New Flemish Alliance
New Flemish Alliance Nieuw-Vlaamse Alliantie | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Leader | Bart De Wever |
| Founder | Geert Bourgeois |
| Founded | 2001 |
| Preceded by |
People's Union (split in 2001) |
| Headquarters |
Koningsstraat 47, bus 6 B-1000 Brussels Belgium |
| Membership (2014) |
|
| Ideology |
Flemish nationalism Regionalism Liberal conservatism[2] |
| Political position | Centre-right[3] |
| European affiliation | European Free Alliance |
| European Parliament group | European Conservatives and Reformists |
| Colors | Black, gold |
| Chamber of Representatives (Flemish seats) |
33 / 87 |
| Senate (Flemish seats) |
12 / 35 |
| Flemish Parliament |
43 / 124 |
| Brussels Parliament (Flemish seats) |
3 / 17 |
| European Parliament (Flemish seats) |
4 / 12 |
| Flemish Provincial Councils |
104 / 351 |
| Website | |
| www.n-va.be | |
The New Flemish Alliance (Dutch: Nieuw-Vlaamse Alliantie, N-VA)[4] is a centre-right Flemish nationalist[5] and conservative[6][7][8] political party in Belgium, founded in 2001.[9] It is a regionalist[10][11] and separatist[12][13][14][15] movement that self-identifies with the promotion of civic nationalism.[16] It is part of the Flemish Movement, and strives for the peaceful[17] and gradual secession of Flanders from Belgium.[18] In recent years it has become the largest party of Flanders as well as of Belgium as a whole, and leads the 2014–19 Flemish Government.
Following the 2014 elections, the New Flemish Alliance is the largest Belgian/Flemish political party in the European Parliament, with four MEPs. It sits in the European Conservatives and Reformists (ECR) parliamentary group, where it co-operates with parties like the UK Conservative Party, Alternative for Germany and Poland's Law and Justice.
The party is also known for its insistence on the exclusive use of Dutch, Flanders' sole official language, in dealings with government agencies, and for the promotion of the use of Dutch in Flanders as the language enabling integration.[16] The main objective of the party is to work on Flemish independence[19] by gradually obtaining more powers for both Belgian communities separately. Furthermore, it emphasizes its non-revolutionary and pro-European character (as opposed to the far-right and Eurosceptic character of the Vlaams Belang) in order to legitimize increased Flemish autonomy.[20] The N-VA advocates free-market economics, and their manifesto proposes immediate tax reductions to stimulate the economy.[21] They also advocate deepening ties with the European Union.[22]
History
Fall of the People's Union
The N-VA stems from the People's Union (Dutch: Volksunie, VU), a Belgian political party and broad electoral alliance of Flemish nationalists. Towards the end of the 20th century, with a steadily declining electorate and the majority of the party's federalist agenda implemented, friction between several wings of the People's Union emerged. In the beginning of the 1990s, Bert Anciaux became party president and led the party in an ever more progressive direction, combining the social-liberal ideas of his new iD21-movement with the regionalist course of the People's Union. These experiments were opposed by the more traditional centre-right party base.
Tension rose towards the end of the decade, as Geert Bourgeois, foreman of the traditional and centre-right nationalist wing, was elected chairman by party members, in preference to the incumbent and progressive Patrik Vankrunkelsven. Factions subsequently clashed multiple times, over the future course of the party and possible support for current state reform negotiations. On 13 October 2001 the party openly split into three factions: the progressive wing around Bert Anciaux, which would later become the Spirit party; the conservative nationalist wing around Geert Bourgeois; and a centrist group opposing the imminent split. A party referendum was held on the future of the party. The right wing gained a substantial plurality of 47% and inherited the party infrastructure.[23] Since no faction got an absolute majority, however, the name Volksunie could no longer be used.
Foundation and the election threshold
In the autumn of 2001, the New Flemish Alliance (Dutch: Nieuw-Vlaamse Alliantie, N-VA) was founded. Seven members of parliament from the People's Union joined the new party. The new party council created a party manifesto and a statement of principles. The first party congress was held in May 2002, voting on a party program and permanent party structures. Geert Bourgeois was elected chairman.
