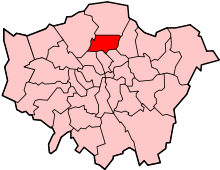
Tottenham
| Tottenham | |
 Grade I listed tower near Bruce Castle |
|
 Tottenham |
|
| Population | 129,237 (2011 census)[1] |
|---|---|
| OS grid reference | TQ344914 |
| – Charing Cross | 8.2 mi (13.2 km) SSW |
| London borough | Haringey |
| Ceremonial county | Greater London |
| Region | London |
| Country | England |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | LONDON |
| Postcode district | N15, N17 |
| Dialling code | 020 |
| Police | Metropolitan |
| Fire | London |
| Ambulance | London |
| EU Parliament | London |
| UK Parliament | Tottenham |
| London Assembly | Enfield and Haringey |
Coordinates: 51°36′18″N 0°03′29″W / 51.605°N 0.058°W
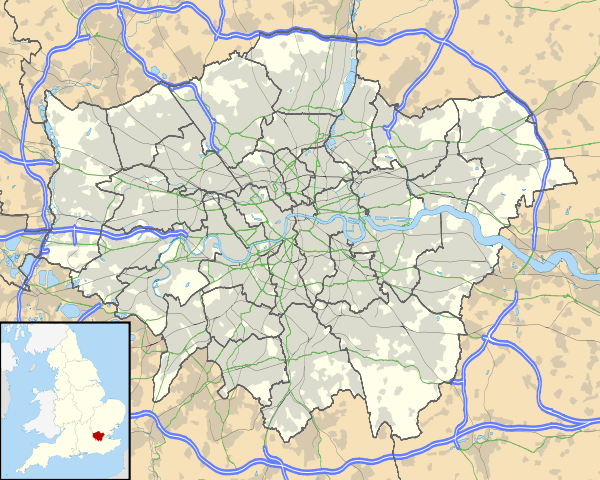
Tottenham (/ˈtɒtᵊnəm/;[2] local /ˈtɒʔnəm/[3]) is an area in the London Borough of Haringey, in north London, England. It is situated 8.2 miles (13.2 km) north-north-east of Charing Cross.
History
Toponymy
Tottenham is believed to have been named after Tota, a farmer, whose hamlet was mentioned in the Domesday Book; hence Tota's hamlet became Tottenham. It was recorded in the Domesday Book as Toteham.[4]
Early history
.jpg)
There has been a settlement at Tottenham for over a thousand years. It grew up along the old Roman road, Ermine Street (some of which is part of the present A10 road), and between High Cross and Tottenham Hale, the present Monument Way.
When the Domesday Book was compiled in 1086, about 70 families lived within the area of the manor, mostly labourers working for the Lord of the Manor. A humorous poem entitled the Tournament of Tottenham, written around 1400, describes a mock-battle between peasants vying for the reeve's daughter.
In 1894, Tottenham was made an urban district and on 27 September 1934 it became a municipal borough. As from 1 April 1965, the municipal borough formed part of the London Borough of Haringey.
The River Lea (or Lee) was the eastern boundary between the Municipal Boroughs of Tottenham and Walthamstow. It is the ancient boundary between Middlesex and Essex and also formed the western boundary of the Viking controlled Danelaw. Today it is the boundary between the London Boroughs of Haringey and Waltham Forest. A major tributary of the Lea, the River Moselle, also crosses the borough from west to east, and often caused serious flooding until it was mostly covered in the 19th century.
From the Tudor period onwards, Tottenham became a popular recreation and leisure destination for wealthy Londoners. Henry VIII is known to have visited Bruce Castle and also hunted in Tottenham Wood. A rural Tottenham also featured in Izaak Walton's book The Compleat Angler, published in 1653.[5] The area became noted for its large Quaker population[6] and its schools (including Rowland Hill's at Bruce Castle.[7]) Tottenham remained a semi-rural and upper middle class area until the 1870s.
Modern era
In late 1870, the Great Eastern Railway introduced special workman's trains and fares on its newly opened Enfield and Walthamstow branch lines. Tottenham's low-lying fields and market gardens were then rapidly transformed into cheap housing for the lower middle and working classes, who were able to commute cheaply to inner London. The workman's fare policy stimulated the relatively early development of the area into a London suburb.
