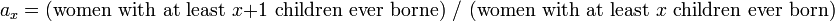Parity progression ratios
A parity progression ratios (PPR) is a measure commonly used in demography to study fertility. The PPR is simply the proportion of women with a certain number of children who go onto have another child.
Calculating the PPR, also known as 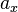 , can be achieved by using the following formula:
, can be achieved by using the following formula:
In more developed countries where two child families are seen as the norm 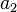 (or the proportion of women with two children who go on to have a third) is of critical importance in determining overall fertility levels.
(or the proportion of women with two children who go on to have a third) is of critical importance in determining overall fertility levels.
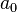 is simply the proportion of women who become mothers.
is simply the proportion of women who become mothers.
References
- ↑ Hinde, A (1998) "Demographic Methods", Hodder Arnold Publication.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/19/2012. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.