Lake Eyre basin
| Lake Eyre basin | |
| Region | |
 | |
| Name origin: Lake Eyre; Edward John Eyre | |
| Country | Australia |
|---|---|
| States and territories |
Queensland, South Australia, Northern Territory, New South Wales |
| Landmarks | Sturt Stony Desert, Tirari Desert, Strzelecki Desert, Lake Eyre, Lake Frome, Lake Yamma Yamma |
| Rivers | Cooper Creek, Finke River, Georgina River, Diamantina River, Neales River, Macumba River |
| Lowest point | |
| - coordinates | 25°59′49″S 137°59′37″E / 25.99694°S 137.99361°E |
| Area | 1,200,000 km2 (463,323 sq mi) |
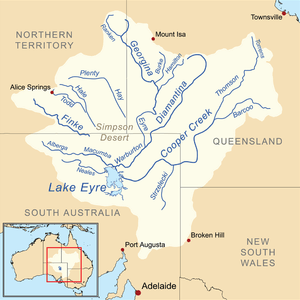 Map of the Lake Eyre Basin showing the major river | |
The Lake Eyre basin (/ˈɛər/ AIR) is a drainage basin that covers just under one-sixth of all Australia.[2] The Lake Eyre Basin is the largest endorheic basin in Australia and amongst the largest in the world, covering about 1,200,000 square kilometres (463,323 sq mi),[3] including much of inland Queensland, large portions of South Australia and the Northern Territory, and a part of western New South Wales.[4]
The deserts that have formed in the basin, including Sturt Stony Desert, Tirari Desert and the Strzelecki Desert, are most probably the southern hemisphere's largest source of airborne dust.[5] The basin is also one of the largest, least-developed arid zone basins with high degrees of variability anywhere.[2] Grazing is the major land use, occupying 82% of the total land within the basin.[6] The grazing is mostly low density due to harsh and variable climatic conditions.
The basin began as a sinking landmass mostly covered by forest and contained many more lakes than now. The climate has changed from wet to arid over the last 60 million years. Most of the rivers in the Lake Eyre basin are now slow flowing, flat and completely dry for lengthy periods. They all flow towards the lowest point in the basin, 16 metres (52 ft) below sea level, at Lake Eyre. Significant mineral deposits can be found in the basin. In 2004 the Lake Eyre Basin Intergovernmental Agreement was formed after concerns with the management of four separate state governments was raised as problems in the Murray-Darling basin arose.
Geology

The basin began to form in the early Paleogene (about 60 million years ago) when south-eastern South Australia started to sink and rivers began to deposit sediment into the large, shallow basin. The basin is still gradually sinking, and still gradually accumulating sediment.[7] For many millions of years, the Lake Eyre Basin was well supplied with water and largely forested. About 20 million years ago, large shallow lakes formed, covering much of the area for about 10 million years. From that time on, as Australia drifted further north and the climate became gradually more arid, the lakes and floodplains started to dry. Only in the last 2.6 million years did the onset of the ice ages bring about the present climatic regime and the consequent fairly rapid desertification of the area.
Significant minerals deposits such as oil and natural gas, including Australia's most significant onshore petroleum reserves, are found within the basin.[8] The mining and petroleum industries account for the greatest economic activity in the Lake Eyre Basin. Opals, coal, phosphate, gypsum and uranium are also mined from the basin.[8] In 2009, the Queensland Environmental Protection Agency confirmed that heavy metals from mining operations near Mount Isa had entered the upper reaches of the Georgina River.[9] The spill has the potential to contaminate parts of the basin as far south as Lake Eyre.
Geography

During years of especially high rainfall, all the riverbeds in this vast, mostly flat, arid and semi-arid area lead inland (not towards the sea) towards Lake Eyre in central South Australia.