An incident occurred on 23 January 1909, which was at the time known as the Tottenham Outrage.[8] Two armed robbers of Russian extraction held up the wages clerk of a rubber works in Chesnut Road. They made their getaway via Tottenham Marshes and fled across the Lea. On the opposite bank of the river they hijacked a Walthamstow Corporation tramcar, hotly pursued by the police on another tram. The hijacked tram was stopped but the robbers continued their flight on foot. After firing their weapons and killing two people, Ralph Joscelyne, aged 10, and PC William Tyler, they were eventually cornered by the police and shot themselves rather than be captured. Fourteen other people were wounded during the chase. The incident later became the subject of a silent film.[9]
During the Second World War Tottenham also became a target of the German air offensive against Britain. Bombs fell within the borough (Elmar Road) during the first air raid on London on 24 August 1940. The borough also received V-1 (four incidents) and V-2 hits, the last of which occurred on 15 March 1945. Wartime shortages led to the creation of Tottenham Pudding, a mixture of household waste food which was converted into feeding stuffs for pigs and poultry. The "pudding" was named by Queen Mary on a visit to Tottenham Refuse Works. Production continued into the post-war period, its demise coinciding with the merging of the borough into the new London Borough of Haringey.

In 1985, the Broadwater Farm housing estate in Tottenham was the scene of rioting between the police and local youths following the death of Cynthia Jarrett, a resident of Tottenham but who lived about a mile from the estate who died of heart failure after four policemen burst into her home. The response of the members of the black community in Tottenham and surrounding areas culminated in a riot beginning on Tottenham High Road and ending in the local Broadwater Farm Estate. One police officer, Keith Blakelock, was murdered; 58 policemen and 24 other people were injured in the fighting. Two of the policemen were injured by gunshots during the riot, the first time that firearms had been used in that type of confrontation.
Tottenham witnessed a high crime rate mostly related to drug dealers and gangs. In 1999, Tottenham was identified as one of the yardies' strongholds in London, along with Stoke Newington, Harlesden, Lambeth and Brixton.[10]
The Mecca Dance Hall was demolished in 2004 to make way for local housing.
The 2011 England riots were precipitated by the fatal shooting of a 29-year-old man in Tottenham, Mark Duggan, by officers of the Metropolitan Police Service on 4 August 2011.[11][12][13][14]
Railways

- The Northern and Eastern Railway – running from Stratford to Broxbourne – was opened on 15 September 1840 with two stations in the district: Tottenham and Marsh Lane.
- The Tottenham & Hampstead Junction Railway was opened on 21 July 1868. South Tottenham station was opened in 1871, while two other stations on this line in the Tottenham area were opened later: Harringay Park (Green Lanes) opened in 1880, and St Ann's Road opened in 1882 but closed after service on 8 August 1942.
- The Stoke Newington & Edmonton Railway – The section between Stoke Newington and Lower Edmonton opened on 22 July 1872 with stations in Tottenham at Stamford Hill (half of the station lies in the borough), Seven Sisters, Bruce Grove and White Hart Lane.
- The Palace Gates Line opened in Tottenham on 1 January 1878 with stations at Seven Sisters and West Green. Passenger services ceased in 1963 with the line finally closing on 7 February 1965.
- The Tottenham & Forest Gate Railway opened on 9 July 1894.
- The London Underground's Piccadilly line extension through Tottenham opened on 19 September 1932.
- The first section of the London Underground's Victoria line opened on 1 September 1968.
Governance
Parliament
Tottenham is covered by the parliamentary constituency of Tottenham. The constituency was created in 1885 when the first MP was Joseph Howard of the Conservative Party, but was replaced by two constituencies: Tottenham North and Tottenham South in 1918. Since being reinstated in 1950 it has been predominantly represented by Labour Party candidates, with the exception of Alan Brown who defected to the Conservatives. The current MP is David Lammy who won a by-election in 2000 following the death of Bernie Grant.
Local Government
Tottenham developed from a parish in Middlesex into an Urban sanitary district in 1875, after a local board of health had been established in 1850, then divided in 1888 so that Wood Green became a separate authority.[15] In 1894 Tottenham was reconstituted first as an urban district then as a municipal borough in 1934, before being subsumed into the larger London Borough of Haringey under the Local Government Act 1963.
