Lenin. When Rivera refused to remove Lenin, the painting was destroyed and a new mural was painted by the Catalan artist Josep Maria Sert.
Sculpture
-

Christ the Redeemer by Paul Landowski, (1931), Soapstone, Corcovado Mountain, Rio de Janeiro
-
.jpg)
Dancer and gazelles by Paul Manship, (1916), bronze, Metropolitan Museum of Art
-
_limestone%2C_60_cm%2C_Kr%C3%B6ller-M%C3%BCller_Museum%2C_Otterlo%2C_Holland.tiff.jpg)
Joseph Csaky, Tête (front and side view), limestone, Kröller-Müller Museum, Otterlo (c.1920)
-

Salon sculpture by Josef Lorenzl (1920)
-

"Speed" by the American sculptor Harriet Whitney Frishmuth (1922)
-

François Pompon, Ours blanc (Polar Bear), Musée d'Orsay (1922)
-

Demetre Chiparus, Tanara, bronze, ivory and onyx (c.1925)
-

Ralph Stackpole's sculpture group over the door of the San Francisco Stock Exchange (1930)
-
_Daily_Express_Building_by_Ronald_Atkinson.jpg)
Relief sculpture in the lobby of the former Daily Express Building in London (1932)
-

Portal decoration "Wisdom" by Lee Lawrie, Rockefeller Center, New York (1933)
-
Prometheus by Paul Manship, Rockefeller Center, New York (1937)
-
Lee Lawrie, 1936–37, Statue of Atlas, in front of the Rockefeller Center in New York (installed 1937)
-
Air, by Aristide Maillol, in the Tuileries Gardens, Paris (1938)
Most of the sculpture of the Art Deco period was, as the name suggests, purely decorative; it was designed not for museums, but to ornament office buildings, government buildings, public squares, and private salons. It was almost always representational, usually of heroic or allegorical figures related to the purpose of the building; the themes were usually chosen by the patron, and abstract sculpture for decoration was extremely rare. It was frequently attached to facade of buildings, particularly over the entrance.
Allegorical sculptures of the dance and music by Antoine Bourdelle were the essential decorative feature of the earliest Art Deco landmark in Paris, the Théâtre des Champs-Elysées in Paris, in 1912. The sculptor Aristide Maillol reinvented the classical ideal for his statue of the River (1939), now at the Museum of Modern Art in New York. In the 1930s, a whole team of sculptors made sculpture for the 1937 Exposition Internationale des Arts et Techniques dans la Vie Moderne at Chaillot. The buildings of the Exposition were covered with low-relief sculpture, statues. Alfred Janniot made the relief sculptures now visible on the facade of the Palais de Tokyo (the Paris City Museum of Modern Art, and the esplanade in front of the Palais de Chaillot, facing the Eiffel Tower, was crowded with new statuary by Charles Malfray, Henry Arnold (sculptor), and many others.[71]
In the United States, many European sculptors trained at the Ecole des Beaux Arts in Paris, came to work; they included Gutzon Borglum, sculptor of the Lincoln Memorial in Washington, D.C. Other American sculpts, including Harriet Whitney Frishmuth, had studied with Auguste Rodin in Paris. The 1929 stock market crash largely destroyed the market for monumental sculpture, but one grand project remained; the new Rockefeller Center. The American sculptors Lee Lawrie and Paul Manship designed heroic allegorical figures for facade and plaza. In San Francisco, Ralph Stackpole provided sculpture for the facade of the new San Francisco Stock Exchange building.
One of the best known and certainly the largest Art Deco sculpture is the Christ the Redeemer by the French sculptor Paul Landowski, completed between 1922 and 1931, located on a mountain top overlooking Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. François Pompon was a pioneer of modern stylized animalier sculpture. He was not fully recognized for his artistic accomplishments until the age of 67 at the Salon d'Automne of 1922 with the work "Ours blanc", also known as "the White Bear", now in the Musee d'Orsay in Paris.[72]
Many early Art Deco sculptures were small, designed to decorate salons. One genre of this sculpture was called the Chryselephantine statuette, named for a style of ancient Greek temple statues made of gold and ivory. One of the best-known Art Deco salon sculptors was the Romanian-born Demetre Chiparus, who produced colorful small sculptures of dancers. Other notable salon sculptors included Ferdinand Preiss, Josef Lorenzl, Alexander Kelety, Dorothea Charol and Gustav Schmidtcassel.[73]
Parallel with these more neoclassical sculptors, more avant-garde and abstract sculptors were at work in Paris and New York. The most prominent were Constantin Brâncuși, Joseph Csaky, Alexander Archipenko, Henri Laurens, Jacques Lipchitz, Gustave Miklos, Jean Lambert-Rucki, Jan et Joël Martel, Chana Orloff, and Pablo Gargallo.[74]
Graphic arts
-

Festival poster by Ludwig Hohlwein (1910)
-

Program for the Ballets Russes by Leon Bakst (1912)
-

Peter Behrens, Deutscher Werkbund exhibition poster (1914)
-

A Vanity Fair cover by Georges Lepape (1919)
-

Interpretation of Harlem Jazz I by Winold Reiss (c.1920)
-

Cover of Harper's Bazaar by Erté (1922)
-

London Underground poster by Horace Taylor (1924)
-

Moulin Rouge poster by Charles Gesmar (1925)
-

Poster for 1931 Paris Colonial Exposition
-

Poster for Chicago World's Fair (1933)
The Art Deco style appeared early in the graphic arts, in the years just before World War I. It appeared in Paris in the posters and the costume designs of Leon Bakst for the Ballets Russes, and in the catalogs of the fashion designers Paul Poiret.[75] The illustrations of Georges Barbier, and Georges Lepape and the images in the fashion magazine La Gazette du bon ton perfectly captured the elegance and sensuality of the style. In the 1920s, the look changed; the fashions stressed were more casual, sportive and daring, with the woman models usually smoking cigarettes. American fashion magazines such as Vogue, Vanity Fair and Harper's Bazaar quickly picked up the new style and popularized it in the United States. It also influenced the work of American book illustrators such as Rockwell Kent. In Germany, the most famous poster artist of the period was Ludwig Hohlwein, who created colorful and dramatic posters for music festivals, beers, and, late in his career, for the Nazi Party.[76]
During the Art Nouveau period, posters usually advertised theatrical products or cabarets. In the 1920s, travel posters, made for steamship lines and airlines, became extremely popular. The style changed notably in the 1920s, to focus attention on the product being advertised. The images became simpler, precise, more linear, more dynamic, and were often placed against a single color background. In France popular Art Deco designers included, Charles Loupot and Paul Colin, who became famous for his posters of American singer and dancer Josephine Baker. Jean Carlu designed posters for Charlie Chaplin movies, soaps, and theaters; in the late 1930s he emigrated to the United States, where, during the World War, he designed posters to encourage war production. The designer Charles Gesmar became famous making posters for the singer Mistinguett and for Air France. Among the best known French Art Deco poster designers was Cassandre, who made the celebrated poster of the ocean liner SS Normandie in 1935.[76]
In the 1930s a new genre of posters appeared in the United States during the Great Depression. The Federal Art Project hired American artists to create posters to promote tourism and cultural events.
Architecture
-
La Samaritaine department store, by Henri Sauvage, Paris, (1925–28)
-
_edit1.jpg)
Los Angeles City Hall by John Parkinson, John C. Austin, and Albert C. Martin, Sr.,(1928)
-
Interior of the Palacio de Bellas Artes (Palace of Fine Arts) in Mexico City (1934)
-

