Three Hummock Island
|
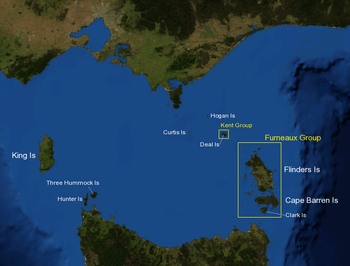
Three Hummock Island is shown in the lower left on the map, in the Bass Strait between Tasmania and Victoria. | |
 Three Hummock Island Location of the Three Hummock Island in the Bass Strait | |
| Etymology | Three prominent hills: North, Middle and South Hummock |
|---|---|
| Geography | |
| Location | Bass Strait |
| Coordinates | 40°26′24″S 144°54′36″E / 40.44000°S 144.91000°ECoordinates: 40°26′24″S 144°54′36″E / 40.44000°S 144.91000°E |
| Archipelago | Hunter Group |
| Area | 70 km2 (27 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 237 m (778 ft) |
| Highest point | South Hummock |
| Administration | |
| State | Tasmania |
| Largest settlement | Chimney Corner |
| Additional information | |
| Official website |
threehummockisland |
The Three Hummock Island, part of the Hunter Group, is a 70-square-kilometre (27 sq mi) granite island, located in the Bass Strait near King Island, lying off the north-west coast of Tasmania, Australia.[1]
The island is named after its three most prominent hills, North, Middle and South Hummock, the latter being the highest with an elevation of 237 metres (778 ft) above mean sea level. Part of the island is a nature reserve, with the rest a pastoral lease where farming took place from the mid-1800s to at least the mid-1970s. The focus of human settlement on the island is the homestead at Chimney Corner at the westernmost point. There is an automated lighthouse at Cape Rochon in the north-east, as well as roads, three airstrips, fencing and a wharf. Seasonal muttonbirding occurs in March and April.[2]
Flora and fauna
Much of the island is composed of dense scrub dominated by Leptospermum scoparium, Melaleuca ericifolia and Banksia marginata, while 25% of the area is covered by Eucalyptus nitida woodland.[2]
The island forms part of the Hunter Island Group Important Bird Area.[3] Breeding seabirds and shorebirds include little penguin, short-tailed shearwater, Pacific gull, pied oystercatcher, sooty oystercatcher and hooded plover. Mammals include the introduced eastern grey kangaroo, feral cat and house mouse. Feral sheep were recorded in a 1999 survey. Tiger snakes are also present.[2]
European settlement
Nichols family
Bill and Amelia ("Ma") Nichols leased Three Hummock Island from 1933 till 1950, and grazed cattle and sheep. They were also involved in fishing and muttonbirding. Over the years they owned several ships including Lady Jean, Lady Flinders, and Jean Nichols which were used to carry cargo and passengers to and from the Bass Strait islands and to Melbourne and Launceston. They built up a small community of workers on the island, including some of their relations. One of these workers was Peggy Puckett, from Stanley. Her story is told in A Walk Along the Shore [4] in which she describes life on the island with the Nichols family during the six years she lived with them from 1937 to 1943. Mrs Nichols named Peg's Paddock after her, mentioned in both A Walk Along the Shore and Eleanor Alliston's Escape to An Island.
The Nicols family left the island in 1950 and the Alliston family arrived in 1951.
Alliston family
Author Eleanor Alliston wrote Escape to an Island and Island Affair about the life of her family on Three Hummock Island. The two books tell the story of how the Alliston family emigrated from England after the end of World War II to start a new life alone on the island in the hope of providing a better and different childhood for their children. The books have much between the lines left to readers' imaginations. The second book ends in 1984, the island having a population of two—the author and her husband; their four children, who were brought up on the island, having left it, married with families and having a total of ten grandchildren.
In the 1990s one of the Alliston children, Rob, returned to the island to run a tourist venture. The Alliston family sold the lease in 2006. The island now operates as an eco-tourism resort with accommodation for up 18 people managed by John and Beverley O’Brien.
The book Island Affair contains mention of Giuseppe Garibaldi's visit to the island in 1852 while in exile from Italy as a captain of the trading vessel Carmen.[5][6]
References
- ↑ "Three Hummock Island (TAS)". Gazetteer of Australia online. Geoscience Australia, Australian Government.
- 1 2 3 Brothers, Nigel; Pemberton, David; Pryor, Helen; & Halley, Vanessa. (2001). Tasmania’s Offshore Islands: seabirds and other natural features. Tasmanian Museum and Art Gallery: Hobart. ISBN 0-7246-4816-X
- ↑ BirdLife International. (2011). Important Bird Areas factsheet: Hunter Island Group. Downloaded from http://www.birdlife.org on 09/07/2011.
- ↑ https://archive.org/details/AWalkAlongTheShore A Walk Along the Shore (Jenny Pearce)
- ↑ 1852-53 - As a "citizen of Peru," he captains a clipper to the far east, returning to Lima via Australia and New Zealand. - Life and Times of Giuseppe Garibaldi - The Reformation Online
- ↑ Garibaldi, Giuseppi (1889). Werner, A., ed. Autobiography of Giuseppi Garibaldi. London: Walter Smith and Innes. pp. 65–66. Retrieved 26 January 2016.
... we passed through Bass's Strait, between Australia and Van Diemen's Land. Touching at one of the Hunter Islands, to take in water, we found a small farm, lately deserted by an Englishman and his wife, on the death of his partner. This information we obtained from a board erected on the settler's grave, which set forth in brief the history of the little colony. "The husband and wife," said the inscription, "unable to bear the loneliness of the desert island, left it, and returned to Van Diemen.