Brodie abscess
| Brodie abscess | |
|---|---|
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | rheumatology |
| ICD-10 | M86.8 |
| ICD-9-CM | 730.1 |
| eMedicine | article/1248682 |
A Brodie abscess is a subacute osteomyelitis, which may persist for years before converting to a frank osteomyelitis. Classically, this may present after conversion as a draining abscess extending from the tibia out through the shin. Occasionally acute osteomyelitis may be contained to a localized area and walled off by fibrous and granulation tissue. This is termed as Brodie's abscess.
Most frequent causative organism is Staphylococcus aureus.
Clinical presentation
Localized pain, often nocturnal, alleviated by aspirin. Often mimics the symptoms of Osteoid osteoma, which is typically less than 1 cm in diameter.
Most frequent sites
Usually occurs at the metaphysis of long bones. Distal tibia, proximal tibia, distal femur, proximal or distal fibula, and distal radius.
Radiographic features
Oval, elliptical, or serpentine radiolucency usually greater than 1 cm surrounded by a heavily reactive sclerosis, granulation tissue, and a nidus often less than 1 cm. The margins often appear scalloped on radiograph. Brodie's abscess is best visualized using Computed tomography (CT) scan. Associated atrophy of soft tissue near the site of infection and shortening of the affected bone. Osteoblastoma may be a classic sign for Brodie's abscess.
 PA view of the left distal tibia showing a lytic lesion in the distal metaphysis with a narrow zone of transition more caudally with a faint sclerotic rim and a wide zone of transition more cephalad. Periostial reaction along the medial cortex indicates an aggressive lesion. Neoplasm such as Ewing sarcoma and osteomyelitis could both have this plain radiographic appearance. Staphylococcus was recovered at surgery.
PA view of the left distal tibia showing a lytic lesion in the distal metaphysis with a narrow zone of transition more caudally with a faint sclerotic rim and a wide zone of transition more cephalad. Periostial reaction along the medial cortex indicates an aggressive lesion. Neoplasm such as Ewing sarcoma and osteomyelitis could both have this plain radiographic appearance. Staphylococcus was recovered at surgery. Fat saturated STIR (short tau inversion recovery) image showing hyperintense edema in the calf musculature, marrow edema, and subperiosteal pus. The intramedullary abscess cavity is hyperintense as well.
Fat saturated STIR (short tau inversion recovery) image showing hyperintense edema in the calf musculature, marrow edema, and subperiosteal pus. The intramedullary abscess cavity is hyperintense as well. Coronal fat suppressed STIR image showing, bone marrow and subcutaneous edema as well as subperiosteal edema. The thin hypointense rim surrounding the intramedullary collection represents the reactive interface between the abscess and the body's attempt to wall it off.
Coronal fat suppressed STIR image showing, bone marrow and subcutaneous edema as well as subperiosteal edema. The thin hypointense rim surrounding the intramedullary collection represents the reactive interface between the abscess and the body's attempt to wall it off.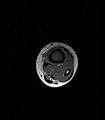 Axial T1-weighted MRI pre-contrast enhancement showing that the intramedullary collection is T1-hyperintense suggesting proteinaceous viscous fluid consistent with infection.
Axial T1-weighted MRI pre-contrast enhancement showing that the intramedullary collection is T1-hyperintense suggesting proteinaceous viscous fluid consistent with infection. Axial T1-weighted fat-saturated MRI image following IV gadolinium contrast demonstrating the intramedullary lytic area seen on radiography to be ring enhancing consistent with a purulent fluid collection. Extensive circumferential periosteal enhancement is noted. There is also substantial bone marrow enhancement.
Axial T1-weighted fat-saturated MRI image following IV gadolinium contrast demonstrating the intramedullary lytic area seen on radiography to be ring enhancing consistent with a purulent fluid collection. Extensive circumferential periosteal enhancement is noted. There is also substantial bone marrow enhancement. Sagittal T1-weighted fat-suppressed post gadolinium image showing the extent of the multiloculated intramedullary abscess.
Sagittal T1-weighted fat-suppressed post gadolinium image showing the extent of the multiloculated intramedullary abscess.
History
Brodie abscess is named after Sir Benjamin Collins Brodie, 1st Baronet.
Treatment
Mainly surgical approach has to be taken. If cavity is small then surgical evacuation & curettage is performed under antibiotic cover. If cavity is large then after evacuation, packing with cancellous bone chips