National Diet Building in Tokyo, Japan (1936)
-

Mayakovskaya Metro Station in Moscow (1936)
The architectural style of art deco made its debut in Paris in 1903-04, with the construction of two apartment buildings in Paris, one by Auguste Perret on rue Trétaigne and the other on rue Benjamin Franklin by Henri Sauvage. The two young architects used reinforced concrete for the first time in Paris residential buildings; the new buildings had clean lines, rectangular forms, and no decoration on the facades; they marked a clean break with the art nouveau style.[77] Between 1910 and 1913, Perret used his experience in concrete apartment buildings to construct the Théâtre des Champs-Élysées, 15 avenue Montaigne. Between 1925 and 1928 he constructed the new art deco facade of the La Samaritaine department store in Paris.[78]
After the First World War, art deco buildings of steel and reinforced concrete began to appear in large cities across Europe and the United States. In the United States the style was most commonly used for office buildings, government buildings, movie theaters, and railroad stations. It sometimes was combined with other styles; The Los Angeles City Hall combined Art Deco with a roof based on the ancient Greek Mausoleum at Halicarnassus, while the Los Angeles railroad station combined Deco with Spanish mission architecture. Art Deco elements also appeared in engineering projects, including the towers of the Golden Gate Bridge and the intake towers of Hoover Dam. In the 1920s and 1930s it became a truly international style, with examples including the Palacio de Bellas Artes (Palace of Fine Arts) in Mexico City by Federico Mariscal, the Mayakovskaya Metro Station in Moscow and the National Diet Building in Tokyo by Watanabe Fukuzo.
The Art Deco style was not limited to buildings on land; the ocean liner SS Normandie, whose first voyage was in 1935, featured Art Deco design, including a dining room whose ceiling and decoration were made of glass by Lalique.
"Cathedrals of Commerce"
-
The Fisher Building in Detroit by Joseph Nathaniel French (1928)
-
.jpg)
Lower lobby of the Guardian Building in Detroit by Wirt Rowland (1929)
-
Lobby of 450 Sutter Street in San Francisco by Timothy Pflueger (1929)
-

Lobby of the Chrysler Building by William Van Alen in New York City (1930)
-
Elevator of the Chrysler Building (1930)
-

The interior of the Palais de la Porte Dorée in Paris (Now the Museum of Immigration) by Albert Laprade, Léon Jaussely and Léon Bazin (1931)
The grand showcases of Art deco interior design were the lobbies of government buildings, theaters, and particularly office buildings. Interiors were extremely colorful and dynamic, combining sculpture, murals, and ornate geometric design in marble, glass, ceramics and stainless steel. An early example was the Fisher Building in Detroit, by Joseph Nathaniel French; the lobby was highly decorated with sculpture and ceramics. ]The Guardian Building (originally the Union Trust Building) in Detroit, by Wirt Rowland (1929), decorated with red and black marble and brightly colored ceramics, highlighted by highly polished steel elevator doors and counters. The sculptural decoration installed in the walls illustrated the virtues of industry and saving; the building was immediately terms the "Cathedral of Commerce". The Medical and Dental Building called 450 Sutter Street in San Francisco by Timothy Pflueger was inspired by Mayan architecture, in a highly stylized form; it used pyramid shapes, and the interior walls were covered highly stylized rows of hieroglyphs.[79]
In France, the best example of an Art Deco interior during period was the Palais de la Porte Dorée (1931) by Albert Laprade, Léon Jaussely and Léon Bazin. The building (now the National Museum of Immigration, with an aquarium in the basement) was built for the Paris Colonial Exposition of 1931, to celebrate the people and products of French colonies. The exterior facade was entirely covered with sculpture, and the lobby created an Art Deco harmony with a wood parquet floor in a geometric pattern, a mural depicting the people of French colonies; and a harmonious composition of vertical doors and horizontal balconies.[79]
Movie palaces
-

Grauman's Egyptian Theater in Hollywood (1922)
-

Grand Rex movie theater in Paris (1932)
-

Four-story high grand lobby of the Paramount Theater, Oakland (1932)
-

Auditorium and stage of Radio City Music Hall, New York City (1932)
-

Gaumont State Cinema in London (1937)
Many of the best surviving examples of Art Deco are movie theaters built in the 1920s and 1930s. The Art Deco period coincided with the conversion of silent films to sound, and movie companies built enormous theaters in major cities to capture the huge audience that came to see movies. Movie palaces in the 1920s often combined exotic themes with art deco style; Grauman's Egyptian Theater in Hollywood (1922) was inspired by Egyptian tombs and pyramids, while the Fox Theater in Bakersfield, California attached a tower in California Mission style to an Art Deco hall. The largest of all is Radio City Music Hall in New York City, which opened in 1932. Originally designed as a stage theater, it quickly transformed into a movie theater, which could seat 6,015 persons The interior design by Donald Deskey used glass, aluminum, chrome, and leather to create a colorful escape from reality The Paramount Theater in Oakland, California, by Timothy Pflueger, had a colorful ceramic facade a lobby four stories high, and separate Art Deco smoking rooms for gentlemen and ladies. Similar grand palaces appeared in Europe. The Grand Rex in Paris (1932), with its imposing tower, was the largest movie theater in Europe. The Gaumont State Cinema in London (1937) had a tower modeled after the Empire State building, covered with cream-colored ceramic tiles and an interior in an Art Deco-Italian Renaissance style. The Paramount Theater in Shanghai, China (1933) was originally built as a dance hall called The gate of 100 pleasures; it was converted to a movie theater after the Communist Revolution in 1949, and now is a ballroom and disco. In the 1930s Italian architects built a small movie palace, the Cinema Impero, in Asmara in what is now Eritrea. Today, many of the movie theaters have been subdivided into multiplexes, but others have been restored and are used as cultural centers in their communities.[80]
Streamline Moderne (1930-39)
-

Paris Building in the Pacquebot or ocean liner style, 3 boulevard Victor (1935)
-

Pan-Pacific Auditorium in Los Angeles (1936)
-

The San Francisco Maritime Museum , originally was a public bath house (1936)
-

The Marine Air Terminal at La Guardia Airport (1937) was the New York terminal for the flights of Pan Am Clipper flying boats to Europe
-

The Hoover Building canteen in Perivale in the London suburbs, by Wallis, Gilber and Partners (1938)
-

The Ford Pavilion at the 1939 New York World's Fair
In the late 1930s, a new variety of Art Deco architecture became common; it was called Streamline Moderne or simply Streamline, or, in France, the Style Paqueboat, or Ocean Liner style. Buildings in the style were had rounded corners, long horizontal lines; they were built of reinforced concrete, and were almost always white; and sometimes had nautical features, such as railings that resembled those on a ship. . The rounded corner was not entirely new; it had appeared in Berlin in 1923 in the Mossehaus by Erich Mendelsohn, and later in the Hoover Building, an industrial complex in the London suburb of Perivale. In the United States, it became most closely associated with transport; Streamline moderne was rare in office buildings, but was often used for bus stations and airport terminals, such as terminal at La Guardia airport in New York City that handled the first transatlantic flights, via the PanAm clipper flying boats; and in roadside architecture, such as gas stations and diners. In the late 1930s a series of diners, modeled after streamlined railroad cars, were produced and installed in towns in New England; at least two examples still remain and are now registered historic buildings.[81]
Decoration and motifs
-
Iron fireplace screen, Rose Iron Works, Cleveland (1930)
-
.jpg)
Elevator doors of the Chrysler Building, by William Van Alen (1927–30)
-