Today, Tottenham is represented by nine local council wards: Seven Sisters, Harringay, St Ann's, Tottenham Hale, Tottenham Green, White Hart Lane, West Green, Northumberland Park and Bruce Grove. Councillors in 8 of these wards represent the Labour Party, the ninth (Harringay) being represented by the Liberal Democrats.
Geography
Districts
Tottenham is a large area incorporating the N15 and N17 postcode areas.
North Tottenham
This area stretches along Tottenham High Road from the Edmonton border in the north to Lordship Lane in the south: districts include Little Russia and Northumberland Park. Landmarks include White Hart Lane, home of Tottenham Hotspur, White Hart Lane station and Northumberland Park station.
Central Tottenham
Continuing along the high road, Central Tottenham includes Bruce Grove, Tottenham Green and Tottenham Hale wards, as well as Tottenham Hale station and retail park, Tottenham Marshes (part of the Lee Valley Regional Park) and Bruce Castle.
South Tottenham
Further along the A10 road until St Ann's Road, this area includes South Tottenham, St Ann's neighbourhood, West Green and Seven Sisters. Transport links include Seven Sisters station and South Tottenham station. Landmarks include the Markfield Beam Engine and Downhills Park.
West Tottenham
To the west of the area are Broadwater Farm, the Tower Gardens Estate and Lordship Recreation Ground.
Neighbouring areas
North
The northern limit of Tottenham is north of Brantwood Road where Upper Edmonton begins. This is also the border between the London Borough of Haringey and the London Borough of Enfield. To the northwest is Palmers Green.
East
The eastern limit of Tottenham is the River Lea, and across the river the neighbouring district is Walthamstow in the London Borough of Waltham Forest
South
The southern limit of Tottenham is the junction of St. Ann's Road with Tottenham High Road, which after becomes Stamford Hill. The district of Stamford Hill borders Tottenham, marking also the border of the London Borough of Hackney. To the southwest, Tottenham borders Manor House and Harringay, briefly meeting the London Borough of Islington.
West
Although the N15 postcode area extends to Green Lanes, the western border of Tottenham is better defined as Black Boy Lane, West Green Road and Downhills Way. The neighbouring districts are Harringay, Hornsey, Wood Green and Noel Park.
Demography and crime
Ethnic composition
Tottenham has a multicultural population, with many ethnic groups inhabiting the area. It contains one of the largest and most significant populations of African-Caribbean people. These were among the earliest immigrant groups to settle in the area, starting the UK's Windrush era. Soon afterwards West African communities – notably the many Ghanaians – began to migrate into the area. Between 1980 and the present day there has been a slow immigration of Colombians, Congolese, Albanian, Kurdish, Turkish-Cypriot, Turkish, Somali, Irish, Portuguese, Polish and Zimbabweans populations. South Tottenham is reported to be the most ethnically-diverse area in Europe, with up to 300 languages being spoken by its residents.[16]
According to David Lammy MP, Tottenham has the highest unemployment rate in London and the 8th highest in the United Kingdom, and it has some of the highest poverty rates within the country.[17] There have also been major tensions between the African-Caribbean community and the police since (and before) the 1985 Broadwater Farm riot.
