Thai solar calendar
The Thai solar calendar, Suriyakhati (Thai: สุริยคติ), was adopted by King Chulalongkorn (Rama V) in AD 1888 as the Siamese version of the Gregorian calendar. It is the legal calendar in Thailand, though Thai lunar calendar dates continue in use. Years are now counted in the Buddhist Era (BE: พ.ศ. พุทธศักราช, pútthasàkkàrât) which began 543 years before the Christian Era (ค.ศ. คริสต์ศักราช, krítsàkkàrât). As a convenience, calendars typically include the year AD in both Arabic and Thai numerals.

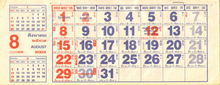
Calendar

- Red numerals mark Sundays and public holidays in Thailand.
- Buddha images mark Buddhist Sabbaths, Wan Phra (วันพระ).
- Red tablets with white Chinese characters mark the New and Full Moons of the Chinese calendar, which typically differ by one day from those of the Thai.
- Thai lunar calendar dates appear below the solar calendar date.
Birthdays
Mundane astrology figures prominently in Thai culture, so modern Thai birth certificates include lunar calendar dates, and the appropriate Chinese calendar zodiacal animal year-name for both Thai Hora (โหราศาสตร์, ho-ra-sat) and Chinese astrology. Thai birth certificates record the date, month and time of birth, followed by the day of the week, lunar date, and the applicable zodiac animal name. Thai traditionally reckon age by the 12-year animal-cycle names, with the twelfth and sixtieth anniversaries being of special significance; but the official calendar determines age at law.
For instance, 12 August 2004 was observed without regard to the lunar date as Queen Sirikit's birthday, a public holiday also observed as Thai Mothers' Day. Her zodiacal animal is the Monkey and her traditionally significant sixtieth anniversary year was 1992. Born on a Friday, her auspicious birthday colour is blue. Thai auspicious colours of the day are given in the table of weekdays, followed below it by a link to the Buddha images for each day of the week.
Years
The Siamese generally used two calendars, a sacred and a popular (vulgar in the classical sense). The vulgar or minor era (จุลศักราช, chula sakarat) was thought to have been instituted when the worship of Gautama was first introduced,[1] [2] and corresponds to the traditional Burmese calendar (abbreviated ME or BE, the latter not to be confused with the abbreviation for the Buddhist Era, which is the sacred era.)
Rattanakosin Era
King Chulalongkorn decreed a change in vulgar reckoning to the Rattanakosin Era (abbreviated RE) (รัตนโกสินทรศก, Rattanakosin Sok abbreviated ร.ศ. and R.S.) The epoch (reference date) for Year 1 was 6 April 1782 with the accession of Rama I, the foundation of the Chakri Dynasty, and the founding of Bangkok (Rattanakosin) as capital in 106 RE, AD 1888.
Buddhist Era
In Thailand the sacred, or Buddhist Era, is reckoned to have an epochal year 0 from 11 March 543 BC, believed to be the date of the death of Gautama Buddha. King Vajiravudh (Rama VI) changed year counting to this Buddhist Era (abbreviated BE) and moved the start of the year back to 1 April in 2455 BE, AD 1912. As there is no longer any reference to a vulgar or popular era, the Common Era may be presumed to have taken the place of the former.
New year
New Year, the time at which a new calendar year begins and the calendar's year count is incremented, originally coincided with the date calculated for Songkran, when the sun transits the constellation of Aries, the first astrological sign in the Zodiac as reckoned by sidereal astrology: thus the year commenced on 11 April 1822.[1] As previously noted, Rama VI moved the start of the year back to 1 April in 2455 BE, AD 1912.