The party participated in elections for the first time in the 2003 federal elections, but struggled with the election threshold of 5%. This threshold was only reached in West Flanders, the constituency of Geert Bourgeois. With only one federal representative and no senator, the party lost government funding and faced irrelevance.
Cartel with CD&V
In February 2004, the N-VA entered into an electoral alliance, commonly known in Belgium as a cartel, with the Christian Democratic and Flemish (CD&V) party, the traditionally largest party, which was then in opposition. They joined forces in the regional elections in 2004 and won. Both parties joined the new Flemish government, led by CD&V leader Yves Leterme. Geert Bourgeois became a minister, and Bart De Wever became the new party leader in October 2004.
The cartel was briefly broken when the former right-wing liberal Jean-Marie Dedecker left the Open Flemish Liberals and Democrats (Open VLD) and entered the N-VA on behalf of the party executive. However, the party congress did not put Dedecker on the election list, instead preferring to continue the cartel with CD&V, who had strongly opposed placing him on a joint cartel list. Dedecker saw this as a vote of no confidence, and left the party after only 10 days, to form his own party, List Dedecker (LDD). Deputy leader Brepoels, who supported Dedecker, stepped down from the party board afterwards.
In the Belgian federal election of 2007 the CD&V/N-VA cartel won a major victory again, with a campaign focusing on good governance, state reform and the division of the electoral district Brussels-Halle-Vilvoorde. The N-VA won five seats in the Chamber of Representatives and two seats in the Senate. Yves Leterme initiated coalition talks, which repeatedly stalled (see 2007–2008 Belgian government formation). On 20 March 2008, a new federal government was finally assembled. N-VA did not join this government, but gave its support pending state reform.
The cartel ended definitively on 24 September 2008, due to lack of progression in state reform matters and a different strategy on future negotiations. N-VA left the Flemish Government and gave up its support of Leterme at the federal level.
Mainstream party
In the regional elections of June 2009, N-VA won an unexpected 13% of the votes, making them the winner of the elections, along with their old cartel partner CD&V. N-VA subsequently joined the government, led by Kris Peeters (CD&V). Bart De Wever chose to remain party leader and appointed Geert Bourgeois and Philippe Muyters as ministers in the Flemish Government and Jan Peumans as speaker of the Flemish Parliament.
Foundation and ideology
The New Flemish Alliance is a relatively young political party, founded in the autumn of 2001. Being one of the successors of the Volksunie (1954–2001), it is, however, based on an established political tradition. The N-VA works towards the same goal as its predecessor: to redefine Flemish nationalism in a contemporary, pro-European setting. Party leader De Wever calls himself a conservative and a nationalist.[24]
The N-VA argues for a Flemish republic, a member state of a democratic European confederation. The party believes that the challenges of the 21st century can best be answered by strong communities and by well-developed international co-operation, a position which is reflected in their tagline: "Necessary in Flanders, useful in Europe." (Dutch: Nodig in Vlaanderen, nuttig in Europa.)
A label for the political orientation of the N-VA is difficult to find as the party combines both left- and right-wing policies. According to its 2009 election programme for Flanders, the N-VA is economically liberal and ecologically green. The N-VA supports public transport, open source software, renewable energy and taxing cars by the number of kilometres driven. It wants more aid for developing countries but also more compulsory measures to require that immigrants learn Dutch.
At European level, the N-VA is part of the European Free Alliance (EFA), a European political party consisting of regionalist, pro-independence and minority interest political parties, of which the People's Union was a founder member. During the 7th European Parliament of 2009–2014, the N-VA was a member of The Greens–European Free Alliance (Greens/EFA) group in the European Parliament. However, following the 2014 European elections, the N-VA moved to the European Conservatives and Reformists (ECR) group.[25]
Party chairmen
| Name | Portrait | From | To | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Geert Bourgeois |  | 2001 | 2004 |
| 2 | Bart De Wever |  | 2004 | present |
Electorate
In the federal elections in 2003 N-VA received 3.1% of the votes, but won only one seat in the federal parliament. In February 2004 they formed an electoral alliance (cartel) with the Christian Democratic and Flemish party (CD&V). The cartel won the elections for the Flemish Parliament. The N-VA received a total of 6 seats. However, on 21 September 2008 the N-VA lost its faith in the federal government and the following day minister Geert Bourgeois resigned. In a press conference he confirmed the end of the CD&V/N-VA cartel.
