Sredačka župa

Sredačka Župa (Serbian Cyrillic: Средачка Жупа; "county of Sredska") is a remote geographical region, a valley, in southeastern Kosovo, below the Šar Mountains at the source of the Prizrenska Bistrica.
Geography

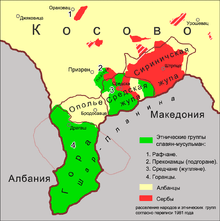
The region, an oval basin, lies below the Šar Mountains, at the source, upper stream of the Prizrenska Bistrica ("Prizren river").[1][2] South of the region between the Prizren mountains and Koritnik mountain, lies the Gora region.[2]
It currently includes Sredska, Pousko, Jablanica, Lokvica, Rečane, Živinjane, Planjane, Nebregošte, Manastirica, Struže, Donje Ljubinje, Gornje Ljubinje, Drajčići, Mušnikovo, Gornje Selo.
History
It was a medieval župa (small administrative division) of the Serbia in the Middle Ages in modern-day southeastern Kosovo. It encompassed seven hamlets and was centered in the town of Sredska. In the early 19th century, Sredačka župa was inhabited by Serbs, and in the first decades Serbian schools were opened here.[3] During the Serbo-Turkish War (1876–78), in the Prizren surroundings there existed the bajrak (district) of Opolje, Ljubinje (Sredačka župa), Suva Reka, Ostrozub, Ljum and Gora.[4]
Between 1918 and 1945 Sredačka Župa was a municipality of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. After World War II, in 1945, the Slavophone Muslims in Sredačka župa were ascribed Albanian ethnicity and names by state institutions (as was the case with Gorani and other Muslim non-Albanian speakers).[5] The region was annexed into the municipality of Prizren by the FPR Yugoslavia (1945–63). In 1953, there were 12 villages in the region, and the region was inhabited by "Serbs [...] divided into Muslims and Orthodox" in all villages except Stružje (Struže) inhabited by Albanian Muslims.[1]
Culture

- Monuments
- Church of the Holy Virgin, Sredska.
- Church of St. George, Sredska.
Demographics and anthropology
The region is inhabited by a majority of Bosniaks and minority of Serbs (who left during and following the Kosovo War). The community was one of several groups noted having Serb origin and language in the Prizren region (Šarplaninska Gora, Sredačka župa, Prizrenski Podgor, Prizrensko Polje, Podrima) that did not submit to Albanization.[6]
Notable people
- Vuk Isakovič (1696-1759), Austrian soldier
- Čolak-Anta (1777-1853), Serbian revolutionary
- Jake Allex (1887-1959), Serbian-American soldier
- Hasbija Kalajdzini (1940-2016) Leader
Annotations
It is known in historiography as Sredačka Župa (Средачка Жупа), Sredska Župa (Средска Жупа) and Sretečka Župa[7] meaning "county of Sredska")
References
- 1 2 Mitar S. Vlahović (1953). Zbornik Etnografskog muzeja u Beogradu. Naučna knjiga. pp. 90–100.
- 1 2 Narodna privreda u prisajedinjenim oblastima: izveštaji komisija ministrstva narodne privede. Izd. ministarstva narodne privrede. 1914. p. 190.
- ↑ Zbornik za historiju školstva i prosvjete. 13-15. Hrvatski školski muzej. 1980. p. 110.
- ↑ Glasnik Srbskog učenog društva. 43. u Državnoj štampariji. 1876. p. 32.
У призренском окружију броје се сљедећи барјаци: опољски, љубински (средска жупа), сухоречки, острозубски, љумски, горански и др. Села опољске жупе расположена су на огранцима Шарпланине са севера.
- ↑ Dve domovini: razprave o izseljenstvu. Inštitut za slovensko izseljenstvo. 2008. p. 75.
- ↑ Srboljub Đ Stamenković (2001). Географска енциклопедиjа насеља Србиjе: М-Р. Универзитет у Београду. Географски факултет. p. 325. ISBN 978-86-82657-15-6.
- ↑ Mitar S. Vlahović (1953). Zbornik Etnografskog muzeja u Beogradu. Naučna knjiga. pp. 92–100.
Sources
- Mitar S. Vlahović (1953). Zbornik Etnografskog muzeja u Beogradu. Naučna knjiga. pp. 90–100.
- Radovanović, Milovan. Шар планина и њене жупе у косовско-метохијској области јужне Србије (PDF) (in Serbian). Retrieved 5 December 2010.
- Vojislav Tanasković (1992). Sredačka župa: monografija. Jedinstvo. ISBN 978-86-7019-095-5.
Further reading
- Mitar S. Vlahović (1931). Средачка Жупа (Sredačka župa). Зборник за етнографију и фолклор Јужне Србије. Скопље. pp. 27–52.