The 2011 ethnic groups in Tottenham are as follows:
- 22.3% White British
- 27.7% Other White
- 10.7% Asian
- 26.7% Black
- 12.6% Other/Mixed
Organised crime
Tottenham has been one of the main hotspots for gangs and gun crime in the United Kingdom during the past three decades. This followed the rise of gangs and drug wars throughout the area, notably those involving the Tottenham Mandem gang and various gangs from Hackney and all of the areas surrounding Tottenham, and the emergence of an organised crime ring known as the Turkish mafia was said to have controlled more than 90% of the UK's heroin market.[19][20]
Riots
- The Broadwater Farm riot occurred around the Broadwater Farm area on 6 October 1985 following the death of Cynthia Jarrett in a police search of her home. The tension between local black youth and the largely white Metropolitan Police had been high due to a combination of local issues and the aftermath of riots in Brixton which had occurred in the previous week. The riots resulted in the murder of a police officer.[21]

- The 2011 Tottenham riots were a series of riots by protesters in Tottenham, London. Attacks were carried out on two police cars, a bus, a Post Office and several local shops from 8:00 pm onwards on 6 August 2011. Riot police vans attended the scene of disturbances on Tottenham High Road. Later in the evening the riot spread, with an Aldi supermarket and a branch of Allied Carpets also destroyed by fire, and widespread looting in nearby Wood Green shopping centre and the retail park at Tottenham Hale. Several flats above shops on Tottenham High Road collapsed due to the fires. 26 shared ownership flats in the Union Point development above the Carpetright store – built in the landmark Cooperative department store building – were also completely destroyed by fire. The triggering event was when a group of over one hundred local Tottenham residents set out to undertake a protest march against the killing of Mark Duggan, who was shot by police officers assigned to Operation Trident earlier in the week. The circumstances surrounding Duggan's death were not entirely clear at the time of the riot. On 17 August 2011 the Prince of Wales and his wife Duchess of Cornwall visited an emergency centre to meet victims of the riots.[22]
Landmarks

- All Hallows Church – This is the oldest surviving building in the borough and dates back to Norman times. For more than 700 years it was the original parish church for Tottenham. Presented in 1802 with a bell from the Quebec Garrison, which was captured from the French in the 1759 Battle of Quebec, Canada. Adjacent to the church is
- Tottenham Cemetery – A large cemetery, which makes up part of an open access area of land and habitat, along with Bruce Castle Park and All Hallows Churchyard.[23]
- Broadwater Farm – Housing estate built in 1967; it was the site of the Broadwater Farm riot in 1985.
- Brook Street Chapel – Non-denominational Christian chapel, established in 1839, and one of the earliest Plymouth Brethren /Open Brethren assemblies in London that still exists. The church was associated with local notable Christians such as Hudson Taylor, Dr Barnardo, John Eliot Howard, Luke Howard and Philip Gosse.[24]
- Bruce Castle, Lordship Lane – Grade 1 listed, it was Tottenham's manor house and dates from the sixteenth century, with alterations by subsequent occupants. It was given the name 'Bruce Castle' during the seventeenth century by the 2nd Lord Coleraine, who was Lord of the Manor at the time. He named it after 'Robert the Bruce', whose family had been lords of the manor during the medieval period. The building was purchased by the Hill family, who turned it into a progressive school. Sir Rowland Hill was its first headmaster, and he was living there in 1840 when he, as Postmaster General, introduced the Uniform Penny Post.[25] Now a local history museum, Bruce Castle holds the archives of the London Borough of Haringey.
- 7 Bruce Grove – The building features an English Heritage blue plaque commemorating Luke Howard (1772–1864), the 'Father of Meteorology', who named the clouds in 1802.
- Northumberland Row – Erected circa 1740 on the site of the former Smithson seat, previously that of the Hynningham family. The gate piers are possibly from Bruce Castle. The wrought iron gate bears the monogram HS for one of the two Hugh Smithsons, both Tottenham landowners and sometime MPs for Middlesex.
 Centre-piece of Northumberland Row. (May 2013).
Centre-piece of Northumberland Row. (May 2013). - Clyde Circus conservation area
- Edmanson’s Close – Previously known as the Almshouses of the Drapers' Company, they were built in 1870 and were established through the generosity of three seventeenth-century benefactors, Sir John Jolles, John Pemel and John Edmanson.
- High Cross – Erected sometime between 1600 and 1609 on the site of an earlier Christian cross, although there is some speculation that the first structure on the site was a Roman beacon or marker, situated on a low summit on Ermine Street. Tottenham High Cross is often mistakenly thought to be an Eleanor cross.
- Markfield Beam Engine
- St Ann's Church – Consecrated in 1861, St Ann's Church houses the organ that was originally in Crosby Hall, Bishopsgate, on which Felix Mendelssohn Bartholdy, who composed the famous Wedding March from A Midsummer Night's Dream, regularly gave recitals.
- St Ignatius' Church and College – Built between 1894 and 1902, with two towers in the style of a 12th-century German cathedral, this Catholic church is situated at the foot of Stamford Hill and dominates the area.
