Palace



A palace is a grand residence, especially a royal residence or the home of a head of state or some other high-ranking dignitary, such as a bishop or archbishop.[1]
The word itself is derived from the Latin name Palātium, for Palatine Hill, the hill which housed the Imperial residences in Rome.[1] In many parts of Europe, the term is also applied to ambitious private mansions of the aristocracy. Many historic palaces are now put to other uses such as parliaments, museums, hotels or office buildings. The word is also sometimes used to describe a lavishly ornate building used for public entertainment or exhibitions.[1]
Etymology
The word palace comes from Old French palais (imperial residence), from Latin Palātium, the name of one of the seven hills of Rome.[1] The original "palaces" on the Palatine Hill were the seat of the imperial power while the "capitol" on the Capitoline Hill was the religious nucleus of Rome. Long after the city grew to the seven hills the Palatine remained a desirable residential area. Emperor Caesar Augustus lived there in a purposely modest house only set apart from his neighbours by the two laurel trees planted to flank the front door as a sign of triumph granted by the Senate. His descendants, especially Nero, with his "Golden House", enlarged the house and grounds over and over until it took up the hill top. The word Palātium came to mean the residence of the emperor rather than the neighbourhood on top of the hill.
Palace meaning "government" can be recognized in a remark of Paul the Deacon, writing c. AD 790 and describing events of the 660s: "When Grimuald set out for Beneventum, he entrusted his palace to Lupus" (Historia Langobardorum, V.xvii). At the same time, Charlemagne was consciously reviving the Roman expression in his "palace" at Aachen, of which only his chapel remains. In the 9th century, the "palace" indicated the housing of the government too, and the constantly travelling Charlemagne built fourteen. In the early Middle Ages, the palas was usually that part of an imperial palace (or Kaiserpfalz), that housed the Great Hall, where affairs of state were conducted; it continued to be used as the seat of government in some German cities. In the Holy Roman Empire the powerful independent Electors came to be housed in palaces (Paläste). This has been used as evidence that power was widely distributed in the Empire; as in more centralized monarchies, only the monarch's residence would be a palace.
In modern times, the term has been applied by archaeologists and historians to large structures that housed combined ruler, court and bureaucracy in "palace cultures". In informal usage, a "palace" can be extended to a grand residence of any kind.
Palaces
The earliest known palaces were the royal residences of the Egyptian Pharaohs at Thebes, featuring an outer wall enclosing labyrinthine buildings and courtyards.[2] Other ancient palaces include the Assyrian palaces at Nimrud and Nineveh, the Minoan palace at Knossos, and the Persian palaces at Persepolis and Susa.[2] Palaces in East Asia, such as the imperial palaces of Korea, Thailand, Vietnam, Japan, large stone and wooden structures in the Philippines and China's Forbidden City, consist of many low pavilions surrounded by vast, walled gardens, in contrast to the single building palaces of Medieval Western Europe.[2]
Americas
Brazil

The Brazilian new capital, Brasília, hosts modern palaces, most designed by the city's architect Oscar Niemeyer. The Alvorada Palace is the official residence of the Brazil's president. The Planalto Palace is the official workplace. The Jaburu Palace is the official residence of Brazil's vice-president.
Canada
In Canada, Government House is a title given to the official residences of the Canadian monarchy and various viceroys (the governor generals and the lieutenant governors). Though not universal, in most cases the title is also the building's sole name; for example, the sovereign's and governor general's principal residence in Ottawa is known as Government House only in formal contexts, being more generally referred to as Rideau Hall. The use of the term Government House is an inherited custom from the British Empire, where there were and are many government houses.
Rideau Hall is, since 1867, the official residence in Ottawa of both the Canadian monarch and his or her representative, the Governor General of Canada, and has been described as "Canada's house". It stands in Canada's capital on a 0.36 km2 (88 acre) estate at 1 Sussex Drive, with the main building consisting of approximately 175 rooms across 9,500 m2 (102,000 sq ft), and 27 outbuildings around the grounds. While the equivalent building in many countries has a prominent, central place in the national capital, Rideau Hall's site is relatively unobtrusive within Ottawa, giving it more the character of a private home.