Lake Eyre itself lies approximately 16 metres (52 ft) below sea level, and usually contains only salt. In flood years it fills and for a short time undergoes a period of rapid growth and fertility: long-dormant marine creatures multiply and large flocks of waterfowl arrive to feed and raise their young before the waters evaporate once more. The annual mean runoff in the Lake Eyre Basin is lowest of any of the world's major drainage basins.[10]
None of the creeks and rivers in the Lake Eyre Basin are permanent: they flow only after heavy rain – a rare to very rare event in the arid interior of Australia. Average annual rainfall in the area surrounding Lake Eyre is 125 millimetres (4.9 in), and the pan evaporation rate 3.5 metres (11 ft). Annualised average figures are misleading: since 1885 annual rainfall over the 1,100,000 square kilometres (420,000 sq mi) of the Lake Eyre Basin has ranged from about 45 millimetres (1.8 in) in 1928 to over 760 millimetres (30 in) in 1974. Most of the water reaching Lake Eyre comes from the river systems of semi-arid inland Queensland, roughly 1,000 kilometres (620 mi) to the north.
To provide a sense of scale, the Lake Eyre Basin is about the size of France, Germany and Italy combined. It is slightly larger than the Murray-Darling basin (which drains inland eastern Australia and is responsible for a large proportion of the continent's agricultural productivity) but has vastly less water. Nevertheless, the entire flow of the Murray-Darling would be insufficient to fill Lake Eyre, merely keeping pace with evaporation. In contrast, the flow of the Mississippi could fill Lake Eyre in 22 days, that of the Amazon in just 3 days.
Other lakes in the basin include Lake Frome, Lake Yamma Yamma and Lake Hart.
Rivers
The Cooper Creek, Finke River, Georgina River and Diamantina River are the four main rivers of the basin. Other desert rivers include the Hale River, Plenty River and Todd River that flow from the south east of the Northern Territory, south. In the western parts of the basin the Neales River and Macumba River flow into Lake Eyre.
Rivers within the basin have a low gradient, slow flow rate and a naturally turbid water quality.[6] Several of the major Lake Eyre Basin river systems are well-known. Because the Lake Eyre Basin is almost flat, rivers flow slowly and frequently split up into floodplains or multiple braided channels. Water is lost to evaporation, to seepage, and in the many ephemeral wetland systems, with the result that downstream flows are typically smaller than upstream flows. Only in exceptional years is there sufficient upstream rain to provide a flow into Lake Eyre itself.
The Finke River, starting roughly west of Alice Springs is thought to be the oldest riverbed in the world and although it flows for only a few days a year (in many years it does not flow at all) is home to seven species of fish, two of which are found nowhere else. The waters of the Finke disappear into the sands of the Simpson Desert and are not definitely known to ever make it as far south as Lake Eyre, although the story is told that this happened once early in the 20th century.
The Georgina River system originates on the Barkly Tableland, near the Northern Territory-Queensland border, north-west of Mount Isa and not far south of the Gulf of Carpentaria. In this relatively humid northern area, rainfall can be as high as 500 millimetres (20 in) per year and evaporation as low as 2.4 metres (7 ft 10 in). The Georgina flows through innumerable channels leading south through far-western Queensland for over 1,000 kilometres (620 mi), eventually reaching Goyder Lagoon in the north-eastern corner of South Australia.
Australia's early bush poets immortalised the Diamantina River, making it a symbol of the remote outback. It too rises in northern Queensland, roughly between Mount Isa and Winton, flowing 800 kilometres south and west through Birdsville and the Channel Country to join the Georgina at Goyder Lagoon (and then, if there is sufficient flow, down Warburton Creek towards Lake Eyre).