Sunrise motif from the Wisconsin Gas Building (1930)
-

Detail of mosaic facade of Paramount Theater (Oakland, California) (1931)
-
Bas-relief on the facade of the Palais de la Porte Dorée in Paris, showing the people of French colonies (1931)
Decoration in the Art Deco period went through several distinct phases. Between 1910 and 1920, as Art Nouveau was exhausted, design styles saw a return to tradition, particularly in the work of Paul Iribe. In 1912 André Vera published an essay in the magazine L'Art Décoratif calling for a return to the craftsmanship and materials of earlier centuries, and using a new repertoire of forms taken from nature, particularly baskets and garlands of fruit and flowers. A second tendency of Art Deco, also from 1910 to 1920, was inspired by the bright colors of the artistic movement known as the Fauves and by the colorful costumes and sets of the Ballets Russes. This style was often expressed with exotic materials such as sharkskin, mother of pearl, ivory, tinted leather, lacquered and painted wood, and decorative inlays on furniture that emphasized its geometry. This period of the style reached its high point in the 1925 Paris Exposition of Decorative Arts. In the late 1920s and the 1930s, the decorative style changed, inspired by new materials and technologies. It became sleeker and less ornamental. Furniture, like architecture, began to have rounded edges and to take on a polished, streamlined look, taken from the streamline moderne style. New materials, such as chrome-plated steel, aluminum and bakelite, an early form of plastic, began to appear in furniture and decoration.[82]
Throughout the Art Deco period, and particularly in the 1930s, the motifs of the decor expressed the function of the building. Theaters were decorated with sculpture which illustrated music, dance, and excitement; power companies showed sunrises, the Chrysler building showed stylized hood ornaments; The friezes of Palais de la Porte Dorée at the 1931 Paris Colonial Exposition showed the faces of the different nationalities of French colonies. The Streamline style made it appear that the building itself was in motion. The WPA murals of the 1930s featured ordinary people; factory workers, postal workers, families and farmers, in place of classical heroes.[83]
Furniture
-
Chair by Paul Follot (1912–14)
-
.jpg)
Armchair by Louis Süe (1912) and painted screen by André Mare (1920)
-
.jpg)
Dressing table and chair of marble and encrusted, lacquered, and glided wood by Paul Follot (1919-1920)
-
._Corner_Cabinet%2C_ca._1923..jpg)
Corner cabinet of Mahogany with rose basket design of inlaid ivory by Emile-Jacques Ruhlmann (1923)
-
_(2132077838).jpg)
Cabinet by Emile-Jacques Ruhlmann (1926)
-
_(5469658728).jpg)
Cabinet design by Emile-Jacques Ruhlmann
-
Cabinet covered with shagreen or sharkskin, by André Groult (1925)
-
Furniture by Gio Ponti (1927)
-

Desk of an administrator, by Michel Roux-Spitz for the 1930 Salon of Decorative Artists
-

An Art Deco club chair (1930s)
-
_(2132078468).jpg)
Late Art Deco furniture and rug by Jules Leleu (1930s)
French furniture from 1910 until the early 1920s was largely an updating of French traditional furniture styles, and the art nouveau designs of Louis Majorelle, Charles Plumet and other manufacturers. French furniture manufacturers felt threatened by the growing popularity of German manufacturers and styles, particularly the Biedermeier style, which was simple and clean-lined. The French designer Frantz Jourdain, the President of the Paris Salon d'Automne, invited designers from Munich to participate in the 1910 Salon. French French designers saw the new German style, and decided to meet the German challenge. The French designers decided to present new French styles in the Salon of 1912. The rules of the Salon indicated that only modern styles would be permitted. All of the major French furniture designers took part in Salon: Paul Follot, Paul Iribe, Maurice Dufrene, André Groult, André Mare and Louis Süe took part, presenting new works that updated the traditional French styles of Louis XVI and Louis Philippe with more angular corners inspired by Cubism and brighter colors inspired by Fauvism and the Nabis.[84]
The painter André Mare and furniture designer Louis Suë both participated the 1912 Salon. After the War the two men joined together to form their own company, formally called the Compagnie des Arts Française, but usually known simply as Suë and Mare. Unlike the prominent art nouveau designers like Louis Majorelle, who personally designed every piece, they assembled a team of skilled craftsmen and produced complete interior designs, including furniture, glassware, carpets, ceramics, wallpaper and lighting. Their work featured bright colors and furniture and fine woods, such ebony encrusted with mother of pearl, abalone and silvered metal to create bouquets of flowers. They designed everything from the interiors of ocean liners to perfume bottles for the label of Jean Patou.The firm prospered in the early 1920s, but the two men were better craftsmen than businessmen. The firm was sold in 1928, and both men left.[85]
The most prominent furniture designer at the 1925 Decorative Arts Exposition was Émile-Jacques Ruhlmann, from Alsace. He first exhibited his works at the 1913 Autumn Salon, then had his own pavilion, the "House of the Rich Collector", at the 1925 Exposition. He used only most rare and expensive materials, including ebony, mahogany, rosewood, ambon and other exotic woods, decorated with inlays of ivory, tortoise shell, mother of pearl, Little pompoms of silk decorated the handles of drawers of the cabinets.[86] His furniture was based upon 18th century models, but simplified and reshaped. In all of his work, the interior structure of the furniture was completely concealed. The framework usually of oak, was completely covered with an overlay of thin strips of wood, then covered by a second layer of strips of rare and expensive woods. This was then covered with a veneer and polished, so that the piece looked as if it had been cut out of a single block of wood. Contrast to the dark wood was provided by inlays of ivory, and ivory key plates and handles. According to Ruhlmann, armchairs had to be designed differently according to the functions of the rooms where they appeared; living room armchairs were designed to be welcoming, office chairs comfortable, and salon chairs voluptuous. Only a small number of pieces of each design of furniture was made, and the average price of one of his beds or cabinets was greater than the price of an average house.[87]
Jules Leleu was a traditional furniture designer who moved smoothly into Art Deco in the 1920s; he designed the furniture for the dining room of the Elysee Palace, and for the first-class cabins of the steamship Normandie. his style was characterized by the use of ebony, Macassar wood, walnut, with decoration of plaques of ivory and mother of pearl. He introduced the style of lacquered art deco furniture at the end of in the late 1920s, and in the late 1930s introduced furniture made of metal with panels of smoked glass.[88] In Italy, the designer Gio Ponti was famous for his streamlined designs. In the United States,
The costly and exotic furniture Ruhlmann and other traditionalists infuriated modernists, including the architect Le Corbusier, causing him to write a famous series of articles denouncing the arts décoratif style. He attacked furniture made only for the rich, and called upon designers to create furniture made with inexpensive materials and modern style, which ordinary people could afford. He designed his own chairs, created to be inexpensive and mass-produced.[89]
In the 1930s, furniture designs adapted to the Streamline Moderne form, with smoother surfaces and curved forms. The masters of the late style included Donald Deskey was one of the most influential designers; he created the interior of the Radio City Music Hall. He used a mixture of traditional and very modern materials, including aluminum, chrome, and bakelite, an early form of plastic.[90]
Streamline Moderne design
-