Along with Rideau Hall, the Citadelle of Quebec, also known as La Citadelle, is an active military installation and official residence of both the Canadian monarch and the Governor General. It is located atop Cap Diamant, adjoining the Plains of Abraham in Quebec City, Quebec. The citadel is the oldest military building in Canada, and forms part of the fortifications of Quebec City, which is one of only two cities in North America still surrounded by fortifications. The fortress is located within the historic district of Old Québec, which was designated a World Heritage Site in 1985.
In addition to the federal residences, most provinces maintain a residences for the Canadian monarch, as well as their provincial viceroys lieutenant-governors. There is no government house for the Lieutenant Governors of Ontario (repurposed in 1937 and demolished in 1961), Quebec (destroyed by fire in 1966), or Alberta (closed in 1938 and repurchased and repurposed in 1964).
Mexico

The capital of Mexico, Mexico City, is traditionally nicknamed the "City of Palaces"; it was dubbed so by Alexander von Humboldt, after he visited it in the late 18th century and early 19th century.
In Central Mexico, the Aztec emperors built many palaces in the capital of their empire, Tenochtitlan (modern day Mexico City), some of which may still be seen. On observing the great city Hernán Cortés wrote, "There are, in all districts of this great city, many temples or palaces,... They are all very beautiful buildings. Amongst these temples there is one, the principal one, whose great size and magnificence no human tongue could describe,... All round inside this wall there are very elegant quarters with very large rooms and corridors. There are as many as forty towers, all of which are so high that in the case of the largest there are fifty steps leading up to the main part of it and the most important of these towers is higher than that of the cathedral of Seville..."[3]
The National Palace, or Palacio Nacional, located in Mexico City's main square, the Plaza de la Constitución (El Zócalo), first built in 1563, is in the heart of the Mexican capital. In 1821, the palace was given its current name and the executive, legislative, and judicial branches of government were housed in the palace; the latter two branches would eventually reside elsewhere. During the Second Mexican Empire, its name was changed, for a time, to the Imperial Palace. The National Palace continues to be the official seat of the executive authority, though it is no longer the official residence of the President.
Also in Mexico City is the Castillo de Chapultepec, or Chapultepec Castle, located in the middle of Chapultepec Park which currently houses the Mexican National Museum of History. It is the only castle, or palace, in North America that was occupied by sovereigns - Emperor Maximilian I of Mexico, a member of the House of Habsburg and his consort, Empress Carlota of Mexico, daughter of Leopold I of Belgium. The palace features many objets d'art ranging from gifts of Napoleon III to paintings by Franz Xaver Winterhalter and Mexican painter Santiago Rebull.
United States
Palaces in the United States include the White House, the official residence of the President, and the official residences of many governors and Roman Catholic bishops. Some palaces of former heads of state, such English and Spanish Royal Governors and the Hawaiian Royal Family still exist.
Examples include: ʻIolani Palace and Hānaiakamalama, the former homes of the Hawaiian monarchs in Honolulu; Hulihee Palace in Kailua-Kona, Hawaii; The Governor's Palace in Williamsburg, a modern reconstruction of the official residence of the Royal governors of the Colony of Virginia; Tryon Palace in New Bern, a modern reconstruction of the historical colonial governors' palace of the Province of North Carolina; and the Palace of the Governors in Santa Fe, New Mexico as well as the Spanish Governor's Palace in San Antonio, Texas, which were residences of both Spanish and Mexican governors.
There are many private buildings or mansions in the United States, which, though not called "palaces", have the grandeur typical of a palace, and which have been used as residences. Hearst Castle and the Biltmore Estate are examples.
Uruguay
The Palacio Legislativo (Legislative Palace) is the house of the Uruguayan Parliament.
