Occluded front
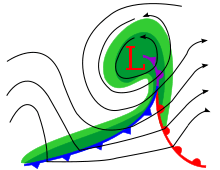
An occluded front is formed during the process of cyclogenesis when a cold front overtakes a warm front. When this occurs, the warm air is separated (occluded) from the cyclone center at the Earth's surface. The point where the warm front and the occluded front meet (and consequently the nearest location of warm air to the center of the cyclone) is called the triple point.[1]
The trowal (short for TROugh of Warm air ALoft) is the projection on the Earth's surface of the trough of warm air aloft formed during the occlusion process of the depression.[2]
Description

Occluded fronts usually form around mature low pressure areas. There are two types of occlusion, warm and cold:
- In a cold occlusion, the air mass overtaking the warm front is cooler than the cool air ahead of the warm front, and plows under both air masses.
- In a warm occlusion, the air mass overtaking the warm front is not as cool as the cold air ahead of the warm front, and rides over the colder air mass while lifting the warm air.
The occluded front symbol should thus be plotted at the position where the cold air is intersecting the surface, as on the adjacent image. It thus varies between warm and a cold occlusions. The trowal on the other hand, being the projection of the warm air trough aloft, is at the same position in both cases. The position of the occluded front is often misplaced with the associated weather on a weather map but this is the position of the trowal.[3]
Related weather

A cold front would be seen as spikes and a warm front as semi-circles in a traditional weather map. An occluded front, is a combination of those two signs. They are indicated on a weather map either by a purple line with alternating semicircles and triangles pointing in direction of travel, or by red semicircles and blue triangles pointing in the same direction. On the other hand, trowal are indicated by junction of blue and red lines like the junction of cold and warm fronts aloft.
A wide variety of weather can be found along an occluded front, with thunderstorms possible, but usually their passage is associated with a drying of the air mass. Additionally, cold core funnel clouds are possible if shear is significant along the cold front. Small isolated occluded fronts often remain for a time after a low pressure system has decayed and these create cloudy conditions with patchy rain or showers.
However, the clouds and precipitation are not really where the projection on the Earth's surface of the occluded front is, but with the trowal position.[3]
See also
- Extratropical cyclone
- Surface weather analysis
- Weather fronts
- Cold front
- Warm front
- Stationary front
References
- ↑ Djurić, D: "Weather Analysis". Prentice Hall, 1994. ISBN 0-13-501149-3.
- ↑ "Trowal". World Meteorological Organisation. Eumetcal. Retrieved 2013-08-28.
- 1 2 Meteorological Service of Canada (January 2011). "9.5 Weather and Trowals". AWARE (PDF). Environment Canada. pp. 82–83. Retrieved 2013-08-28.
Schultz, D. M., and G. Vaughan, 2011: Occluded fronts and the occlusion process: A fresh look at conventional wisdom. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 92, 443–466, ES19–ES20.
External links
- A film clip AIR MASSES AND FRONTS - THE OCCLUDED FRONT (1962) is available at the Internet Archive
- Occluded Front.