- Tower Gardens Estate – Previously known as the LCC White Hart Lane Estate, this "out of county" LCC cottage housing estate was constructed beginning in 1904. The architectural style is said to be inspired by houses in Ghent, Belgium. The estate was the home of Harry Champion, a well-known music hall star and performer of the song "I'm Henery the Eighth, I Am".
Transport
Two London Underground lines serve the Tottenham area.[26] The Piccadilly line, which opened in 1932, has one station Turnpike Lane, which was the first Underground station within the then Tottenham Borough boundaries.[26] The Victoria line, which opened in 1968, has its operating depot in Tottenham at Northumberland Park, as well as two stations, Seven Sisters and Tottenham Hale, in the area.[26] Stations Seven Sisters, Tottenham Hale, Bruce Grove, White Hart Lane and Northumberland Park also serve the area with train services provided by London Overground, apart from Tottenham Hale and Northumberland Park which is only a National Rail stations, however if Crossrail 2 gets planning permission to be made then both those stations will also be served by Crossrail services between Hertford East and several destinations in Surrey. Those two stations are on the main Lea Valley Line; the West Anglian Main Line, with services provided by Abellio Greater Anglia, while Seven Sisters, Bruce Grove and White Hart Lane are all on the Lea Valley; Cheshunt/Enfield Town Line which services are provided by London Overground. London Overground trains also serve South Tottenham station on the Gospal Oak-Barking Line.[26][27]
Sport
Tottenham is the home of Premier League football club Tottenham Hotspur. Tottenham have won the Football League twice, the FA Cup eight times, the UEFA Cup twice, the UEFA Cup Winners' Cup once and the Football League Cup, four times. In 2010, they qualified for the UEFA Champions League, Europe's elite competition for the first time.[28] The club's home ground is White Hart Lane, located on Park Lane, rather than the road of the same name. The ground is named after the White Hart Inn that it was built behind, and the nearest station to the ground.
Tottenham also has two non-League football clubs, Haringey Borough F.C. and Haringey & Waltham Development F.C., which both play at Coles Park.
Namesakes

Tottenham cake is a sponge cake baked in large metal trays, covered either in pink icing or jam (and occasionally decorated with shredded desiccated coconut). Tottenham Cake "was originally sold by the baker Henry Chalkley, who was a Friend (or Quaker), at the price of one old penny, with smaller mis-shaped pieces sold for half an old penny." The pink colouring was derived from mulberries found growing at the Tottenham Friends burial ground.[29] Originally "a peculiar local invention"[30] of north London, the cake is now mass-produced by the Greggs chain of bakers.
Mentioned in films
- In Bruges. "Purgatory's kind of like the in-betweeny one. You weren't really s*, but you weren't all that great either. Like Tottenham."
Notable people
- Dotun Adebayo radio presenter, writer and publisher, lived and attended school in Tottenham.
- Adele (b. May 1988, Adele Laurie Blue Adkins), singer-songwriter and musician, was born in Tottenham.
- Alex Boyé, Mormon singer and actor.
- Dave Clark, leader of the Dave Clark Five.
- Teriy Keys, music executive, entrepreneur founder and co-chief executive officer of R.O.A.D. Group.
- George Harrison Marks, English glamour photographer and director of adult films born in Tottenham.
- Mark Hollis, English musician and songwriter known for Talk Talk and a short solo career.
- Richard Hudson, singer-songwriter and musician (Elmer Gantry's Velvet Opera, Strawbs) born in Tottenham.
- David Lindon Lammy, Labour Party politician, MP for Tottenham since 2000.
- Meridian Dan, MC born & raised in Tottenham known for his track "German Whip" which peaked at #13 in the UK Singles Chart.
- Ron Moody, actor, born in Tottenham.
- Trevor Peacock, actor, born in Tottenham.
- Leslie Phillips, actor, born in Tottenham.
- Skepta and Jme, MCs and members of the Boy Better Know (BBK) group.
- Chip (rapper), MC born & raised in Tottenham.
- David Triesman, former chairman of the Football Association and Labour peer in the House of Lords, is from Tottenham.
- Shani Wallis, actress and singer. Played Nancy in the 1968 film of Oliver.