On 6 September 1940, Prime Minister Phibunsongkhram decreed[3] 1 January 1941 as the start of the year 2484 BE, so year 2483 BE had only nine months. To convert dates from 1 January to 31 March prior to that year, the number to add or subtract is 542; otherwise, it is 543. Example:
| 1992Month | 1–3 | 4–6 | 7–9 | 10–12 | 1–3 | 4–6 | 7–9 | 10–12 | 1–3 | 4–6 | 7–9 | 10–12 | 1–3 | 4–6 | 7–9 | 10–12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AD | 1939 | 1940 | 1941 | 1942 | ||||||||||||
| BE | 2481 | 2482 | 2483 | 2484 | 2485 | |||||||||||
| 1992Thai Month | 10-12 | 1-3 | 4–6 | 7–9 | 10-12 | 1-3 | 4–6 | 7–9 | 1-3 | 4-6 | 7-9 | 10-12 | 1-3 | 4-6 | 7-9 | 10-12 |
Today, both the Common Era New Year's Day (1 January) and the traditional Thai New Year (สงกรานต์, Songkran) celebrations (13–15 April) are public holidays in Thailand. In the traditional Thai calendar, the change to the next Chinese zodiacal animal occurs at Songkran (now fixed at 13 April.)[4] For Thai Chinese communities in Thailand, however, the Chinese calendar determines the day that a Chinese New Year begins, and assumes the name of the next animal in the twelve-year animal cycle.
Months
Names of the months derive from Hindu astrology names for the signs of the zodiac. Thirty-day-month names end in -ayon (-ายน), from Sanskrit root āyana : the arrival of; 31-day-month names end in -akhom (-าคม), from Sanskrit āgama (cognate to English "come") that also means the arrival of.
February's name ends in -phan (-พันธ์), from Sanskrit bandha : "fettered" or "bound". The day added to February in a solar leap year is Athikasuratin (อธิกสุรทิน, respelled to aid pronunciation (อะทิกะสุระทิน) from Sanskrit adhika : additional; sura : move).[5]
| English name | Thai name | Abbr. | Thai Pronunciation | Sanskrit word | Zodiac sign |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | มกราคม | ม.ค. | mákàraa-khom, mókkàraa-khom | makara "sea-monster" | Capricorn |
| February | กุมภาพันธ์ | ก.พ. | kumphaa-phan | kumbha "pitcher, water-pot" | Aquarius |
| March | มีนาคม | มี.ค. | miinaa-khom | mīna "(a specific kind of) fish" | Pisces |
| April | เมษายน | เม.ย. | meesaǎ-yon | meṣa "ram" | Aries |
| May | พฤษภาคม | พ.ค. | phrɯ́tsaphaa-khom | vṛṣabha "bull" | Taurus |
| June | มิถุนายน | มิ.ย. | míthùnaa-yon | mithuna "a pair" | Gemini |
| July | กรกฎาคม | ก.ค. | kàrákàdaa-khom | karkaṭa "crab" | Cancer |
| August | สิงหาคม | ส.ค. | sǐnghǎa-khom | sinha "lion" | Leo |
| September | กันยายน | ก.ย. | kanyaa-yon | kanyā "girl" | Virgo |
| October | ตุลาคม | ต.ค. | tùlaa-khom | tulā "balance" | Libra |
| November | พฤศจิกายน | พ.ย. | phrɯ́tsacìkaa-yon | vṛścika "scorpion" | Scorpio |
| December | ธันวาคม | ธ.ค. | thanwaa-khom | dhanu "bow, arc" | Sagittarius |
Weeks
A week (สัปดาห์, sapda or สัปดาหะ, sapdaha from Sanskrit "seven") is a 7-day period beginning on Sunday and ending Saturday.[6]
Days of the week are named after the first seven of the nine Indian astrological Navagraha; i.e., the sun, moon, and five classical planets.
| English name | Thai name | Thai Pronunciation | Color | Sanskrit word | Planet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sunday | วันอาทิตย์ | wan aathít | red | Aditya | Sun |
| Monday | วันจันทร์ | wan can | yellow | Chandra | Moon |
| Tuesday | วันอังคาร | wan angkhaan | pink | Angaraka | Mars |
| Wednesday | วันพุธ | wan phút | green | Buddha | Mercury |
| Thursday | วันพฤหัสบดี | wan phrɯ́hàtsàbɔɔdii | orange | Brihaspati | Jupiter |
| Friday | วันศุกร์ | wan sùk | blue | Shukra | Venus |
| Saturday | วันเสาร์ | wan sǎo | purple | Shani | Saturn |
Note: Colours are those considered auspicious for the given days of the week, that of Wednesday day being green and of Wednesday night, light green. Of Buddha images representing episodes (ปาง) from his life, there is one that represents a week and others for each day of the week: Monday has three options that are similar and Wednesday, entirely different ones for day and night.[7]
Thai representations of the planets in deity form are below:
 Phra Athit
Phra Athit Phra Chan
Phra Chan Phra Angkhan
Phra Angkhan Phra Phut
Phra Phut Phra Rahu
Phra Rahu Phra Phruehat
Phra Phruehat Phra Suk
Phra Suk Phra Sao
Phra Sao
Weekends and holidays
Saturdays and Sundays (Thai: เสาร์-อาทิตย์ sao athit) are observed as legal non-workdays (วันหยุดราชการ, wan yut ratchakan) and are generally shown on calendars in red, as are public holidays. Since 1996 and subject to declaration by the Cabinet of Thailand, public holidays that fall on weekends are followed by Substitution days (วันชดเชย, wan chot choei) generally shown in a lighter shade of red, as shown above for Monday, 2 August 2004. Buddhist feasts that are public holidays are calculated according to the Thai lunar calendar, so their dates change every year with respect to the solar calendar. Chinese New Year and other feasts observed by Thai Chinese vary with respect to both, as these are calculated according to the Chinese calendar.
