2-Oxazolidone
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,3-Oxazolidin-2-one | |||
| Other names
2-Oxazolidone 2-Oxazolidinone | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 497-25-6 | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChemSpider | 66579 | ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.129 | ||
| KEGG | C06695 | ||
| PubChem | 73949 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H5NO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 87.077 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Solid | ||
| Melting point | 86 to 89 °C (187 to 192 °F; 359 to 362 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 220 °C (428 °F; 493 K) at 48 torr | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Related compounds |
Oxazolidine | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
2-Oxazolidone is a heterocyclic organic compound containing both nitrogen and oxygen in a 5-membered ring.
Oxazolidinones
Evans auxiliaries
Oxazolidinones are a class of compounds containing 2-oxazolidone in the structure. In chemistry, they are useful as Evans auxiliaries, which are used for chiral synthesis. Usually, the acid chloride substrate reacts with the oxazolidinone to form an imide. Substituents at the 4 and 5 position of the oxazolidinone direct any aldol reaction to the alpha position of the carbonyl of the substrate.
Pharmaceuticals
Oxazolidinones are mainly used as antimicrobials. The antibacterial effect of oxazolidinones is by working as protein synthesis inhibitors, targeting an early step involving the binding of N-formylmethionyl-tRNA to the ribosome.[1] (See Linezolid#Mechanism_of_action)
Some of the most important oxazolidinones are the last generation of antibiotics used against gram-positive pathogens, including superbugs such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. These antibiotics are considered as a choice of last resort where every other antibiotic therapy has failed.
Examples of antibiotic oxazolidinones include:
- Linezolid (Zyvox), which is available for intravenous administration and also has the advantage of having excellent oral bioavailability.
- Posizolid, which appears to have excellent, targeted bactericidal activity against all common gram-positive bacteria, regardless of resistance to other classes of antibiotics.[2]

- Tedizolid, (Sivextro) which is approved for acute skin infections
- Radezolid (RX-1741) has completed some phase-II clinical trials.[3]
- Cycloserine is a second line drug against tuberculosis. Note that cycloserine, while technically an oxazolidone, has a different mechanism of action and substantially different properties from the aforementioned compounds.
- (S)-5-((isoxazol-3-ylamino)methyl)-3-(2,3,5-trifluoro-4-(4-oxo-3,4-dihydropyridin-1(2H)-yl)phenyl)oxazolidin-2-one (MRX-I) has reported phase 1 data[4] and completed phase II trials in 2015, and is starting a phase 3 trial in 2016.[5]
An oxazolidinone derivative used for other purposes is rivaroxaban, which is approved by the FDA for venous thromboembolism prophylaxis.
History

The first ever used oxazolidinone was cycloserine (4-amino-1,2-oxazolidin-3-one), a second line drug against tuberculosis since 1956.[6]
Developed during the nineties when several bacterial strains were becoming resistant against such antibiotics as vancomycin. Linezolid (Zyvox) is the first approved agent in the class (FDA approval April 2000).
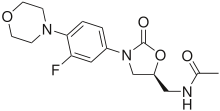
The first commercially available 1,3-oxazolidinone antibiotic was linezolid, discovered and developed by Pharmacia & Upjohn.

In 2002 AstraZeneca introduced posizolid (AZD2563).
See also
- Oxazolidine - the ring without the carbonyl group
- Oxazolone - the unsaturated analogues
References
- ↑ Shinabarger, D. (1999). "Mechanism of action of the oxazolidinone antibacterial agents". Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 8 (8): 1195–1202. doi:10.1517/13543784.8.8.1195. PMID 15992144.
- ↑ Wookey, A.; Turner, P. J.; Greenhalgh, J. M.; Eastwood, M.; Clarke, J.; Sefton, C. (2004). "AZD2563, a novel oxazolidinone: definition of antibacterial spectrum, assessment of bactericidal potential and the impact of miscellaneous factors on activity in vitro". Clinical Microbiology and Infection. 10 (3): 247–254. doi:10.1111/j.1198-743X.2004.00770.x. PMID 15008947.
- ↑ "Rx 1741". Rib-X Pharmaceuticals. 2009. Retrieved 2009-05-17.
- ↑ New Potent Antibacterial Oxazolidinone (MRX-I) with an Improved Class Safety Profile. 2014
- ↑ MicuRx Initiates Phase 3 Clinical Trial for MRX-I... 2016
- ↑ A. W. Frahm, H. H. J. Hager, F. v. Bruchhausen, M. Albinus, H. Hager: Hagers Handbuch der pharmazeutischen Praxis: Folgeband 4: Stoffe A-K., Birkhäuser, 1999, ISBN 978-3-540-52688-9

