Transport in North Korea
Transport in North Korea is constrained by economic problems and government restrictions. Public transport predominates, and most of it is electrified.
Restrictions on freedom of movement
Travel to North Korea is tightly controlled. The standard route to and from North Korea is by plane or train via Beijing, China. Transport directly to and from South Korea was possible on a limited scale from 2003 until 2008, when a road was opened (bus tours, no private cars). Freedom of movement in North Korea is also limited,[1] as citizens are not allowed to move around freely inside their country.[2]
Roads

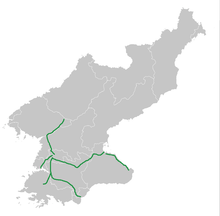
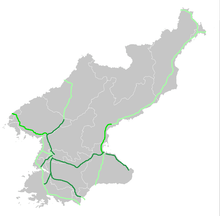

Fuel constraints and the near absence of private automobiles have relegated road transportation to a secondary role. The road network was estimated to be around 31,200 km in 1999 up from between 23,000 and 30,000 km in 1990, of which only 1,717 kilometers—7.5 percent—are paved; the rest are of dirt, crushed stone, or gravel, and are poorly maintained. However, The World Factbook (published by the US Central Intelligence Agency) lists 25,554 km of roads with only 724 km paved as of 2006.[3] As for the road quality, drivers will often swerve and change langes to evade potholes, and this includes going into opposite-direction lanes at times. Likewise, sections under repair may not be properly signalled, so oncoming traffic should always be expected even on a divided motorway.
There are three major multilane highways: a 200-kilometer expressway connecting Pyongyang and Wonsan on the east coast, a 43-kilometer expressway connecting Pyongyang and its port, Namp'o, and a four-lane 100-kilometer motorway linking Pyongyang and Kaesong. The overwhelming majority of the estimated 264,000 vehicles in use in 1990 were for the military. Rural bus service connects all villages, and cities have bus and tram services. Since 1945/1946, there is right-hand traffic on roads. In cities, driving speeds are set by which lane a driver is in.[4] The speed limits are 40 km/h (24 mph), 60 km/h (37 mph) and 70 km/h (43 mph) for the first, second, and subsequent (if existing) lanes from the right, respectively. A white-on-blue sign informs about this.[4] The leftmost lane, if it is number 3 from the right or higher and is not a turning lane, is often left vacant, even by tourist buses, while the second-from-right lane is generally used to overtake vehicles from lane one, such as public transport buses and trams.
Besides the blue in-city sign, all other occasions, such as motorways and roads outside cities, use the more widely known red-circle-with-number-inside sign to post speed limits. On motorways, the typical limit is 80 and 100 km/h for lanes from the right, respectively, as posted on the Pyongyang–Kaesong highway, for example. The rightmost lane of a motorway is sometimes, as seen on the Pyongyang–Myohyang highway, limited to 60 near onramp joining points.
Automobile transportation is further restricted by a series of regulations. According to North Korean exile Kim Ji-ho, unless a driver receives a special permit it is forbidden to drive alone (the driver must carry passengers).[5] Other permits are a military mobilization permit (to transport soldiers in times of war), a certificate of driver training (to be renewed every year), a fuel validity document (a certificate confirming that the fuel was purchased from an authorized source) and a mechanical certificate (to prove that the car is in working order).[5]
Although it drives on the right, North Korea has imported various used RHD vehicles from Japan (through Russia), from tourist buses to Toyota Land Cruisers.
 A highway outside of Pyongyang
A highway outside of Pyongyang Roadworks in North Korea. The blue truck in the foreground is a Chinese-made Dongfeng
Roadworks in North Korea. The blue truck in the foreground is a Chinese-made Dongfeng- A main road in Pyongyang
- A side road in Kaesong
Public transport
There is a mix of locally built and imported trolleybuses and trams in the major urban centres of North Korea. Earlier fleets were obtained from Europe and China.
 Pyongyang tram in 2009
Pyongyang tram in 2009 Trolleybus near Pyongyang Railway Station in 2007
Trolleybus near Pyongyang Railway Station in 2007 Former Zurich type Be 4/4 tram on the Kumsusan Memorial Palace line
Former Zurich type Be 4/4 tram on the Kumsusan Memorial Palace line A Pyongyang Trolleybus Works Chongnyonjunwi
A Pyongyang Trolleybus Works Chongnyonjunwi A Proton Wira yellow taxi in Pyongyang.
A Proton Wira yellow taxi in Pyongyang.