See also
| Wikisource has original text related to this article: |
- Buddhist calendar
- Public holidays in Thailand
- Thai 6-hour clock
- Thai lunar calendar
- Time in Thailand
Notes
- 1 2 Crawfurd, John (21 August 2006) [1830]. "Chapter I". Journal of an Embassy from the Governor-general of India to the Courts of Siam and Cochin China. Volume 2 (2nd ed.). London: H. Colburn and R. Bentley. p. 32. OCLC 3452414. Retrieved 6 August 2012.
The Siamese year does not commence with the first month, but corresponds with that of the Chinese. In the year 1822, the new year fell on the 11th of April, being the 5th day of the dark half of the moon.... The Siamese have two epochs, or, as they describe them, Sa-ka-rat. The sacred one dates from the death of Gautama, and the year which commenced on the 11th of April, 1822, was the year 2365, according to this reckoning.
- ↑ Roberts, Edmund (Digitized 12 October 2007) [First published in 1837]. "Chapter XX―Division of Time". Embassy to the Eastern courts of Cochin-China, Siam, and Muscat : in the U. S. sloop-of-war Peacock ... during the years 1832-3-4 (Digital ed.). Harper & brothers. p. 310. Retrieved 25 April 2012.
The Siamese have two epochs, sacred and popular. The sacred era dates from the death of Gautama, and the year 1833 corresponded to the 2376 year. The vulgar era was instituted when the worship of Gautama was first introduced; and the year 1833 corresponded with the year 1194, and was the fifth, or Dragon year.
Check date values in:|date=(help) - ↑ พระราชบัญญัติปีปฏิทิน พุทธศักราช ๒๔๘๓ (PDF). Royal Gazette (in Thai). 57 (0 ก): 419. 1940-09-17.
- ↑ J.C. Eade. The calendrical systems of mainland southeast asia. E.J. Brill, Leiden. p. 22. ISBN 90-04-10437-2. According to some scholars including George Coedes the change occurred at the beginning of the 5th lunar month originally a few days before Songkhran.
- ↑ Thai2english.com, dictionary
- ↑ Royal Institute Dictionary 1999
- ↑ "Thai birth day colors and Buddha image". United States Muay Thai Association Inc. 16 October 2004. Retrieved 14 November 2009.
An innovation of the Ayutthaya period.
References
- Eade, John Christopher. 1995. The Calendrical Systems of Mainland South-East Asia. Handbuch der Orientalistik: Dritte Abteilung, Südostasien 9. Leiden and New York: E. J. Brill. ISBN 90-04-10437-2
- na Nakorn, Bleung (comp.). [1971]. นายเปลื้อง ณ นคร ผู้รวบรวม ปทานุกรมนักเรียน ไทยวัฒนาพานิช กทม. Student's Handbook. Bangkok: Thai Wattana Panit, 2514.
- Sethaputra, So. 1999. New Model English - Thai Dictionary. [Krung Thep Maha Nakhon?: Thai Watthana Phanit?]. ISBN 974-08-3253-9
- Thai calendar for August 2004.
- Web dictionary Thai-English English-Thai
External links
- Thai Time by Anthony Diller
- Thai Buddha Images for the Days of the Week
- Thai Lunar/Solar Calendar (BE.2300-2584) (Thai Language)