Asia
Brunei
Istana Nurul Iman is the world's largest palace and is the official residence of the Sultan of Brunei, Hassanal Bolkiah, and the seat of the Brunei government. The palace is located on a leafy sprawl of hills on the banks of the Brunei River, a few kilometres south of Bandar Seri Begawan, Brunei's capital.
China

A famed example of Chinese palaces is the Forbidden City: the imperial palace of the Chinese empire from the Ming Dynasty to the end of the Qing Dynasty. It is the largest palace complex in the world and is located in the middle of Beijing, China. The palace complex exemplifies traditional Chinese palatial architecture.[4] Another example is the Summer Palace located in the northern suburb of Beijing and Mukden Palace in Shenyang. The Presidential Palace in Nanjing displays European architectural influences.
Chinese palaces are designed in regular square grids and arranged in a formal layout consisting of main buildings and a number of pavilions enclosed within walls. Unlike massive single-structured European palaces or castles, Chinese palaces are a multitude of complexes containing several larger and smaller structures with parks and courtyards.
India


India is home to many palaces and vast empires. Its history is full of numerous dynasties that have ruled over various parts of the country. While most monuments of the ancient period have been destroyed or lie in ruins, some medieval buildings have been maintained or restored to good condition. Several medieval forts and palaces still stand all over India. These are examples of the achievements of the architects and engineers of that age. The palaces of India offer an insight into the life of the royalty of the country. While some royal palaces have been maintained as museums or hotels over the last decades, some are still homes for the members of the erstwhile royal families. These forts and palaces are the largest illustrations and legacy of the princely states of India. They feature floats of flowers in grand fountains, shimmering blue water of magnificent baths and private pools, doric pillars, ornamental brackets, decorative staircases, and light streaming in through large windows. India possesses some of the most fascinating forts and palaces, a true royal retreat. It is not just a romantic longing for a royal experience, but also the search for the truly authentic Indian experience that brings thousands of heritage lovers to India's palaces.
Rajasthan has many forts and palaces that are major tourist destinations in North India. (See List of palaces in Rajasthan.) The Rajputs (collective term for the rulers of the region) were known as brave soldiers who preferred to die than be taken prisoners. They were also great connoisseurs of art and brilliant builders. The most famous forts and palaces in Rajasthan are located in Chittor, Jodhpur, Jaipur, Udaipur, Saphieree, Amber and Nahargarh. Taj Hotels Resorts and Palaces manages some of the most iconic palaces of the region, Lake Palace, Udaipur; Umaid Bhawan Palace, Jodhpur; Fort Madhogarh, Jaipur and Rambagh Palace, Jaipur; and offer authentic royal retreats to the guests in all its grandeur, splendour and magnificence.
Kolkata is known as the City of Palaces within the Indian context, referring to the numerous grand residential buildings that dotted the city from the end of the 18th century onwards, as it grew to become one of the largest cities of the British Raj.
Karnataka is famous for the Amba Vilas Palace (commonly known as Mysore Palace) in Mysuru / Mysore, which was the palace of the Wodeyar kings. It was said to have been built of wood until it had to be rebuilt after a fire that burned down the entire palace complex.
Indonesia
In Indonesia, palaces are known as istana (Malay and Indonesian), or kraton (Javanese and Sundanese). In Bali the royal palace compound is called puri. The palaces reflect the long history and diverse culture of the Indonesian archipelago.
Although Indonesia is now a republic, some of its parts and provinces still retain and preserve their traditional royal heritage, for example the Sultanate of Yogyakarta, Surakarta, Mangkunegaran princedom, Kasepuhan palace in Cirebon, and Kutai in East Kalimantan. Remnants of palaces and royal houses still can be found in Banten, Medan, Ternate, Bali and Bima.
The layout of traditional Balinese and Javanese kratons is similar to the Chinese concept of walled compounds of royal pavilions, squares and gardens. Most of these kratons took the form of wooden pavilions called pendopo, while the istana of Sumatra usually consist of a single large structure. Typical Minangkabau vernacular architecture can be found in Pagaruyung Palace, West Sumatra. An example of Malay palace is Istana Maimun in Medan.
