Osaka Metropolis plan
The Osaka Metropolis plan (大阪都構想 Ōsaka-to kōsō) or Osaka Metropolis is a plan to transform Osaka Prefecture from a fu, an urban prefecture, into a to, a metropolis. Under the initially envisioned plan, Osaka city, Sakai city, and other surrounding cities in Osaka prefecture, were to be dissolved and – similarly to Tokyo urban wards within Tokyo – subdivided into special wards that have a status as municipalities but leave some municipal tasks and revenues to the prefectural administration. As political resistance grew, notably the opposition to the plan in Sakai city expressed in the 2013 mayoral election, the concrete plan was reduced to, at least as a first step, abolish only Osaka city. As in Tokyo, the metropolis would have continued to include all other municipalities of the prefecture and serve as prefectural government for them.
The plan was defeated by a slim margin of 0.76% in the Osaka Metropolis Plan referendum, 2015 in Osaka city.
Proponents
The plan is a main goal of the Osaka Restoration Association, a political party led by former Osaka governor and current Osaka city mayor Tōru Hashimoto. The party currently includes the governor of Osaka, the mayor of Osaka city, a majority in the Osaka Prefectural Assembly and a plurality of seats in the assemblies of Osaka city and Sakai city.
Proposals

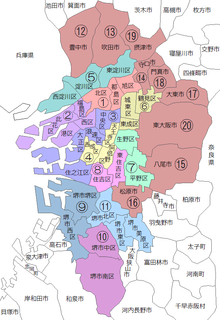
Under the Association's plan, the 24 wards of Osaka, seven wards of Sakai, and nine other municipalities in Osaka Prefecture would be reorganized into twenty special wards, each having municipal status similar to the special wards of Tokyo. As is the case in Tokyo, the prefectural government would be responsible for collecting fixed asset taxes and regional corporate taxes within this area, and would provide water, fire protection, public transit and other services through a unified administration for all 20 wards, while resident services and other administrative tasks would be handled by the wards themselves.
In July 2012, seven established parties in the National Diet (DPJ, LDP, Komeito, PNP, LF, Minna no To, Kizuna) and the Kaikaku-Mushozoku no Kai House of Representatives parliamentary group jointly submitted a bill that would create the legal framework to allow Ōsaka and Sakai cities to be split into special wards; the name change of Osaka prefecture from Osaka-fu to Osaka-to is not included, reserving the to designation for the prefecture of Tokyo. The law would also allow other major cities and their surrounding municipalities to reorganize as special wards and transfer municipal tasks to the prefectural government. Condition for application is an agglomeration population of 2 million and the agreement of all participating municipalities (by assembly vote and referendum)[1] and the prefecture involved. Namely this would give the cities of Sapporo, Saitama, Chiba, Yokohama and Kawasaki, Nagoya, Kyoto, and Kobe the option to dissolve[2][3] and transform Hokkaido, Saitama, Chiba, Kanagawa, Aichi, Kyoto or Hyōgo into "metropolises" like Tokyo. The bill was passed by the Diet in August 2012.[4]

Four plans of special wards divided from Osaka City, as proposed by the project team in 2012:



Referendum
See also
References
- ↑ Jiji Press, August 29, 2012: 都構想法が成立=大阪など8地域、特別区可能に
- ↑ The Japan Times, July 31, 2012: Bill to transform Osaka government jointly submitted to Diet
- ↑ Tokyo Shimbun, July 31, 2012: 大阪都構想の法案提出
- ↑ msn/Sankei News, August 29, 2012: 参院本会議で駆け込み採決も、都構想など15法成立
External links
- Yahoo News: News on the Osaka Metropolis plan (Japanese)
- Ōsaka Ishin no Kai: Policies, About the Osaka Metropolis plan (Japanese)
- Ōsaka shisei chōsakai (Osaka Institute for Municipal Research): Osaka Metropolis Plan Q&A (Japanese)
- Daily Yomiuri Online, Mar. 3, 2012: Revitalizing Japan: Creative use of land / Revive a 'great Osaka' that can compete with Tokyo