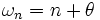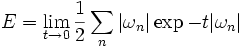Spectral asymmetry
In mathematics and physics, the spectral asymmetry is the asymmetry in the distribution of the spectrum of eigenvalues of an operator. In mathematics, the spectral asymmetry arises in the study of elliptic operators on compact manifolds, and is given a deep meaning by the Atiyah-Singer index theorem. In physics, it has numerous applications, typically resulting in a fractional charge due to the asymmetry of the spectrum of a Dirac operator. For example, the vacuum expectation value of the baryon number is given by the spectral asymmetry of the Hamiltonian operator. The spectral asymmetry of the confined quark fields is an important property of the chiral bag model.
Definition
Given an operator with eigenvalues 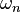 , an equal number of which are positive and negative, the spectral asymmetry may be defined as the sum
, an equal number of which are positive and negative, the spectral asymmetry may be defined as the sum
where 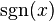 is the sign function. Other regulators, such as the zeta function regulator, may be used.
is the sign function. Other regulators, such as the zeta function regulator, may be used.
The need for both a positive and negative spectrum in the definition is why the spectral asymmetry usually occurs in the study of Dirac operators.
Example
As an example, consider an operator with a spectrum
where n is an integer, ranging over all positive and negative values. One may show in a straightforward manner that the spectral asymmetry in this case is  .
.
Discussion
Related to the spectral asymmetry is the vacuum expectation value of the energy associated with the operator, the Casimir energy, which is given by
This sum is formally divergent, and the divergences must be accounted for and removed using standard regularization techniques.
References
- MF Atiyah, VK Patodi and IM Singer, Spectral asymmetry and Riemannian geometry I, Proc. Camb. Phil. Soc., 77 (1975), 43-69.
- Linas Vepstas, A.D. Jackson, A.S. Goldhaber, Two-phase models of baryons and the chiral Casimir effect, Physics Letters B140 (1984) p. 280-284.
- Linas Vepstas, A.D. Jackson, Justifying the Chiral Bag, Physics Reports, 187 (1990) p. 109-143.