During VOC and the colonial era of the Dutch East Indies, the colonial government built several European stately palaces as the residence of the Governor General. Most of these European palaces have now become the state palace of the Republic of Indonesia. Indonesian state palaces are the neoclassic Merdeka Palace and Bogor Palace.
Iran
Niavarān Palace Complex is a historical complex situated in the northern part of Tehran, Iran. It consists of several buildings and a museum. The Sahebqraniyeh Palace, from the time of Naser al-Din Shah of the Qajar dynasty, is also inside this complex. The main Niavaran Palace, completed in 1968, was the primary residence of the last shah, Mohammad Reza Pahlavi and the Imperial family until the Iranian Revolution. The main palace was designed by the Iranian architect Mohsen Foroughi.
Israel/Palestine
The pre-Israelite Canaanite site of Tel Kabri, destroyed ca 1600 BCE, was built around a palace core. Though palace culture of ancient Israel and Judea can be inferred through the Hebrew Bible, no palace of Solomon or David has been securely identified. In Israel there are many ancient palaces like the Masada. In Roman Judaea palaces of the Herodian line of client-kings have been identified at several sites, including the main palace at Jerusalem and a winter palace at Herodium, in the Judean desert. Herod's palace at Caesarea Maritima preserved its palatial function as the official residence of the Roman procurators and governors of Judaea. There are other palaces in the Old City of Jerusalem, such as the Lady Tonsok Palace.
In Israel there are a number of magnificent buildings that are not considered "palaces", but they have the grandeur of a typical palace, and serve as residences, such as the House of Yehudayoff Hefetz, and the Sergei courtyard in Jerusalem.
Lebanon

Palaces have existed in Lebanon since the time of the Phoenicians. Almost all of the palaces of Ancient Phoenicia have been destroyed.
During the Renaissance palaces were built in Lebanon, especially in the Chouf region of Mount Lebanon. Lebanese palaces are very diverse architecturally, being influenced by Arabs, Italians, French, Persians, Turkish and East Asians. This is seen in the Beiteddine Palace, which is a mixture of traditional Lebanese, Italian, Arabic and Persian architecture.
Today in Lebanon there are at least ten buildings that can be classified as palaces, including the Beiteddine Palace, Grand Serail (one of the biggest in the world), Baabda Palace, Sursock Museum, and Fakhreddine Palace.
Malaysia
.jpg)
Malaysia is a constituent of nine state rule by hereditary sultans which one of them elected every five years to Yang di-Pertuan Agong post (Supreme King) as the head of state of Malaysia. In Malaysia, the palace is called istana. Other nine sultans have their own istana in their state and throughout the country sometimes called Istana Hinggap. Yang di-Pertuan Agong official residence are Istana Negara, Jalan Duta and Istana Melawati in Putrajaya latter as second palace and retreat while the Istana Negara, Jalan Istana is converted as Royal Museum. Some of the other sultan's official palace is Istana Besar, Istana Anak Bukit, Istana Pekan, Istana Maziah, Istana Alam Shah, Istana Besar Seri Menanti, Istana Iskandariah and Istana Arau. Several appointed non-royal head of state (governor), Yang di- Pertua Negeri also assign to have their official seat and residence such as The Astana, Istana Negeri Sabah and Seri Mutiara.
Nepal

Narayanhiti Palace Museum which long served as residence and principal workplace of the reigning Monarch of Kingdom of Nepal.It was built by king Mahendra in 1961 under the design of Californian architect Benjamin Polk. After 2006 revolution, this royal palace is turned into a public museum.
Philippines

In pre-Hispanic Philippines, the ancestors of today's Filipinos built large wooden residences for the ancient nobility (such as rajahs and datus) called Torogan ("king's house").
During the Spanish Era, the government of the Spanish East Indies built a succession of palaces in and around Manila for high colonial officials and religious authorities. The most famous of these is the 18th-century Malacañang Palace, which originally housed Spanish and American Governors-General and, since the Commonwealth, the President of the Philippines.