Philips Art Deco radio set (1931)
-

Chrysler Airflow sedan, designed by Carl Breer (1934)
-

Grand dining room of the ocean liner SS Normandie (1935)
-
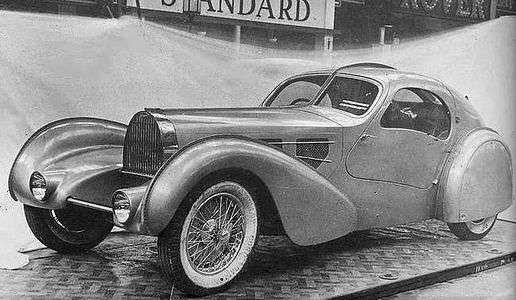
Bugatti Aérolithe (1936)
-

Electrolux Vacuum cleaner (1937)
-

Streamlined railroad locomotive (1939)
Streamline Moderne (or Streamline) was a variety of Art Deco which emerged during the mid-1930s. It was influenced by modern aerodynamic principles developed for aviation and ballistics to reduce air friction at high velocities. The bullet shapes were applied by designers to cars, trains, ships, and even objects not intended to move, such as refrigerators, gas pumps, and buildings.[49] One of the first production vehicles in this style was the Chrysler Airflow of 1933. It was unsuccessful commercially, but the beauty and functionality of its design set a precedent; Streamline Moderne meant modernity. It continued to be used in car design well after World War II.[91][92][93][94]
New industrial materials began to influence design of cars and household objects. These included aluminum, chrome, and bakelite, an early form of plastic. Bakelite could be easily molded into different forms, and soon was used in telephones, radios and other appliances.
Ocean liners also adopted a style of Art Deco, known in French as the Style Paquebot, or "Ocean Liner Style". The most famous example was the SS Normandie, which made its first transatlantic trip in 1935. It was designed particularly to bring wealthy Americans to Paris to shop. The cabins and salons featured the latest Art Deco furnishings and decoration. The Grand Salon of the ship, which was the restaurant for first-class passengers, was bigger than the Hall of Mirrors of the Palace of Versailles. It was illuminated by electric lights within twelve pillars of Lalique crystal; thirty-six matching pillars lined the walls. This was one of the earliest examples of illumination being directly integrated into architecture. The style of ships was soon adapted to buildings. A notable example is found on the San Francisco waterfront, where the Maritime Museum building, built as a public bath in 1937, resembles a ferryboat, with ship railings and rounded corners. The Star Ferry Terminal in Hong Kong also used a variation of the style.[25]
Jewellery
-
_Museum_of_Decorative_Arts.jpg)
Art Deco bracelet of gold, coral and jade (1925) (Musée des Arts Décoratifs, Paris)
-

René Lalique (1925–30), molded glass pendants on silk cords
-
.jpg)
Boucheron (1925), a gold buckle set with diamonds and carved onyx, lapis lazuli, jade, and coral
-

Cartier, (1930), Mackay Emerald Necklace, emerald, diamond and platinum, Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History, USA
In the 1920s and 1930s, designers including René Lalique and Cartier tried reduce the traditional dominance of diamonds by introducing more colorful gemstones, such as small emeralds, rubies and sapphires. They also placed greater emphasis on very elaborate and elegant settings, featuring less-expensive materials such as enamel, glass, horn and ivory. Diamonds themselves were cut in less traditional forms; the 1925 Exposition saw a large number of diamonds cut in the form of tiny rods or matchsticks. The settings for diamonds also changed; More and more often jewellers used platinum instead of gold, since it was strong and flexible, and could set clusters of stones. Jewellers also began to use more dark materials, such as enamels and black onyx, which provided a higher contrast with diamonds.[95]
Jewellry became much more colorful and varied in style. Cartier and the firm of Bucheron combined diamonds with colorful other gemstones cut into the form of leaves, fruit or flowers. to make brooches, rings, earrings, clips and pendants Far eastern themes also became popular; plaques of jade and coral were combined with platinum and diamonds, and vanity cases, cigarette cases and powder boxes were decorated with Japanese and Chinse landscapes made with mother of pearl, enamel and lacquer.[95]
Rapidly changing fashions in clothing brought new styles of jewelry. Sleeveless dresses of the 1920s meant that arms needed decoration, and designers quickly created bracelets of gold, silver and platinum encrusted with lapis-lazuii, onyx, coral, and other colorful stones; Oher bracelets were intended for the upper arms, and several bracelets were often worn at the same time. The short haircuts of women in the twenties called for elaborate deco earring designs. As women began to smoke in public, designers created very ornate cigarette cases and ivory cigarette holders. The invention of the wrist-watch before World War I inspired jewelers to create extraordinary decorated watches, encrusted with diamonds and plated with enamel, gold and silver. Pendant watches, hanging from a ribbon, also became fashionable.[96]
The established jewelry houses of Paris in the period, Cartier, Chaumet, Georges Fouquet, Mauboussin, and Van Cleef & Arpels all created jewellry and objects in the new fashion. The firm of Chaumet made highly geometric cigarette boxes, cigarette lighters, pillboxes and notebooks, made of hard stones decorated with jade, lapis lazuli, diamonds and sapphires. They were joined by many young new designers, each with his own idea of deco. Raymond Templier designed pieces with highly intricate geometric patterns, including silver earrings that looked like skyscrapers. Gerard Sandoz was only 18 when he started to design jewelry in 1921; he designed many celebrated pieces based on the smooth and polished look of modern machinery. The glass designer René Lalique also entered the field, creating pendants of fruit, flowers, frogs, fairies of mermaids made of sculpted glass in bright colors, hanging on cords of silk with tassels.[96] The jeweller Paul Brandt contrasted rectangular and triangular patterns, and embedded pearls in lines on onyx plaques. Jean Despres made necklaces of contrasting colors by bringing together silver and black lacquer, or gold with lapis lazuli. Many of his designs looked like highly polished pieces of machines. Jean Dunand was also inspired by modern machinery, combined with bright reds and blacks contrasting with polished metal.[96] .
Glass art
-
The Firebird by René Lalique (1922)
-
Parrot vase by René Lalique (1922)
-

