Necklace splitting problem
Necklace splitting is a picturesque name given to several related problems in combinatorics and measure theory. Its name and solutions are due to mathematicians Noga Alon [1] and Douglas B. West.[2]
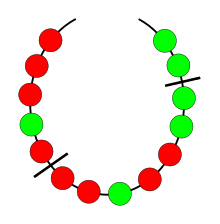
The basic setting involves a necklace with beads of different colors. The necklace should be divided between several partners, such that each partner receives the same amount of every color. Moreover, the number of cuts should be as small as possible (in order to waste as little as possible of the metal in the links between the beads).
Variants
The following variants of the problem have been solved in the original paper:
- Discrete splitting:[1]:Th 1.1 The necklace has beads. The beads come in different colors. There are beads of each color , where is a positive integer. Partition the necklace into parts (not necessarily contiguous), each of which has exactly beads of color i. Use at most cuts. Note that if the beads of each color are contiguous on the necklace, then at least cuts must be done inside each color, so is optimal.
- Continuous splitting:[1]:Th 2.1 The necklace is the real interval . Each point of the interval is colored in one of different colors. For every color , the set of points colored by is Lebesgue-measurable and has length , where is a non-negative real number. Partition the interval to parts (not necessarily contiguous), such that in each part, the total length of color is exactly . Use at most cuts.
- Measure splitting:[1]:Th 1.2 The necklace is a real interval. There are different measures on the interval, all absolutely continuous with respect to length. The measure of the entire necklace, according to measure , is . Partition the interval to parts (not necessarily contiguous), such that the measure of each part, according to measure , is exactly . Use at most cuts. This is a generalization of the Hobby–Rice theorem, and it is used to get an exact division of a cake.
Each problem can be solved by the next problem:
- Discrete splitting can be solved by continuous splitting, since a discrete necklace can be converted to a coloring of the real interval in which each interval of length 1 is colored by the color of the corresponding bead. In case the continuous splitting tries to cut inside beads, the cuts can be slid gradually such that they are made only between beads.[1]:249
- Continuous splitting can be solved by measure splitting, since a coloring of an interval in colors can be converted to a set measures, such that measure measures the total length of color . The opposite is also true: measure splitting can be solved by continuous splitting, using a more sophisticated reduction.[1]:252–253
Proof
The case can be proved by the Borsuk-Ulam theorem.[2]
When is an odd prime number, the proof involves a generalization of the Borsuk-Ulam theorem.[3]
When is a composite number, the proof is as follows (demonstrated for the measure-splitting variant). Suppose . There are measures, each of which values the entire necklace as . Using cuts, divide the necklace to parts such that measure of each part is exactly . Using cuts, divide each part to parts such that measure of each part is exactly . All in all, there are now parts such that measure of each part is exactly . The total number of cuts is plus which is exactly .
Further results
One cut fewer than needed
In the case of two thieves [i.e. k = 2] and t colours, a fair split would require at most t cuts. If, however, only t − 1 cuts are available, Hungarian mathematician Gábor Simonyi[4] shows that the two thieves can achieve an almost fair division in the following sense.
If the necklace is arranged so that no t-split is possible, then for any two subsets D1 and D2 of { 1, 2, ..., t }, not both empty, such that , a (t − 1)-split exists such that:
- If colour , then partition 1 has more beads of colour i than partition 2;
- If colour , then partition 2 has more beads of colour i than partition 1;
- If colour i is in neither partition, both partitions have equally many beads of colour i.
This means that if the thieves have preferences in the form of two "preference" sets D1 and D2, not both empty, there exists a (t − 1)-split so that thief 1 gets more beads of types in his preference set D1 than thief 2; thief 2 gets more beads of types in her preference set D2 than thief 1; and the rest are equal.
Simonyi credits Gábor Tardos with noticing that the result above is a direct generalization of Alon's original necklace theorem in the case k = 2. Either the necklace has a (t − 1)-split, or it does not. If it does, there is nothing to prove. If it does not, we may add beads of a fictitious colour to the necklace, and make D1 consist of the fictitious colour and D2 empty. Then Simonyi's result shows that there is a t-split with equal numbers of each real colour.
Negative result
For every there is a measurable -coloring of the real line such that no interval can be fairly split using at most cuts.[5]
Splitting multidimensional necklaces
The result can be generalized to n probability measures defined on a d dimensional cube with any combination of n(k − 1) hyperplanes parallel to the sides for k thieves.[6]
Approximation algorithm
An approximation algorithm for splitting a necklace can be derived from an algorithm for consensus halving.[7]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Alon, Noga (1987). "Splitting Necklaces". Advances in Mathematics. 63 (3): 247–253. doi:10.1016/0001-8708(87)90055-7.
- 1 2 Alon, Noga; West, D. B. (December 1986). "The Borsuk-Ulam theorem and bisection of necklaces". Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society. 98 (4): 623–628. doi:10.1090/s0002-9939-1986-0861764-9.
- ↑ I.Barany and S.B.Shlosman and A.Szucs (1981). "On a topological generalization of a theorem of Tverberg" (PDF). Journal of London Mathematical Society. 2 (23): 158–164.
- ↑ Simonyi, Gábor (2008). "Necklace bisection with one less cut than needed". Electronic journal of combinatorics. 15 (N16).
- ↑ "Splitting necklaces and measurable colorings of the real line". Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society. November 25, 2008. doi:10.1090/s0002-9939-08-09699-8. ISSN 1088-6826.
- ↑ de Longueville, Mark; Rade T. Živaljević (2008). "Splitting multidimensional necklaces". Advances in Mathematics. 218 (3): 926–939. doi:10.1016/j.aim.2008.02.003.
- ↑ Simmons, Forest W.; Su, Francis Edward (February 2003). "Consensus-halving via theorems of Borsuk-Ulam and Tucker". Mathematical Social Sciences. 45 (1): 15–25. doi:10.1016/s0165-4896(02)00087-2.