Solar eclipse of July 11, 1953
| Solar eclipse of July 11, 1953 | |
|---|---|
 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Partial |
| Gamma | 1.4388 |
| Magnitude | 0.2015 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Coordinates | 64°18′N 71°42′W / 64.3°N 71.7°W |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 2:44:14 |
| References | |
| Saros | 116 (69 of 70) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9406 |
A partial solar eclipse occurred on July 11, 1953. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses of 1953-1956
Each member in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.
Note: Partial solar eclipse of February 14, 1953 and August 9, 1953 belong to the last lunar year set.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1953–1956 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||
| Saros | Map | Saros | Map | |
| 116 |  July 11, 1953 Partial |
121 |  January 5, 1954 Annular | |
| 126 |  June 30, 1954 Total |
131 |  December 25, 1954 Annular | |
| 136 |  June 20, 1955 Total |
141 | 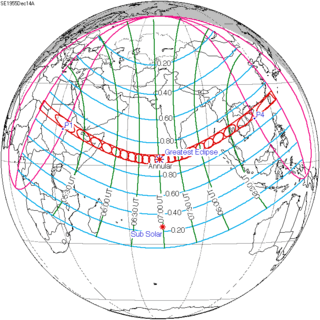 December 14, 1955 Annular | |
| 146 | 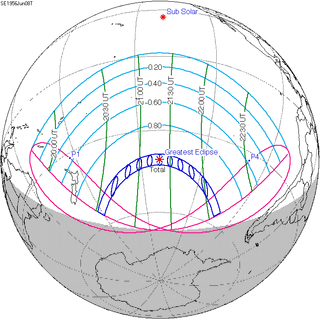 June 8, 1956 Total |
151 | 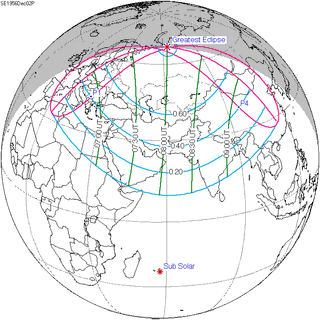 December 2, 1956 Partial | |
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days).
| 21 eclipse events, progressing from north to south between July 11, 1953 and July 11, 2029 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| July 10-11 | April 29-30 | February 15-16 | December 4 | September 21-23 |
| 116 | 118 | 120 | 122 | 124 |
 July 11, 1953 |
 April 30, 1957 |
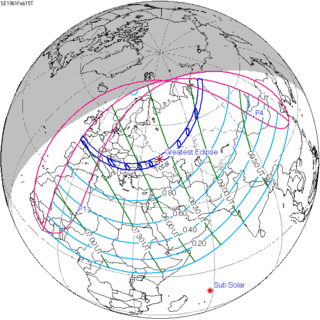 February 15, 1961 |
 December 4, 1964 |
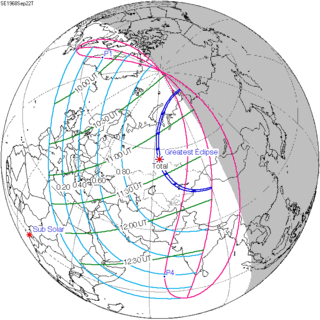 September 22, 1968 |
| 126 | 128 | 130 | 132 | 134 |
 July 10, 1972 |
 April 29, 1976 |
 February 16, 1980 |
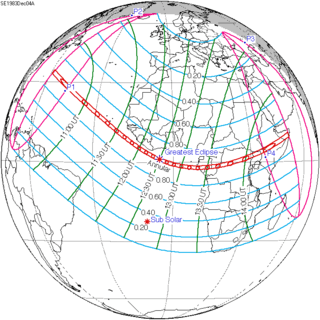 December 4, 1983 |
 September 23, 1987 |
| 136 | 138 | 140 | 142 | 144 |
 July 11, 1991 |
 April 29, 1995 |
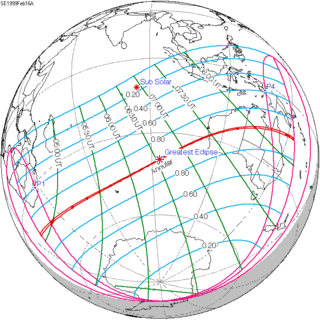 February 16, 1999 |
 December 4, 2002 |
 September 22, 2006 |
| 146 | 148 | 150 | 152 | 154 |
 July 11, 2010 |
 April 29, 2014 |
 February 15, 2018 |
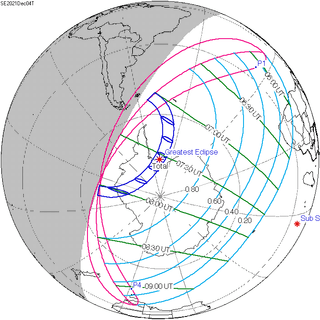 December 4, 2021 |
 September 21, 2025 |
| 156 | ||||
 July 11, 2029 | ||||
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 1953 July 11. |