- John Williams, shipbuilder, and missionary in the South Pacific.
- Ted Willis, playwright, best known for the BBC TV programme Dixon of Dock Green.
- Wretch 32, MC born & raised in Tottenham
- Bob Bradbury, musician, lead singer and founder member of 70's Glam Rock band Hello, lived and attended school in Tottenham.
References
- ↑ http://www.neighbourhood.statistics.gov.uk/dissemination/LeadTableView.do?a=7&b=6508207&c=tottenham&d=27&e=62&g=6326938&i=1001x1003x1032x1004&o=322&m=0&r=1&s=1462472756642&enc=1&dsFamilyId=2477
- ↑ "Tottenham". Oxford English Dictionary (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press. September 2005. (Subscription or UK public library membership required.)
- ↑ How to pronounce place names with "ham" in them
- ↑ "DocumentsOnline | Image Details". The National Archives. Retrieved 10 December 2009.
- ↑ "The Complete Angler by Isaak Walton – Free eBook". Manybooks.net. Retrieved 10 December 2009.
- ↑ "Tottenham Quaker Meeting (Religious Society of Friends)". Tottenhamquakers.org.uk. Retrieved 10 December 2009.
- ↑ "E.Howard, ''Eliot Papers'', 1895". Archive.org. Retrieved 10 December 2009.
- ↑ The Tottenham Outrage. Retrieved 2 February 2008.
- ↑ Tottenham outrage- silent film. Retrieved 10 November 2008.
- ↑ http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/uk/398197.stm
- ↑ Lewis, Paul (7 August 2011). "Tottenham riots: a peaceful protest, then suddenly all hell broke loose". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 7 August 2011.
- ↑ "Tottenham in flames as protesters riot". The Guardian. London. 6 August 2011. Retrieved 6 August 2011.
- ↑ "Tension builds in Enfield Town as small groups arrive in area". Enfield Independent. Retrieved 7 August 2011.
- ↑ Bracchi, Paul (8 August 2011). "Violence, drugs, a fatal stabbing and a most unlikely martyr". Daily Mail. London: Associated Newspapers. Archived from the original on 8 August 2011. Retrieved 8 August 2011.
- ↑ Great Britain Historical GIS / University of Portsmouth, Tottenham parish (historic map). Retrieved on 10 February 2008.
- ↑ JUMANA FAROUKY (15 February 2007). "Unity Begins at Home – TIME". TIME<!. Retrieved 10 December 2009.
- ↑ David Lammie. "Response to the Comprehensive Spending Review". Retrieved 25 February 2011.
- ↑ http://ukpollingreport.co.uk/2015guide/tottenham/
- ↑ TONY THOMPSON (17 November 2002). "Heroin 'emperor' brings terror to UK streets". The Guardian. London.
- ↑ BBC (17 May 2002). "Yardies convicted in torture case". BBC News.
- ↑ Newman, K. [http://www.police-foundation.org.uk/files/POLICE0001/speeches/1986%20Sir%20Kenneth%20Newman.pdf Police-Public Relations: The Pace of Change: Police Foundation Lecture 1986, The Police Foundation, 1986
- ↑ News report Retrieved 22 August 2011
- ↑ Archived 8 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Brook Street Chapel". Brook Street Chapel. 31 October 2009. Retrieved 10 December 2009.
- ↑ "Bruce Castle Museum". Haringey.gov.uk. Retrieved 10 December 2009.
- 1 2 3 4 Transport for London (January 2016). Standard Tube Map (PDF) (Map). Not to scale. Transport for London. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 January 2015.
- ↑ Transport for London (October 2015). London Overground Map (PDF) (Map). Not to scale. Transport for London. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 January 2016.
- ↑ Tottenham Hotspur at the Football Club History Database
- ↑ Ferris, Ken; Lane, Wyart. "Frequently Asked Questions about the Spurs" (HTTP). The 'My Eyes Have Seen the Glory' website. Retrieved 22 September 2009.
- ↑ "Dressed in Simplicity: 300 years of Quakers in Tottenham". Retrieved 30 January 2014.
External links
- Tottenham: Growth before 1850
- World War Two memories (V2 rocket attack on Tottenham Grammar School)
- 1909 Tottenham Outrage
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tottenham. |