Wilson's snipe
| Wilson's snipe | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Subclass: | Neornithes |
| Infraclass: | Neognathae |
| Superorder: | Neoaves |
| Order: | Charadriiformes |
| Suborder: | Scolopaci |
| Family: | Scolopacidae |
| Genus: | Gallinago |
| Species: | G. delicata |
| Binomial name | |
| Gallinago delicata Ord, 1825 | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Gallinago gallinago delicata Ord, 1825 | |
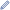
Wilson's snipe (Gallinago delicata) is a small, stocky shorebird. The genus name gallinago is New Latin for a woodcock or snipe from Latin gallina, "hen" and the suffix -ago, "resembling". The specific delicata is Latin for "dainty".[2]
This species was considered to be a subspecies of the common snipe (G. gallinago) until 2003 when it was given its own species status, though not all authorities recognized this immediately.[3] Wilson's snipe differs from the latter species in having a narrower white trailing edge to the wings, and eight pairs of tail feathers instead of the typical seven of the common snipe.[4] Its common name commemorates the American ornithologist Alexander Wilson.
Description
Adults are 23–28 cm (9.1–11.0 in) in length with a 39–45 cm (15–18 in) wingspan. They have short greenish-grey legs and a very long straight dark bill. The body is mottled brown on top and pale underneath. They have a dark stripe through the eye, with light stripes above and below it. The wings are pointed.
Breeding and habits
They breed in marshes, bogs, tundra and wet meadows in Canada and the northern United States. They are year-round residents on the U.S. Pacific coast. The eastern population migrates to the southern United States and to northern South America. It may be that climate change causes these birds to move to their breeding range earlier and leave later than 100 years ago. In Ohio for example, late April was recorded as an average migration date in 1906, but now most of the local population is present on the breeding grounds by then already.[5][6]
They forage in soft mud, probing or picking up food by sight and eating insects, earthworms, and plant material. Well-camouflaged, they are usually shy and conceal themselves close to ground vegetation, flushing only when approached closely. They fly off in a series of aerial zig-zags to confuse predators.
The male performs "winnowing" display during courtship, flying high in circles and then taking shallow dives to produce a distinctive sound. They have been observed "winnowing" throughout the day and long into the night. The "winnowing" sound is similar to the call of a boreal owl. They nest in a well-hidden location on the ground.
Population
The Wilson's snipe was reduced near the end of the 19th century by hunting and habitat destruction. However, this bird remains fairly common and not considered threatened by the IUCN. It is apparently less tolerant of habitat destruction than the American woodcock, declining markedly when faced with large-scale draining of marshland.[5]
References
- ↑ BirdLife International (2005). "Gallinago delicata". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2006. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 12 May 2006.
- ↑ Jobling, James A (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. pp. 132, 170. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.
- ↑ Wilson's Snipe (Gallinago delicata) - BirdLife species factsheet
- ↑ "Wilson's Snipe". Cornell Lab of Ornithology.
The Wilson's Snipe typically has 16 tail feathers, whereas the common snipe has 14.
- 1 2 Henninger, W.F. (1906). "A preliminary list of the birds of Seneca County, Ohio" (PDF). Wilson Bulletin. 18 (2): 47–60.
- ↑ Ohio Ornithological Society (2004). Annotated Ohio state checklist.
Further reading
- Bezener, A. (2000). Birds of Ontario p. 149. Lone Pine Publishing, Edmonton.
Identification
- Carey, Geoff and Urban Olsson (1995). Field identification of Common, Wilson's, Pintail and Swinhoe's Snipes. Birding World 8(5): 179–190.
- Leader, Paul (1999). Identification forum: Common Snipe and Wilson's Snipe Birding World 12(9): 371–4.
- Reid, Marin (2008). Identification of Wilson's and Common Snipe British Birds 101(4): 189–200.
European occurrences
- Bland, Bryan (1998). The Wilson's Snipe on the Isles of Scilly. Birding World 11(10): 382–5.
- Bland, Bryan (1999). The Wilson's Snipe on the Isles of Scilly revisited. Birding World 12(2): 56–61.
- Legrand, Vincent (2005). Identification of a Wilson's Snipe on Ouessant, Finistere. Birding World 18(11): 482–4.
- Lidster, James (2007). The Wilson's Snipe on the Isles of Scilly. Birding World 20(10):432-5.
- Millington, Richard (2008). The Wilson's Snipe on St Agnes, Isles of Scilly. Birding World 21(11): 467–9.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Wilson's Snipe. |
| Wikispecies has information related to: Gallinago delicata |
- Wilson's snipe species account – Cornell Lab of Ornithology
- "Gallinago delicata". Avibase.
- Wilson's snipe photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)

%2C_Lamoille%2C_Nevada%2C_USA.jpg)