In the 2004 European elections, N-VA had 1 MEP elected as part of the cartel with CD&V.
In the 10 June 2007 federal elections, the cartel won 30 out of 150 seats in the Chamber of Representatives and 9 out of 40 seats in the Senate.
In the regional elections of 11 June 2009, N-VA (now on its own after the split of the cartel with CD&V) won an unexpected 13% of the votes, making them the winner of the elections along with their former cartel partner. In the 2009 European elections held on the same day, the N-VA had one MEP elected.
In the 2010 federal elections, N-VA became the largest party of Flanders and of Belgium altogether.
In the 2014 federal elections, N-VA increased their dominant position, taking votes and seats from the far-right Flemish Interest. In the simultaneous 2014 regional elections and 2014 European elections, the N-VA also became the largest party in the Flemish Parliament and in the Belgian delegation to the European Parliament.
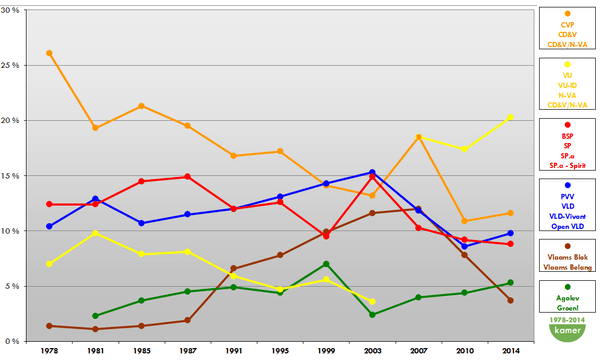
Electoral results
Federal Parliament (Federaal Parlement)
| Chamber of Representatives (Kamer van Volksvertegenwoordigers) | |||||||
| Election year | No. of overall votes |
% of overall vote |
% of language group vote |
No. of overall seats won |
No. of language group seats won |
+/– | Government |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2003 | 201,399 | 3.1% | 1 / 150 |
1 / 88 |
in opposition | ||
| 2007 | 1,234,950 | 18.5% | 29.6% (1st) | 5 / 150 |
5 / 88 |
|
in opposition |
| In cartel with CD&V; 30 seats won by CD&V/N-VA. | |||||||
| 2010 | 1,135,617 | 17.40% | 27.8% (1st) | 27 / 150 |
27 / 88 |
|
in opposition |
| 2014 | 1,366,073 | 20.32% | (1st) | 33 / 150 |
33 / 87 |
|
in coalition |
| Senate (Senaat) | |||||||
| Election year | No. of overall votes |
% of overall vote |
% of language group vote |
No. of overall seats won |
No. of language group seats won |
+/– | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2003 | 200,273 | 3.1% | 0 / 71 |
0 / 41 |
|||
| 2007 | 1,287,389 | 19.4% | 31.4% (1st) | 2 / 71 |
2 / 41 |
| |
| In cartel with CD&V; 14 seats won by CD&V/N-VA. | |||||||
| 2010 | 1,268,780 | 19.6% | 31.7% (1st) | 14 / 71 |
14 / 41 |
| |
| 2014 | N/A | N/A | N/A (1st) | 12 / 60 |
12 / 35 |
| |
Regional parliaments
Brussels Parliament
| Election year | No. of overall votes |
% of overall vote |
% of language group vote |
No. of overall seats won |
No. of language group seats won |
+/– | Government |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | 10,482 | 16.8% (4th) | 0 / 89 |
0 / 17 |
in opposition | ||
| In cartel with CD&V; 3 seats won by CD&V/N-VA | |||||||
| 2009 | 2,586 | 5.0% (6th) | 1 / 89 |
1 / 17 |
|
in opposition | |
| 2014 | 9,085 | 17.0% (4th) | 3 / 89 |
3 / 17 |
|
in opposition | |
Flemish Parliament
| Election year | No. of overall votes |
% of overall vote |
No. of overall seats won |
+/– | Government | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | 1,060,580 | 26.1 (1st) | 6 / 124 |
in coalition | |||
| In cartel with CD&V; 35 seats won by CD&V/N-VA. | |||||||
| 2009 | 537,040 | 13.1 (5th) | 16 / 124 |
|
in coalition | ||
| 2014 | 1,339,946 | 31.88% (1st) | 43 / 124 |
|
in coalition | ||
European Parliament