Former president and strongman Ferdinand Marcos had Coconut Palace constructed in 1978 to showcase the country's varied uses for the coconut. It serves as the home and office of the vice-president. In 2004, President Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo converted the former Aduana (customs house) in Cebu City into a small palace, called Malacañang sa Sugbo.
Europe
France
In France there has been a clear distinction between a château and a palais. The palace has always been urban, like the Palais de la Cité in Paris, which was the royal palace of France and is now the supreme court of justice of France, or the palace of the Popes at Avignon.
The château, by contrast, has always been in rural settings, supported by its demesne, even when it was no longer actually fortified. Speakers of English think of the "Palace of Versailles" because it was the residence of the king of France, and the king was the source of power, though the building has always remained the Château de Versailles for the French, and the seat of government under the Ancien Régime remained the Palais du Louvre. The Louvre had begun as a fortified Château du Louvre on the edge of Paris, but as the seat of government and shorn of its fortified architecture and then completely surrounded by the city, it developed into the Palais du Louvre.
The hôtel particulier remains the term for an urban residence sited entre cour et jardin, behind a forecourt and opening onto a garden; when fronting directly on streets, they are maisons, "houses". Bishops always had a palais in the town of their diocese, an hôtel in other towns, though they might possess chateaux.
The usage is essentially the same in Italy, Spain and Portugal, as well as the former Austrian Empire. In Vienna, Austria, all large mansions belonging to aristocratic or very wealthy families were traditionally called palais, but this never applied to imperial palaces themselves which were called Burg within the city and Schloss when outside it. In Germany, the wider term was a relatively recent importation, and was used rather more restrictively.
Germany

The German term for "palace" is Palast, which is used especially for large palatial complexes and gardens. More commonly, palaces are called Schloss (chateaux or stately home in English usage).
Germany offers a variety of more than 25,000 castles and palaces and thousands of manor houses. The country is known for its fairy tale-like scenery palatial buildings, such as Sanssouci, Linderhof Palace, Herrenchiemsee, Schwetzingen, Nordkirchen and Schwerin Palace. Many of these buildings have a history of over 1000 years, ranging from fortifications to royal residences. Many German castles after the middle ages were mainly built as royal or ducal palaces rather than as a fortified building.
Greece
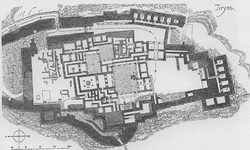
The best examples of the Bronze Age Greece palace are seen in the excavations at Mycenae, Tiryns and Pylos. That these were administrative centers is shown by the records found there. From an architectural point of view, they were the heirs of the Minoan palaces and also of other palaces built earlier on the Greek mainland. They were ranged around a group of courtyards each opening upon several rooms of different dimensions, such as storerooms and workshops, as well as reception halls and living quarters. The heart of the palace was the megaron. This was the throne room, laid out around a circular hearth surrounded by four columns, the throne generally being found on the right-hand side upon entering the room. The staircases found in the palace of Pylos indicate palaces had two stories. Located on the top floor were probably the private quarters of the royal family and some storerooms. These palaces have yielded a wealth of artifacts and fragmentary frescoes.
Hungary
_(5819._sz%C3%A1m%C3%BA_m%C5%B1eml%C3%A9k).jpg)
In Hungary distinction is made between urban and rural residencies. Only the urban residencies of the higher aristocracy were called palota (palace), rural stately homes were named kastély (mansion), or in case of smaller country houses kúria. Noble landowner families, like the House of Esterházy, often had several mansions in the countryside and palaces in towns. The office of the President of the Republic of Hungary, Sándor Palace was the residence of the Sándor family in the 19th century. Royal residencies were also called palaces, for example the Early Renaissance summer palace of King Matthias Corvinus in Visegrád or Buda Castle which was called Királyi-palota (Royal Palace). In the second half of the 19th century splendid new townhouses of the bourgeoisie on Andrássy út and elsewhere in Budapest were named palaces. A typical example is the Art Nouveau Gresham Palace which was built by an insurance company. Grand public buildings and even blocks of flat of higher standard were regularly called palaces (the contemporary term of the latter were bérpalota meaning rent palace). For contemporary buildings the term is seldom used with the notable exemption of the Palace of Arts.