Railways
The Korean State Railway is the only rail operator in North Korea. It has a network of over 6000 km of standard gauge and 400 km of narrow gauge (762 mm) lines; as of 2007, over 5400 km of the standard gauge (well over 80%), along with 295.5 km of the narrow gauge lines are electrified.[6] The narrow gauge segment runs in the Haeju peninsula.[7]
Because of lack of maintenance on the rail infrastructure and vehicles, the travel time by rail is increasing. It has been reported that the 190 km (120 mi) trip from Pyongyang to Kaesong can take up to 6 hours.[8]
Water transport
Water transport on the major rivers and along the coasts plays a growing role in freight and passenger traffic. Except for the Yalu and Taedong rivers, most of the inland waterways, totaling 2,250 kilometers, are navigable only by small boats. Coastal traffic is heaviest on the eastern seaboard, whose deeper waters can accommodate larger vessels. The major ports are Nampho on the west coast and Rajin, Chongjin, Wonsan, and Hamhung on the east coast. The country's harbor loading capacity in the 1990s was estimated at almost 35 million tons a year. There is a continuing investment in upgrading and expanding port facilities, developing transportation—particularly on the Taedong River—and increasing the share of international cargo by domestic vessels.
| Ports in North Korea |
|---|
| Chongjin, Haeju, Hamhung, Kimchaek, Kaesong, Rasŏn, Nampo, Sinuiju, Songnim, Sonbong (formerly Unggi), Ungsang, Wonsan |
Merchant marine
In the early 1990s, North Korea possessed an oceangoing merchant fleet, largely domestically produced, of 68 ships (of at least 1,000 gross-registered tons), totalling 465,801 gross-registered tons (709,442 tonnes deadweight (DWT)), which included fifty-eight cargo ships and two tankers. As of 2008, this has increased to a total of 167 vessels consisting mainly of cargo and tanker ships.
| Fleet by type | |
|---|---|
| Total | 167 |
| Bulk carrier | 11 |
| Cargo | 121 |
| Carrier | 1 |
| Chemical tanker | 4 |
| Container | 3 |
| Cargo liner | 3 |
| Petroleum tanker | 19 |
| Reefer ship | 4 |
| Roll on/Roll off | 1 |
Air transport
North Korea's international air connections are limited in frequency and numbers. As of 2011, scheduled flights operate only from Pyongyang's Pyongyang Sunan International Airport to Beijing, Dalian, Shenyang, Shanghai, Bangkok, Kuala Lumpur, Singapore, Moscow, Khabarovsk, Vladivostok and Kuwait International Airport. Charters to other destinations operate as per demand. Prior to 1995 many routes to Eastern Europe were operated including services to Sofia, Belgrade, Prague, Budapest along with others.
Air Koryo is the country's national airline. Air China also operates flights between Beijing and Pyongyang. In 2013, MIAT Mongolian Airlines began operating direct charter services from Ulaanbattar to Pyongyang with Boeing 737-800 aircraft.[9]
Internal flights are available between Pyongyang, Hamhung, Haeju (HAE), Hungnam (HGM), Kaesong (KSN), Kanggye, Kilju, Najin (NJN), Nampo (NAM), Sinuiju (SII), Samjiyon, Wonsan (WON), Songjin (SON) and Chongjin (CHO). All civil aircraft are operated by Air Koryo, which has a fleet of 19 passenger and cargo aircraft, all of which are Soviet or more modern Russian types.
As of 2013, the CIA estimates that North Korea has 82 usable airports, 39 of which have permanent-surface runways.[10]
| Airports - with paved runways | |
|---|---|
| Total | 39 |
| > 3,047 m | 3 |
| 2,438 to 3,047 m | 22 |
| 1,524 to 2,437 m | 8 |
| 914 to 1,523 m | 2 |
| < 914 m | 4 |
| Airports - with unpaved runways | |
|---|---|
| Total | 43 |
| 2,438 to 3,047 m | 3 |
| 1,524 to 2,437 m | 17 |
| 914 to 1,523 m | 15 |
| < 914 m | 8 |
See also
References
-
 This article incorporates public domain material from the Library of Congress Country Studies website http://lcweb2.loc.gov/frd/cs/.
This article incorporates public domain material from the Library of Congress Country Studies website http://lcweb2.loc.gov/frd/cs/.
- ↑ United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (July 2, 2008). "UNHCR Freedom in the World 2008 - North Korea". Unhcr.org. Retrieved 2011-04-08.