A Daum vase with sculpted grapes (1925)
-

Window for a steel mill office by Louis Majorelle (1928)
-
_(4782889920).jpg)
Daum vase (1930–35)
Like the Art Nouveau period before it, Art Deco was an exceptional period for fine glass and other decorative objects, designed to fit their architectural surroundings. The most famous producer of glass objects was René Lalique, whose works, from vases to hood ornaments for automobiles, became symbols of the period. He had made ventures into glass before World War I, designing bottles for the perfumes of François Coty, but he did not begin serious production of art glass until after World War I. In 1918, at the age of 58, he bought a large glass works in Combs-la-Ville and began to manufacture both artistic and practical glass objects. He treated glass as a form of sculpture, and created statuettes, vases, bowls, lamps and ornaments. He used demi-crystal rather than lead crystal, which was softer and easier to form, though not as lustrous. He sometimes used colored glass, but more often used opalescent glass, where part or the whole of the outer surface was stained with a wash. Lalique provided the decorative glass panels, lights and illuminated glass ceilings for the ocean liners SS Ile de France in 1927 and the SS Normandie in 1935, and for some of the first-class sleeping cars of the French railroads. At the 1925 Exposition of Decorative Arts, he had his own pavilion, designed a dining room with a table settling and matching glass ceiling for the Sèvres Pavilion, and designed a glass fountain for the courtyard of the Cours des Métier, a slender glass column which spouted water from the sides and was illuminated at night.[97]
Other notable Art Deco glass manufacturers included Marius-Ernest Sabino, who specialized in figurines, vases, bowls, and glass sculptures of fish, nudes, and animals. For these he often used an opalescent glass which could change from white to blue to amber, depending upon the light. His vases and bowls featured molded friezes of animals, nudes or busts of women with fruit or flowers. His work was less subtle but more colorful than that of Lalique.[97]
Other notable Deco glass designers included Edmond Etling, who also used bright opalescent colors, often with geometric patterns and sculpted nudes; Albert Simonet, and Aristide Colotte and Maurice Marinot, who was known for his deeply etched sculptural bottles and vases. The firm of Daum from the city of Nancy, which had been famous for its Art Nouveau glass, produced a line of Deco vases and glass sculpture, solid, geometric and chunky in form. More delicate multicolored works were made by Gabriel Argy-Rousseau, who produced delicately colored vases with sculpted butterflies and nymphs, and Francois Decorchemont, whose vases were streaked and marbled.[97]
The Great Depression ruined a large part of the decorative glass industry, which depended upon wealthy clients. Some artists turned to designing stained glass windows for churches. In 1937 the Steuben glass company began the practice of commissioning famous artists to produce glassware.[97] Louis Majorelle, famous for his Art Nouveau furniture, designed a remarkable Art Deco stained glass window portraying steel workers for the offices of a steel mill in Longwy, France.
Metal art
-

A grill with two wings called "The Pheasants", made by Paul Kiss and displayed at the 1925 Exposition of Decorative and Industrial Arts
-

Iron and copper grill called "Oasis" by Edgar Brandt, displayed at the 1925 Paris Exposition
-

Metal grilles in the lobby of the Palais de la Porte Dorée in Paris by Raymond Subes (1931)
-

Cocktail set of chrome-plated steel by Norman Bel Geddes (1937)
Art Deco artists produced a wide variety of practical objects in the Art Deco style, made of industrial materials from traditional wrought iron to chrome-plated steel. The American artist Norman Bel Geddes designed a cocktail set resembling a skyscraper made of chrome-plated steel. Raymond Subes designed an elegant metal grille for the entrance of the Palais de la Porte Dorée, the centerpiece of the 1931 Paris Colonial Exposition. The French sculptor Jean Dunand produced magnificent doors on the theme "The Hunt", covered with gold leaf and paint on plaster (1935).[98]
Art Deco architecture around the World
Art Deco architecture began in Europe, but by 1939 there were examples in large cities on every continent and in almost every country. This is a selection of prominent buildings on each continent. (For a comprehensive of existing buildings by country, see List of Art Deco architecture)
Africa
-
Cinema Impero in Asmara, Eritrea (1937)
-
Fiat Tagliero Building in Asmara, Eritrea by Giuseppe Pettazzi (1938)[1]
-

St. Peter's Cathedral in Rabat, Morocco (1938)
Most Art Deco buildings in Africa were built during European colonial rule, and often designed by Italian and French architects.
Asia
-

New India Assurance Building in Mumbai, India (1936)
-

Broadway Mansions in Shanghai, China (1934)
-

Capitol Theater in Manila, Philippines by Juan Nakpil (1935)
-

National Diet Building in Tokyo, Japan (1936)
-
Kologdam Building building in Bandung, Indonesia (1920)
-
_(6847539946).jpg)
The Central Market in Phnom Penh, Cambodia (1937)
-
Ankara railway station in Ankara, Turkey (1937)
A large number of the Art Deco buildings in Asia were designed by European architects, but in the Philippines local architect Juan Nakpil was preeminent. Many art deco landmarks in Asia were demolished during the great economic expansion of Asia the late 20th century, but some notable enclaves of the architecture still remain, particularly in Shanghai and Mumbai.
Central America and the Caribbean
-

The Bacardi Building in Havana, Cuba (1930)
-

The Hotel Nacional de Cuba in Havana, Cuba (1930)
-
.jpg)
Havana art deco building
-

The Plaza del Mercado de Ponce in Ponce, Puerto Rico (1941)
Art Deco buildings can be found throughout Central America. A particularly rich collection is found in Cuba, built largely for the large number of tourists who came to the island from the United States.
South America
-

The Palacio Salvo in Montevideo, Uruguay (1928)
-

Kavanagh building in Buenos Aires, Argentina (1934)
The Kavanagh building in Buenos Aires (1934), by Sánchez, Lagos and de la Torre, was the tallest reinforced concrete structure when it was completed, and a notable example of late Art Deco style.
Art deco buildings are also prominent in Montevideo, Uruguay, including the Palacio Salvo, which was South America's tallest building when it was built in 1928.
Europe
-

Théâtre des Champs-Élysées in Paris, France (1910–13)
-

The Mossehaus with Art Deco elements by Erich Mendelsohn in Berlin, Germany (c.1923)
-
.jpg)
Basilica of the Sacred Heart in Brussels, Belgium (1925)
-
.jpg)
Vytautas the Great War Museum in Kaunas, Lithuania (1936)
-
Mayakovskaya Station in Moscow, Russia (1938)
-

The Cine Rialto in Valencia, Spain
-
Rivoli Theater in Porto, Portugal (1937)
-

Daily Express Building in Manchester, UK (1939)
The architectural style first appeared in Paris with the Théâtre des Champs-Élysées (1910–13) by Auguste Perret but then spread rapidly around Europe, until examples could be found in nearly every large city, from London to Moscow. In Germany two variations of Art Deco flourished in the 1920s and 30s: The Neue Sachlichkeit style and Expressionist architecture. Notable examples include Erich Mendelsohn's Mossehaus and Schaubühne theater in Berlin, Fritz Höger's Chilehaus in Hamburg and his Kirche am Hohenzollernplatz in Berlin, the Anzeiger Tower in Hannover and the Borsig Tower in Berlin.[99]
One of the largest Art Deco buildings in Western Europe is the Basilica of the Sacred Heart in Koekelberg, Brussels. In 1925, architect Albert van Huffel won the Grand Prize for Architecture with his scale model of the basilica at the Exposition Internationale des Arts Décoratifs et Industriels Modernes in Paris.[100]
Spain and Portugal have some striking examples of Art Deco buildings, particularly movie theaters, including the Rivoli Theater in Porto (1937) and the Cine Rialto in Valencia, Spain (1939).
During the 1930s, Art Deco had a noticeable effect on house design in the United Kingdom,[47] as well as the design of various public buildings.[66] Straight, white-rendered house frontages rising to flat roofs, sharply geometric door surrounds and tall windows, as well as convex-curved metal corner windows, were all characteristic of that period.[67][101][102]
The London Underground is famous for many examples of Art Deco architecture,[103] and there are a number of buildings in the style situated along the Golden Mile in Brentford. Also in West London is the Hoover Building, which was originally built for The Hoover Company and was converted into a superstore in the early 1990s.
Canada, Mexico, and the United States
-

The Price Building in Quebec City, Canada (1930)
-

Vancouver City Hall in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada (1935)
-
Interior of the Palacio de Bellas Artes in Mexico City, Mexico (1934)
-

The Verizon Building in New York City, US (1923–27)
-
Buffalo City Hall in Buffalo, US (1931)
-