| Election year | No. of Belgian votes |
% of Belgian vote |
% of language group vote |
No. of Belgian seats won |
No. of language group seats won |
+/– |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | 1,131,119 | 17.4% | 28.2% (1st) | 1 / 24 |
1 / 14 |
|
| In cartel with CD&V; 4 seats won by CD&V/N-VA | ||||||
| 2009 | 402,545 | 6.13% | 9.88% (#5) | 1 / 22 |
1 / 13 |
|
| 2014 | 1,123,363 | 16.85% | 26.67% (1st) | 4 / 21 |
4 / 12 |
|
Representation
European Politics
N-VA holds four seats in the eighth European Parliament (2014–2019) for the Dutch-speaking electoral college.
| European Parliament | ||
|---|---|---|
| Name | In office | Parliamentary group |
| Sander Loones | 2014–present | European Conservatives and Reformists |
| Helga Stevens | 2014–present | |
| Anneleen Van Bossuyt | 2015–present | |
| Mark Demesmaeker (delegation leader) | 2013–present | |
Federal Politics
| Chamber of Representatives (2014–2019) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Constituency | Name | Notes |
| | Rita Bellens | |
| | Siegfried Bracke | |
| | Peter Buysrogge | |
| | An Capoen | |
| | Inez De Coninck | |
| | Peter Dedecker | |
| | Koenraad Degroote | |
| | Zuhal Demir | |
| | Peter De Roover | |
| | Bart De Wever | |
| | Sophie De Wit | |
| | Christoph D'Haese | |
| | Daphne Dumery | |
| | Theo Francken | |
| | Rita Gantois | |
| | Karolien Grosemans | |
| | Jan Jambon | Floor leader |
| | Werner Janssen | |
| | Peter Luykx | |
| | Koen Metsu | |
| | Sarah Smeyers | |
| | Jan Spooren | |
| | Goedele Uyttersprot | |
| | Yoleen Van Camp | |
| | Steven Vandeput | |
| | Rob Van de Velde | |
| | Valerie Van Peel | |
| | Kristien Van Vaerenbergh | |
| | Jan Vercammen | |
| | Brecht Vermeulen | |
| | Hendrik Vuye | |
| | Bert Wollants | |
| | Veerle Wouters | |
| Senate (2014–2019) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Type | Name | Notes |
| Community Senator | Geert Bourgeois | |
| Community Senator | Cathy Coudyser | |
| Community Senator | Annick De Ridder | |
| Community Senator | Lieve Maes | |
| Community Senator | Philippe Muyters | |
| Community Senator | Jan Peumans | |
| Community Senator | Elke Sleurs | |
| Community Senator | Pol Van Den Driessche | |
| Community Senator | Wilfried Vandaele | |
| Community Senator | Karl Vanlouwe | |
| Co-opted senator | Jan Becaus | |
| Co-opted senator | Pol Van Den Driessche | |
Regional politics
| Flemish Government Bourgeois (2014–2019) | |
|---|---|
| Name | Function |
| Geert Bourgeois | Minister-President of the Flemish Government and Flemish Minister for Foreign Policy and Tourism |
| Liesbeth Homans | Vice Minister-President and Flemish Minister for Local Government, Poverty Reduction, Housing, Civic Integration, Equal Opportunities, Cities and Social Economy |
| Ben Weyts | Flemish Minister for Mobility and Public Works, the Brussels Periphery and Animal Welfare |
| Philippe Muyters | Flemish Minister for Work, Economy, Innovation, Science Policy and Sport |
| Brussels Regional Parliament (2014–2019) | |
|---|---|
| Name | Notes |
| Liesbet Dhaene | |
| Cieltje Van Achter | |
| Johan Van den Driessche | |
References
- ↑ "Open VLD heeft de meeste leden en steekt CD&V voorbij". deredactie.be. 30 October 2014.