- ↑ North Korea: Freedom of movement, opinion and expression - Information sheet, Amnesty International, PDF, published 2 August 2009, accessed 2011-04-08
- ↑ "North Korea: Transportation". CIA World Factbook. Retrieved July 13, 2013.
- 1 2 "Driving in North Korea and Speed Limit Regulations". New Focus International. Feb 24, 2013. Retrieved July 13, 2013.
- 1 2 "North Korean traffic police moonlight as service stations". New Focus International. July 12, 2013. Retrieved July 13, 2013.
- ↑ Kokubu, Hayato, 将軍様の鉄道 (Shōgun-sama no Tetsudō), ISBN 978-4-10-303731-6
- ↑ Rob Dickinson. "A Glimpse of North Korea's Railways". The International Steam Pages. Archived from the original on 2 May 2008. Retrieved 4 July 2009.
- ↑ Paul French (2007). North Korea: The Paranoid Peninsula – A Modern History. 2nd ed. New York: Zed Books, p. 18, ISBN 1842779052.
- ↑ http://www.routesonline.com/news/29/breaking-news/222819/miat-mongolian-airlines-launches-north-korea-service-in-october-2013/
- ↑ https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/kn.html
Further reading
- Download a map of the entire North Korean Railway system to Google Earth here.
- Ducruet, Cesar et Jo, Jin-Cheol (2008) Coastal Cities, Port Activities and Logistic Constraints in a Socialist Developing Country: The Case of North Korea, Transport Reviews, Vol. 28, No. 1, pp. 1–25: http://www.informaworld.com/smpp/462288788-26821155/content~content=a782923580~db=all~tab=content~order=page
- Jo, Jin-Cheol et Ducruet, Cesar (2007) Rajin-Seonbong, new gateway of Northeast Asia, Annals of Regional Science, Vol. 41, No. 4, pp. 927–950: http://www.springerlink.com/content/625g177v07722201
- Jo, Jin-Cheol et Ducruet, Cesar (2006) Maritime trade and port evolution in a socialist developing country : Nampo, gateway of North Korea, The Korea Spatial Planning Review, Vol. 51, pp. 3–24: http://library.krihs.re.kr/file/publication/att_file/publication2/PR51_01.pdf
- DUCRUET, Cesar, JO, Jin-Cheol, LEE, Sung-Woo, ROUSSIN, Stanislas, 2008, Geopolitics of shipping networks: the case of North Korea's maritime connections, Sustainability in International Shipping, Port and Logistics Industries and the China Factor, International Association of Maritime Economists (IAME), Dalian, China, April 2–4.
- DUCRUET, Cesar, ROUSSIN, Stanislas, 2007, The changing relations between hinterland and foreland at North Korean ports (1985–2006), 6th Inha & Le Havre International Conference, Inha University, Incheon, Republic of Korea, October 10–11.
- DUCRUET, Cesar, ROUSSIN, Stanislas, 2007, Inter-Korean maritime linkages: economic integration vs. hub dependence, 15th European Conference on Theoretical and Quantitative Geography, Montreux, Switzerland, September 7–11, pp. 133–139 ISBN 978-2-940368-05-1.
- ROUSSIN, Stanislas, DUCRUET, Cesar, 2007, The Nampo-Pyongyang corridor: a strategic area for European investment in DPRK, Recent Changes in North Korea and the Role of the European Union, Institute of Unification Studies & Hans Seidel Foundation, Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea, June 1.
- ROUSSIN, Stanislas, DUCRUET, Cesar, 2007, Doing business in DPRK for the European companies: the logistic issue, Seogang University, Seoul, Republic of Korea, May 26.
- ROUSSIN, Stanislas, DUCRUET, Cesar, 2006, Logistic perspectives in DPRK, Annual Fall Meeting of the Korean Society of Coastal and Ocean Engineers, Seoul, Republic of Korea, September 15–16.
- Ducruet, Cesar et Roussin, Stanislas (2007) Coree du Nord : vers l'ouverture des ports maritimes, Journal de la Marine Marchande, No. 4566, Juin 22, pp. 6–9.
- Ducruet, Cesar et Roussin, Stanislas (2007) L'archipel nord-coreen : transition economique et blocages territoriaux, Mappemonde, Vol. 87, http://mappemonde.mgm.fr/num15/articles/art07302.html
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Transport in North Korea. |
- Air Koryo Official Web Site
- Pyongyang Metro System Unofficial Web Site
- Drive through central Pyongyang at rush hour on National Day Holiday on YouTube