Italy
In Italy, any urban building built as a grand residence is a palazzo; these are often no larger than a Victorian townhouse. It was not necessary to be a nobleman to have your house considered a palazzo; the hundreds of palazzi in Venice nearly all belonged to the patrician class of the city. In the Middle Ages these also functioned as warehouses and places of business, as well as homes. Each family's palazzo was a hive that contained all the family members, though it might not always show a grand architectural public front. In the 20th century, palazzo in Italian came to apply by extension to any large fine apartment building, as so many old palazzi were converted to this use.
Bishop's townhouses were always palazzi, and the seat of a localized regime would also be so called. Many former capitals display a Palazzo Ducale, the seat of the local duke or lord. In Florence (just as for other strong communal governments), the seat of government was known as Palazzo della Signoria (see Palazzo della Signoria). When the Medici were made Grand Dukes of Tuscany, however, the centre of power shifted to their new residence in Palazzo Pitti, and the old centre of power began to be referred to as the Palazzo Vecchio.
Shops on the ground floor and flats at the top of a modern palazzo are not at all incongruous: historically, the ground floors of even a great family's palazzo could be trade and domestic offices often open to servants, tradesmen, customers and the public, while the smartest and most prestigious floor (known as the piano nobile) was kept for the family along with the upper floors and apartments, all of which were considered cleaner and safer than those on the ground floor. There were (and are) often separate, sometimes external, stairs to the humblest attic rooms and roofs used by the staff.
The most important royal palazzi in Italy are those in Naples, Palermo, Turin, as well as the Quirinale Palace in Rome.
Malta
Until the sixteenth century, Malta was part of the Kingdom of Sicily, and the capital Mdina housed many palaces for the nobility, such as Palazzo Falson and Palazzo Santa Sofia. After the arrival of the Order of Saint John in 1530, the knights settled in Birgu, where part of Fort St Angelo was used as a palace for the Grand Master. The knights themselves lived in auberges, but these were more large houses rather than palaces.
When the Order began to build a new capital Valletta in 1566, a new Grandmaster's Palace and a series of new auberges were built. The auberges in Valletta are much larger than their counterparts in Birgu, and can be considered as palaces. The most important auberge still standing is Auberge de Castille, which currently houses the Office of the Prime Minister of Malta. Over the years, the Grand Masters also built a number of large residences in the countryside, such as Verdala Palace and San Anton Palace. Both of these now serve as official residences of the President of Malta.
The Arhcbishop of Malta has a palace in Mdina. The inquisitor also had a palace in Birgu and another in Girgenti until the abolition of the inquisition in 1798. The nobility, upper classes and individual knights of the Order built a number of private palaces, especially in Valletta, but also in the countryside. There are other palaces built by the nobility, such as, most notably Palazzo Parisio in Valletta and Palazzo Dragonara in St Julians.
Portugal
Due to its relatively small dimension, most of Portugal's are former royal residences. Some examples of Portuguese palaces are Mafra National Palace, Pena National Palace, Belém Palace, Ajuda National Palace, Palácio das Necessidades, Mateus Palace, Palace Hotel of Bussaco, Palácio da Regaleira, and Palácio da Brejoeira.
Romania
Palaces in Romania, as elsewhere in Europe, were originally built for royalty, nobles and bishops. Three former royal palaces in Romania are the Cotroceni Palace (now the Presidential residence); the Royal Palace in Bucharest, which now houses the National Museum of Art of Romania; and the Elisabeta Palace. Although Romania is no longer a monarchy, its former King Michael now resides at Elisabeta Palace.