Bullocks Wilshire in Los Angeles, US (1929)
-

Louisiana State Capitol in Baton Rouge, US (1930–32)
-

Jefferson County Courthouse in Kyle, US (1931)
In Canada Art Deco structures that survive are mainly in the major cities; Montreal, Toronto, Hamilton, Ontario, and Vancouver. They range from public buildings like Vancouver City Hall to commercial buildings (College Park) to public works (R. C. Harris Water Treatment Plant).
In Mexico, the most imposing Art Deco example is interior of the Palacio de Bellas Artes Palace of Fine Arts, finished in 1934 with its elaborate decor and murals. Examples of Art Deco residential architecture can be found in the Condesa neighborhood, many designed by Francisco J. Serrano.
In the United States, Art Deco buildings are found from coast to coast, in all the major cities. It was most widely used for office buildings, train stations, airport terminals, and movie theaters; residential buildings are rare. In the 1930s, the more austere streamline style became popular. Many buildings were demolished between 1945 and the late 1960s, but then efforts began to protect the best examples. The City of Miami Beach established the Miami Beach Architectural District to preserve the colorful collection of Art Deco buildings found there.
Australia and New Zealand
-

Manchester Unity Building in Melbourne (1932)
-

Central Hotel in Napier, New Zealand, a town rebuilt in Art Deco after a 1931 earthquake [1]
-

ANZAC War Memorial in Sydney (1934)
- ^ "Central Hotel". Register of Historic Places. Heritage New Zealand. Retrieved 12 July 2014.
Melbourne, Australia and Sydney, Australia have several notable Art Deco buildings, including the Manchester Unity Building and the former Russell Street Police Headquarters in Melbourne and the Grace Building (Sydney) and the AWA Tower and the ANZAC War Memorial in Sydney.
Several towns in New Zealand, including Napier and Hastings were rebuilt in Art Deco style after the 1931 Hawke's Bay earthquake, and many of the buildings have been protected and restored. Napier has been nominated for UNESCO World Heritage Site status, the first cultural site in New Zealand to be nominated.[104][105] Wellington has retained a sizeable number of Art Deco buildings.[106]
Preservation and Neo Art Deco
-
The Miami Beach Architectural District protects historic Art Deco buildings
-

The U-Drop Inn, a roadside gas station and diner on U.S. Highway 66 in Shamrock, Texas (1936), now an historic monument
-

Smith Center for the Performing Arts in Las Vegas, Nevada, a Neo-Art Deco building (2012))
In many cities, efforts have been made to protect the remaining Art Deco buildings. In many U.S. cities, historic art deco movie theaters have been preserved and turned into cultural centers. Even more modest art deco buildings have been preserved as part of America's architectural heritage; an art deco cafe and gas station along Route 66 in Shamrock, Texas is an historic monument. The Miami Beach Architectural District protects several hundred old buildings, and requires that new buildings comply with the style. In Havana, Cuba, a large number of Art Deco buildings have badly deteriorated. Efforts are underway to bring the buildings back to their original color and appearance.
In the 21st century, modern variants of Art Deco, called Neo Art Deco, have appeared in some American cities, inspired by the classic Art Deco buildings of the 1920s and 1930s. Examples include the Smith Center for the Performing Arts in Las Vegas, Nevada, which includes art deco features from Hoover Dam, fifty miles away, and from the Will Rogers Memorial Center in Fort Worth, Texas, an art deco landmark built in 1936.
Gallery
%2C_bas-relief%2C_Th%C3%A9%C3%A2tre_des_Champs_Elys%C3%A9es_DSC09313.jpg)
-

1941 Packard Custom Super Eight One-Eighty Formal sedan
-

Pennsylvania RR's S-1 locomotive, designed by Raymond Loewy, at the 1939 New York World's Fair
-

Guardians of Traffic pylon on Hope Memorial Bridge in Cleveland, US (1932)
-

Municipal Auditorium of Kansas City, Missouri: Hoit Price & Barnes, and Gentry, Voskamp & Neville, 1935
-

U.S. Works Progress Administration poster, John Wagner, artist, ca. 1940
-

"Beau Brownie" camera, Walter Dorwin Teague 1930 design for Eastman Kodak
-

1937 Cord automobile model 812, designed in 1935 by Gordon M. Buehrig and staff
-

Palacio de Bellas Artes, Mexico City, Federico Mariscal, completed 1934
-

Women's Smoking Room at the Paramount Theatre, Oakland. Timothy L. Pflueger, architect, 1931
-

U.S. postage stamp commemorating the 1939 New York World's Fair, 1939
-

Henryk Kuna, "Rytm" (Rhythm), in Skaryszewski Park, Warsaw, Poland, 1925
-
.jpg)
Disused Snowdon Theatre, Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Opened 1937, closed 1984. Daniel J. Crighton, architect
-

Union Terminal in Cincinnati, Ohio; Paul Philippe Cret, Alfred T. Fellheimer, Steward Wagner, Roland Wank, 1933
-