- ↑ Parties and Elections in Europe: The database about parliamentary elections and political parties in Europe, by Wolfram Nordsieck
- ↑ Alison Pullen; Carl Rhodes (2015). The Routledge Companion to Ethics, Politics and Organizations. Routledge. p. 90. ISBN 978-1-136-74624-6.
- ↑ Pronunciation:
 Nieuw-Vlaamse Alliantie
Nieuw-Vlaamse Alliantie - ↑ Austin Sarat (2013). Special Issue: Immigration, Citizenship, and the Constitution of Legality. Emerald Group Publishing. p. 132. ISBN 978-1-78190-431-2.
- ↑ Kris Deschouwer; M. Theo Jans (2007). Politics Beyond the State: Actors and Policies in Complex Institutional Settings. Asp / Vubpress / Upa. p. 75. ISBN 978-90-5487-436-2.
- ↑ Hans Slomp (2011). Europe, a Political Profile: An American Companion to European Politics. ABC-CLIO. p. 465. ISBN 978-0-313-39181-1.
- ↑ Jan Erk; Lawrence M. Anderson (13 September 2013). PARADOX FEDERALISM. Routledge. p. 73. ISBN 978-1-317-98772-7.
- ↑ n-va.be, english information page
- ↑ Régis Dandoy; Arjan Schakel (19 November 2013). Regional and National Elections in Western Europe: Territoriality of the Vote in Thirteen Countries. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 54. ISBN 978-1-137-02544-9.
- ↑ Peter Starke; Alexandra Kaasch; Franca Van Hooren (7 May 2013). The Welfare State as Crisis Manager: Explaining the Diversity of Policy Responses to Economic Crisis. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 192. ISBN 978-1-137-31484-0.
- ↑ Anuradha Kataria (2011). Democracy on Trial, All Rise!. Algora Publishing. p. 119. ISBN 978-0-87586-811-0.
- ↑ Larry Johnston (13 December 2011). Politics: An Introduction to the Modern Democratic State. University of Toronto Press. p. 256. ISBN 978-1-4426-0533-6.
- ↑ European Politics. Oxford University Press. p. 92. ISBN 978-0-19-928428-3.
- ↑ Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc. (1 March 2011). Britannica Book of the Year 2011. Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc. p. 29. ISBN 978-1-61535-500-6.
- 1 2 Manifesto of the New Flemish Alliance point 13: "Inclusion for newcommers" (in Dutch)
- ↑ Manifesto of the New Flemish Alliance point 6: "Pacifisme" (in Dutch)
- ↑ Manifesto of the New Flemish Alliance point 3: "Flanders member state of the European Union" (in Dutch)
- ↑ Beginselverklaring N-VA
- ↑ Internationale persconferentie, N-VA.be. Retrieved on 2010-06-14.
- ↑ Knack Magazine election manifesto review 2014
- ↑ FAQ | Nieuw-Vlaamse Alliantie "Is the N-VA a pro-Europe party?"
- ↑ New Parties in Old Party Systems. Oxford University Press. p. 26. ISBN 978-0-19-964606-7.
- ↑ Trouw: "Laat Belgie maar rustig verdampen", last seen April 8th, 2010.
- ↑ Van Overtveldt, Johan (2014-06-18). "N-VA kiest voor ECR-fractie in Europees Parlement" [N-VA chooses ECR Group in the European Parliament]. standaard.be (in Dutch). Retrieved 2014-06-18.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Nieuw-Vlaamse Alliantie. |