Of all the Lake Eyre Basin river systems, however, Cooper Creek is by far the most famous, in particular because it was along Cooper Creek that the explorers Burke and Wills met their deaths. It rises in the form of two central Queensland rivers, the Thomson between Longreach and Charters Towers, and the Barcoo in the area around Barcaldine, about 500 kilometres (310 mi) inland from Rockhampton. Cooper Creek spreads out into a vast area of meandering ephemeral channels, making its way roughly south into the far south-west corner of Queensland before turning due west into South Australia towards Lake Eyre. It takes almost a year for water to reach Lake Eyre from the headwaters. In most years, none does: it is absorbed into the earth, goes to fill channels and the many permanent waterholes, or simply evaporates. Water from Cooper Creek reached Lake Eyre in 1990 and then not again until 2010.[11]
Management
Management of the area has been problematic as it is covered by four different states' jurisdiction. As the ecological significance of the basin has become known and mis-management of the Murray-Darling Basin became apparent during the recent drought in Australia it became clear that ongoing management issues had to be resolved. The Lake Eyre Basin Intergovernmental Agreement was set up, between 2000 and 2004, to ensure the sustainability of the Lake Eyre Basin river systems, particularly to avoid or eliminate cross-border impacts. The Lake Eyre Basin Ministerial Forum was established as the decision making body responsible for overseeing of the Agreement.[12] The Ministerial Forum created a Community Advisory Committee to provide advice and facilitate community participation and a Scientific Advisory Panel to advise on scientific and technical issues.[12]
Protected areas
The Kati Thanda-Lake Eyre National Park, Strzelecki Regional Reserve, Witjira National Park, Sturt National Park and Simpson Desert National Park are among a number of protected areas established within the Lake Eyre Basin.
Fauna
A total of 27 individual species of fish are found in Lake Eyre basin, 13 of them are endemic.[13] The largest fish species is the Macquaria, reaching a maximum weight of about 3 kilograms (6.6 lb).[14]
References
- ↑ "Location Showcase". South Australian Film Corporation. Retrieved 5 March 2007.
- 1 2 Chrissy Arthur (2009-06-02). "Lake Eyre Basin needs more support: study". ABC News. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 2009-07-01.
- ↑ Map of the Lake Eyre basin
- ↑ Lake Eyre Basin. Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts.
- ↑ "Ghostly Face In South Australian Desert". NASA Earth Observatory. Retrieved 2008-06-23.
- 1 2 "Australian Catchment, River and Estuary Assessment 2002 - Integrated findings: Lake Eyre Drainage Division". Australian Natural Resources Atlas. Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts. Retrieved 2009-07-03.
- ↑ Sprigg, R.C. (1991): Geological Summary in: A natural history of the Lake Eyre Region. The South Australian National Parks and Wildlife Service's Northern Consultative Committee. State Print, Adelaide. ISBN 0 646 07 183 1
- 1 2 "Mining and petroleum within the Lake Eyre Basin". Lake Eyre Basin Ministerial Forum. Commonwealth of Australia. 2008-10-07. Retrieved 2009-07-01.
- ↑ "Floodplain group demands basin toxin details". ABC News Online. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 2009-03-09. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
- ↑ Laity, Julie J. (2009). Deserts and Desert Environments. John Wiley & Sons. p. 114. ISBN 1444300741. Retrieved 20 December 2012.
- ↑ Lockyer, Paul (15 June 2010). "Lake Eyre brims with life". ABC News Online. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 29 September 2010.
- 1 2 "Lake Eyre Basin Agreement". Lake Eyre Basin Ministerial Forum. Commonwealth of Australia. Retrieved 2009-07-01.
- ↑ Szaro, Robert C.; David W. Johnston (1996). Biodiversity in Managed Landscapes: Theory and Practice. Oxford University Press. p. 378. ISBN 0195079582. Retrieved 20 December 2012.
- ↑ Robin, Libby; Leo Joseph; Rob Heinshohn (2009). Boom & Bust: Bird Stories for a Dry Country. Csiro Publishing. p. 107. ISBN 064309606X. Retrieved 20 December 2012.
External links
25°59′49″S 137°59′57″E / 25.99686697°S 137.99905382°ECoordinates: 25°59′49″S 137°59′57″E / 25.99686697°S 137.99905382°E