Lobby, Empire State Building, New York City. William F. Lamb, opened 1931
-

Federal Art Project poster promoting milk drinking in Cleveland, Ohio, 1940
-

Interior drawing, Eaton's College Street department store, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
-
.jpg)
Niagara Mohawk Building, Syracuse, New York. Melvin L. King and Bley & Lyman, architects, completed 1932
See also
- Art Deco jewelry (1915–1935)
- Roaring Twenties
- 1920s in Western fashion
- 1933 Chicago World's Fair Century of Progress
- 1936 Fair Park built for Texas Centennial Exposition
- Art Deco stamps
- Paris architecture of the Belle Époque
- Paris between the Wars (1919-1939)
- Socialist realism, the Soviet version of Art Deco architecture.
References
- ↑ Texier 2012, p. 128.
- 1 2 Hillier 1968, p. 12.
- 1 2 Benton et al. 2003, p. 16.
- ↑ Renaut, Christophe and Lazé, Christophe, Les Styles de l'architecture et du mobilier, (2006), Editions Jean-Paul Gisserot, pages=110-116
- ↑ Benton, Benton and Wood & Art Déco (1910-1939)" 2010, pp. 13-28.
- ↑ "M. Cunny présente une Note sur un procédé vitro-héliographique applicable aux arts décoratifs", Bulletin de la Société française de photographie, Société française de photographie. Éditeur: Société française de photographie (Paris), 1858, Bibliothèque nationale de France, département Sciences et techniques, 8-V-1012, Bibliothèque nationale de France
- ↑ "Enfin, dans les ateliers, on travaille à l'achèvement des objets d'art décoratifs, qui sont très nombreux", Le Figaro, Éditeur: Figaro (Paris), 1869-09-18, no. 260, Bibliothèque nationale de France
- ↑ L'Art décoratif à Limoges, La Voix de la province : Revue littéraire, artistique, agricole et commerciale, 1862, (1862/04/01 (N1)-1863/01/01 (N12)), Bibliothèque francophone multimédia de Limoges, 2013-220524, Bibliothèque nationale de France
- ↑ Revue des arts décoratifs (Paris), 1880-1902, Bibliothèque nationale de France, département Sciences et techniques, 4-V-1113
- ↑ Le Corbusier, L'Art décoratif d'aujourd'hui, Éditions Crès, Collection de "L'Esprit Nouveau", Paris, 1925, p. 70-81.
- ↑ David Raizman, Carma Gorman, Objects, Audiences, and Literatures: Alternative Narratives in the History of Design, Cambridge Scholars Publishing, Mar 26, 2009, ISBN 1443809462
- ↑ Richard Poulin, Graphic Design and Architecture, A 20th Century History: A Guide to Type, Image, Symbol, and Visual Storytelling in the Modern World, Rockport Publishers, 2012, ISBN 1610586336
- ↑ Benton et al. 2003, p. 430.
- ↑ Hillier, Bevis (1971). The World of Art Deco: An Exhibition Organized by The Minneapolis Institute of Arts, June- September 1971. E.P. Dutton. ISBN 978-0-525-47680-1.
- ↑ Benton, Charlotte, Benton, Tim, Wood, Ghislaine, Art Déco dans le monde- 1910-39, 2010, Renaissance du Livre, ISBN 9782507003906, pages 16-17
- ↑ Benton 2002, pp. 165-170.
- ↑ Salon d'Automne 2012, exhibition catalogue
- ↑ Laurent, Stephane, "L'artiste décorateur, in Art Deco- 1910-1939 by Charlotte Benton, Tim Benton and Ghislain Wood (2002), Renaissance du Livre, pages 165-171
- ↑ Peter Collins, Concrete: The Vision of a New Architecture, New York: Horizon Press, 1959
- ↑ Poisson 2009, pp. 318–319.
- ↑ Descriptive text in the decorative arts display at the Musee d'Orsay, Paris
- 1 2 Arwas 1992, p. 51-55.
- ↑ Erle Lora, Cézannes Composition: Analysis of His Form with Diagrams and Photographs of His Motifs, Forward by Richard Shiff, University of California Press, April 30, 2006
- ↑ La Section d'or, 1912-1920-1925, Cécile Debray, Françoise Lucbert, Musées de Châteauroux, Musée Fabre, exhibition catalogue, Éditions Cercle d'art, Paris, 2000
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Goss, Jared. "French Art Deco". Metropolitan Museum of Art. Retrieved 2016-08-29.
- ↑ André Vera, Le Nouveau style, published in L'Art décoratif, January 1912, pp. 21–32
- ↑ Eve Blau, Nancy J. Troy, "The Maison Cubiste and the meaning of modernism in pre-1914 France", in Architecture and Cubism, Montreal, Cambridge, MA, London: MIT Press−Centre Canadien d'Architecture, 1998, pp. 17−40, ISBN 0262523280
- ↑ Nancy J. Troy, Modernism and the Decorative Arts in France: Art Nouveau to Le Corbusier, New Haven CT, and London: Yale University Press, 1991, pp. 79−102, ISBN 0300045549
- ↑ Christopher Green, Art in France: 1900–1940, Chapter 8, Modern Spaces; Modern Objects; Modern People, 2000
- ↑ André Mare, Salon Bourgeois, Salon d'Automne, The Literary Digest, Doom of the Antique, November 30, 1912, p. 1012
- ↑ The Sun. (New York, N.Y.), 10 Nov. 1912. Chronicling America: Historic American Newspapers. Lib. of Congress
- ↑ Ben Davis, "Cubism" at the Met: Modern Art That Looks Tragically Antique, Exhibition: "Cubism: The Leonard A. Lauder Collection", Metropolitan Museum of Art, ArtNet News, 6 November 2014
- ↑ La Maison Cubiste, 1912
- ↑ Arwas 1992, p. 52.
- 1 2 Arwas 1992, p. 54.
- ↑ Kubistische werken op de Armory Show
- ↑ Detail of Duchamp-Villon's Façade architecturale, catalog number 609, unidentified photographer, 1913. Walt Kuhn, Kuhn family papers, and Armory Show records, 1859-1984, bulk 1900-1949. Archives of American Art, Smithsonian Institution
- ↑ "Catalogue of international exhibition of modern art: at the Armory of the Sixty-ninth Infantry, 1913, Duchamp-Villon, Raymond, Facade Architectural
- ↑ Victor Arwas, Frank Russell, Art Deco, publisher Harry N. Abrams. Inc. New York, 1980, pp. 52, 198, ISBN 0-8109-0691-0
- ↑ Joseph Csaky's staircase in the home of Jacques Doucet. Books.google.es. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ↑ Aestheticus Rex (14 April 2011). "Jacques Doucet's Studio St. James at Neuilly-sur-Seine". Aestheticusrex.blogspot.com.es. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ↑ ''The Modernist Garden in France'', Dorothée Imbert, 1993, Yale University Press. Books.google.es. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ↑ Joseph Csáky: A Pioneer of Modern Sculpture, Edith Balas, 1998, p. 5. Books.google.es. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ↑ Arwas 1982, p. 70.
- ↑ "Eugène Grasset, ''Méthode de composition ornementale, Éléments rectilignes'', 1905, Librarie Centrale des Beaux-Arts, Paris (in French)" (in French). Gallica.bnf.fr. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ↑ "Eugène Grasset, ''Méthode de composition ornementale'', 1905, Full Text (in French)". Archive.org. 10 March 2001. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 "Art Deco Style". Museum of London. Archived from the original on 26 October 2008. Retrieved 6 November 2008.
- ↑ Wood, Ghislaine. Essential Art Deco. London: VA&A Publications. ISBN 0-8212-2833-1.
- 1 2 Hauffe, Thomas (1998). Design: A Concise History (1 ed.). London: Laurence King.
- ↑ "Art Deco Study Guide". Victoria and Albert Museum. Archived from the original on 25 October 2008. Retrieved 1 November 2008.
- ↑ Juster, Randy. "Introduction to Art Deco". decopix.com. Archived from the original on 29 October 2008. Retrieved 7 November 2008.
- ↑ "How Art Deco came to be". University Times. University of Pittsburgh. 36 (4). 9 October 2003.