Other palaces include the Crețulescu Palace in Bucharest, built for the Crețulescu family, Peles palace, built by King Carol I of Romania and the Palace of Culture from Iași. The Palace of the Parliament (Casa Poporului) from Bucharest is a large government building. Despite containing the word "palace" in its name, the building was never intended to serve as a residence for royalty.
Russia

The first palaces in Russia were built about a thousand years ago for the Grand Dukes of Kiev. These are not preserved, having been destroyed by the Mongols. The first palaces in European style were built during the reign of Tsar Peter the Great and his immediate successors. Examples of Russian palaces include
- the Palace of Facets (1487–1491) in Moscow at the Kremlin,
- the Tsarevich Dmitry Ivanovich Palace (1489) in Uglich,
- the Kolomensky Wooden Palace (1528—1532) in Kolomenskoye,
- the Terem Palace (1635–1636) at the Kremlin,
- the Menshikov Palace (1710—1727) in Saint Petersburg,
- the Oranienbaum Palace (1710) in Lomonosov,
- the Peterhof Palace (1709—1755) in Petergof, and
- Kikin Hall (1714) in Saint Petersburg.
- Winter Palace (1732 - 1917), was the official residence of the Russian monarchs
Scandinavia


The three Scandinavian countries of Denmark, Norway and Sweden all have long monarchic histories, and possess several palaces. In Denmark Christiansborg Palace in Copenhagen was built as a royal palace, but is now only used for royal receptions; Amalienborg Palace has been the Danish royal residence since 1794. In Norway the Royal Palace in Oslo has been used as the royal residence since 1849. In Sweden the large Stockholm Palace was built in 1760, and remains the official royal residence, but at the current time is only used for official purposes while the Swedish royal family resides in the more modest Drottningholm Palace.
Serbia
The two dynasties of post-Ottoman Serbia, Karađorđević and Obrenović built numerous residences throughout their domain. The most prominent and official palaces are the Stari Dvor and the Novi Dvor (Old and New Court, respectively) in the center of Belgrade and the Royal Compound which includes the Beli Dvor and Kraljevski Dvor (Royal Palace) in the Belgrade suburb, Dedinje.
Spain
With over a thousand years of monarchic history, Spain has many palaces of its own that were built for different monarchs or nobles. Among these palaces are the Royal Palace of Madrid, also referred to as the Palacio Real. The palace is the largest palace in Europe with over 2,800 rooms but at the current time is of use for only governmental business while the royal family resides in the smaller Palacio de la Zarzuela.
In addition to the Royal Palace of Madrid, Alcázar of Seville (which mixes, with the delicate Moorish filigree, European Christian architectural styles), the Alhambra, the Monastery of San Lorenzo de El Escorial and the Royal Palace of Aranjuez, fine baroque palace is surrounded by gardens. Currently, the royal family and prime minister live in the more modest Palace of Zarzuela and Palace of Moncloa respectively.
United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom, by tacit agreement, there have been no "palaces" other than those used as official residences by royalty or bishops, regardless of whether located in town or country. However, not all palaces use the term in their name - see Holyrood Palace. Thus the Palace of Beaulieu gained its name precisely when Thomas Boleyn sold it to Henry VIII in 1517. Previously, it had been known as Walkfares, but like several other palaces, the name stuck even once the royal connection ended.
Blenheim Palace was built, on a different site, in the grounds of the disused royal Palace of Woodstock, and the name was also part of the extraordinary honour when the house was given by a grateful nation to a great general, the Duke of Marlborough. Along with several royal and episcopal palaces in the countryside, Blenheim does demonstrate that "palace" has no specific urban connotation in English. On the use of the term "palace" in the UK, it is notable that Buckingham Palace was known as Buckingham House before it was acquired by the monarchy.
Blenheim Palace (in England) and Hamilton Palace (in Scotland, demolished in 1927) are the only non-royal (and non-episcopal) residences to have the word "palace" in their name, other than Dalkeith Palace in Scotland, which used to be the seat of the Dukes of Buccleuch (who descend from Charles II of England).