- ↑ Duncan 1988, p. 8-10.
- ↑ Jirousek, Charlotte (1995). "Art, Design and Visual Thinking". Archived from the original on 2 December 2008. Retrieved 7 November 2008.
- ↑ Duncan 1988, pp. 7-8.
- ↑ Arwas 1992, p. 82.
- ↑ Home Page of the Brooklyn Museum
- ↑ Arwas 1992, p. 77.
- ↑ Charles 2013, pp. 35-104.
- ↑ John Burchard and Albert Bush Brown, The Architecture of America (1966), Atlantic, Little and Brown, page 277
- ↑ Benton & 202, pp. 249-258.
- ↑ Morel 2012, pp. 125-30.
- ↑ Le Corbusier, Vers une architecture, Flammarion, republished in 1995, page xix
- ↑ Larousse Encylopedia on-line edition (in French)
- ↑ Duncan 1988, p. 8.
- 1 2 Fell, Charlotte; Fell, Peter (2006). Design Handbook: Concepts, Materials and Styles (1 ed.). Taschen.
- 1 2 Heindorf, Anne (24 July 2006). "Art Deco (1920s to 1930s)". Archived from the original on 26 October 2008. Retrieved 6 November 2008.
- ↑ Gaunt, Pamela (August 2005). "The Decorative in Twentieth Century Art: A Story of Decline and Resurgence" (PDF).
- ↑ Louis René Vian, Les Arts décoratifs à bord des paquebots français, Éditions Fonmare, 1992
- ↑ Blondel, Alain (1999). Tamara de Lempicka: a Catalogue Raisonné 1921–1980. Lausanne: Editions Acatos.
- ↑ Arwas 1992, pp. 165-66.
- ↑ Kjellberg, Pierre (1994). Bronzes of the 19th Century (First ed.). Atglen, Pennsylvania: Schiffer Publishing, Ltd. p. 551. ISBN 0-88740-629-7.
- ↑ Arwas 1992, pp. 141-163.
- ↑ Edith Balas, 1998, Joseph Csaky: A Pioneer of Modern Sculpture, Philadelphia: American Philosophical Society
- ↑ Paul Iribe, Les robes de Paul Poiret, 1908
- 1 2 Duncan 1988, pp. 148-150.
- ↑ Poisson & 2009 pages 299 and 318.
- ↑ Plum 2014, p. 134.
- 1 2 Duncan 1988, pp. 198-200.
- ↑ Duncan 1988, pp. 197-199.
- ↑ Duncan 1988, p. 197.
- ↑ Explanatory text on Art Deco in the Museum of Decorative Arts, Paris
- ↑ Duncan 1988, p. 250.
- ↑ Benton 2002, pp. 91-93.
- ↑ Arwas 1992, p. 51.
- ↑ Duncan 1988, p. 15.
- ↑ Arwas 1992, p. 56.
- ↑ Duncan 1988, pp. 18-19.
- ↑ Alexandra Griffith Winton, Design, 1925–50. The Metropolitain Museum of Art, Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History, October 2008
- ↑ Duncan 1988, p. 36.
- ↑ Gartman, David (1994). Auto Opium. Routledge. pp. 122–124. ISBN 978-0-415-10572-9.
- ↑ "Curves of Steel: Streamlined Automobile Design". Phoenix Art Museum. 2007. Retrieved 1 September 2010.
- ↑ Armi, C. Edson (1989). The Art of American Car Design. Pennsylvania State University Press. p. 66. ISBN 978-0-271-00479-2.
- ↑ Hinckley, James (2005). The Big Book of Car Culture: The Armchair Guide to Automotive Americana. MotorBooks/MBI Publishing. p. 239. ISBN 978-0-7603-1965-9.
- 1 2 Arwas 1992, pp. 121-123.
- 1 2 3 Arwas 1992, pp. 125.
- 1 2 3 4 Arwas 1992, pp. 245-250.
- ↑ Duncan 1988, pp. 71-81.
- ↑ James, Kathleen (1997). Erich Mendelsohn and the Architecture of German Modernism. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521571685.
- ↑ "Basilica of the Sacred Heart, Koekelberg". Basilicakoekelberg.be. 8 March 2011. Retrieved 7 December 2012.
- ↑ "Art Deco Buildings". london-footprints.co.uk. 2007. Archived from the original on 11 December 2008. Retrieved 6 November 2008.
- ↑ "Art Deco in Frinton on sea". Art Deco Classics. 2006. Archived from the original on 1 December 2008. Retrieved 6 November 2008.
- ↑ "Four Programmes – Art Deco Icons". BBC. 14 November 2009. Retrieved 8 July 2010.
- ↑ "Napier Earthquake". Artdeconapier.com. 3 February 1931. Archived from the original on 6 July 2010. Retrieved 8 July 2010.
- ↑ "Home – Art Deco Trust". Artdeconapier.com. Archived from the original on 30 June 2010. Retrieved 8 July 2010.
- ↑ "Art Deco heritage trail" (PDF). wellington.gov.nz. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
Bibliography
- Arwas, Victor (1992). Art Deco. Harry N. Abrams Inc. ISBN 0-8109-1926-5.
- Bayer, Patricia (1999). Art Deco Architecture: Design, Decoration and Detail from the Twenties and Thirties. Thames & Hudson. ISBN 978-0-500-28149-9.
- Benton, Charlotte; Benton, Tim; Wood, Ghislaine; Baddeley, Oriana (2003). Art Deco: 1910–1939. Bulfinch. ISBN 978-0-8212-2834-0.
- Blondel, Alain (1999). Tamara de Lempicka: a Catalogue Raisonné 1921–1980. Lausanne: Editions Acatos.
- Breeze, Carla (2003). American Art Deco: Modernistic Architecture and Regionalism. W. W. Norton. ISBN 978-0-393-01970-4.
- Charles, Victoria (2013). Art Déco. Parkstone International. ISBN 978-1-84484-864-5.
- Ducher, Rpbert (2014). La charactéristique des styles (in French). Flammarion. ISBN 978-2-0813-4383-2.
- Duncan, Alastair (1988). Art déco. Thames & Hudson. ISBN 2-87811-003-X.
- Duncan, Alastair (2009). Art Deco Complete: The Definitive Guide to the Decorative Arts of the 1920s and 1930s. Abrams. ISBN 978-0-8109-8046-4.
- Gallagher, Fiona (2002). Christie's Art Deco. Pavilion Books. ISBN 978-1-86205-509-4.
- Hillier, Bevis (1968). Art Deco of the 20s and 30s. Studio Vista. ISBN 978-0-289-27788-1.
- Le Corbusier (1996). L'Art Decoratif Aujourd'hui. Flammarion. ISBN 978-2-0812-2062-1.
- Long, Christopher (2007). Paul T. Frankl and Modern American Design. Yale University Press. ISBN 0-300-12102-4.
- Lucie-Smith, Edward (1996). Art Deco Painting. Phaidon Press. ISBN 978-0-7148-3576-1.
- Ray, Gordon N. (2005). Tansell, G. Thomas, ed. The Art Deco Book in France. Bibliographical Society of The University of Virginia. ISBN 978-1-883631-12-3.
- Lehmann, Niels (2012). Rauhut, Christoph, ed. Modernism London Style. Hirmer. ISBN 978-3-7774-8031-2.
- Morel, Guillaume (2012). Art Déco (in French). Éditions Place des Victoires. ISBN 978-2-8099-0701-8.
- Okroyan, Mkrtich (2008–2011). Art Deco Sculpture: From Root to Flourishing (vol.1,2). Russian Art Institute. ISBN 978-5-905495-02-1.
- Plum, Giles (2014). Paris architectures de la Belle Epoque (in French). Parigramme. ISBN 978-2-84096-800-9.
- Poisson, Michel (2009). 1000 Immeubles et monuments de Paris (in French). Parigramme. ISBN 978-2-84096-539-8.
- Savage, Rebecca Binno; Kowalski, Greg (2004). Art Deco in Detroit (Images of America). Arcadia. ISBN 978-0-7385-3228-8.
- Texier, Simon (2012). Paris: Panorama de l'architecture (in French). Parigramme. ISBN 978-2-84096-667-8.
- Unes, Wolney (2003). Identidade Art Déco de Goiânia (in Portuguese). Ateliê. ISBN 85-7480-090-2.
- Vincent, G.K. (2008). A History of Du Cane Court: Land, Architecture, People and Politics. Woodbine Press. ISBN 978-0-9541675-1-6.
- Ward, Mary; Ward, Neville (1978). Home in the Twenties and Thirties. Ian Allan. ISBN 0-7110-0785-3.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Art Deco. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Exposition internationale des Arts Décoratifs et industriels modernes (1925). |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Art Deco architecture. |
- Art Deco Miami Beach
- Art Deco Montreal
- Art Deco Society of Washington
- Art Deco Society of California
- Art Deco Rio de Janeiro
- Art Deco Shanghai
- Art Deco Museum in Moscow

_(3679648700).jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)