Turkey
After the conquest of Istanbul by Mehmed the Conqueror at 1453, construction of the Topkapı Palace was started in the year 1460 and completed in 1478. The palace was built upon a 700,000 square meter area on an Eastern Roman Acropolis located on the Istanbul Peninsula between the Sea of Marmara, Bosphorus and the Golden Horn. Topkapı Palace was the administrative, educational, and art center of the Empire for nearly four hundred years from Mehmed the Conqueror until Sultan Abdulmecid who was the thirty-first Sultan. Although Topkapi Palace was abandoned by the Ottoman Dynasty by moving to the Dolmabahçe Palace in the middle of the 19th century, Topkapı Palace retained its importance.
After the establishment of the Republic of Turkey, Topkapı Palace was transformed into a museum on April 3, 1924. It was also the first museum of the Republic of Turkey. Topkapı Palace Museum covers approximately 400,000 square meters at the present day. Topkapı Palace is separated from the city on the land-side by the Imperial Walls, which were constructed by Mehmed the Conqueror. It is separated from the city on the sea-side by the Byzantine Walls. Topkapı Palace is one of the largest palace-museums with its architectural structures, collections, and approximately 300,000 archive papers.
Other
In Continental Europe royal and episcopal palaces were not merely residences; the clerks who administered the realm or the diocese laboured there as well. (To this day many bishops' palaces house both their family apartments and their official offices.) However, unlike the "Palais du Justice" which is often encountered in the French-speaking world, modern British public administration buildings are never called "palaces"; although the formal name for the "Houses of Parliament" is the Palace of Westminster, this reflects Westminster's former role as a royal residence and centre of administration.
In more recent years, the word has been used in a more informal sense for other large, impressive buildings, such as The Crystal Palace of 1851 (an immensely large, glazed hall erected for The Great Exhibition) and modern arenas-convention centers like Alexandra Palace.
The largest in the world is Palace of the Parliament in Bucharest, Romania. Built during the socialist regime, no effort or expense was spared to raise this colossal neo-classic building.
The Palace of the Olowo, ruler of the Yoruba Owo clan of Nigeria, is acknowledged to be the largest palace in all of Africa. It consists of more than 100 courtyards, each with a unique traditional usage.
The largest palace in Asia is Singha Durbar literally known as Lion Palace.
The Singha Durbar (literally, Lion Palace) in Kathmandu is the official seat of government of Nepal and the largest Palace in Asia. Originally built by the Rana dynasty and it was known as the largest palace of Nepal and in Asia. In 1904 This was the private Property of Prime Minister Dev S J B Rana who was forced to abdicate by Prime Minister Chandra S J B Rana and his brothers, claimed to be the biggest and most luxurious palace in Asia and until 1973 was the largest government secretariat in Asia. It was the private residence of the hereditary Prime Minister of Nepal, now the Singha Durbar now houses both chambers of the Parliament of Nepal (the Pratinidhi Sabha, or House of Representatives, and the Rashtriya Sabha, or House of the States), as well as ministries and government offices.
Singha Durbar is also the headquarters of Radio Nepal and Nepal Television.
Singha Darbar was designed by Kishore Narsingh Rana as neo-classical architecture typical of the style of the 19th century.
A substantial portion of the Singha Durbar was destroyed by fire in 1973; much of the damage has since been rebuilt.
See also
- Palatine Hill
- List of palaces
- Castle
- Official residence
- Great house
- Luxury real estate
- Palas
- Kaiserpfalz (or Königspfalz)
- Imperial castle (Reichsburg)
References
- 1 2 3 4 American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language (4th ed.). Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company. ISBN 0-618-08230-1.
- 1 2 3 Merriam-Webster's Collegiate Encyclopedia. Springfield, Mass.: Merriam-Webster. 2000. ISBN 0-87779-017-5.
- ↑ Mexico-Tenochtitlan: Ancient City
- ↑ "UNESCO World Heritage List: Imperial Palaces of the Ming and Qing Dynasties in Beijing and Shenyang". UNESCO. Retrieved 2007-05-04.


_06.jpg)

