GQ Lupi b
| Exoplanet | List of exoplanets | |
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| Parent star | ||
| Star | GQ Lupi | |
| Constellation | Lupus | |
| Right ascension | (α) | 15h 49m 12.144s[1] |
| Declination | (δ) | −35° 39′ 03.95″[1] |
| Distance | ~500 ly (~160[2] pc) | |
| Spectral type | K7V[1] | |
| Observed separation Observation epoch 2004–2007[2] | ||
| Angular separation | (ρ) | 732.1 ± 2.1[2] mas |
| Position angle | (θ) | 275.98 ± 0.25[2]° |
| Projected separation | (d) | 114 ± 33[2] AU |
| Physical characteristics | ||
| Mass | (m) | 1 – 36[3][2] MJ |
| Radius | (r) | 3.0 ± 0.5[2] RJ |
| Temperature | (T) | 2650 ± 100[2] |
| Discovery information | ||
| Discovery date | April 2005 | |
| Discoverer(s) | Neuhäuser et al. | |
| Discovery method | Imaged | |
| Discovery site | Paranal Observatory, Chile | |
| Discovery status | Published[4] | |
| Database references | ||
| Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia | data | |
| SIMBAD | data | |
| Exoplanet Archive | data | |
| Open Exoplanet Catalogue | data | |
GQ Lupi b is a possible extrasolar planet or brown dwarf orbiting the star GQ Lupi. Its discovery was announced in April 2005. Along with 2M1207b, this was one of the first extrasolar planet candidates to be directly imaged. The image was made with the VLT telescope at Paranal Observatory, Chile on June 25, 2004.[4]
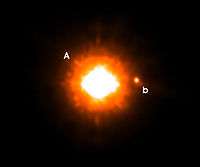
GQ Lupi b has a spectral type between M6 and L0, corresponding to a temperature of around 2650 kelvins.[2] Located at a projected distance of about 100 AU from its companion star, giving it an orbital period of perhaps about 1200 years, it is believed to be several times more massive than Jupiter. Because the theoretical models which are used to predict planetary masses for objects in young star systems like GQ Lupi b are still tentative, the mass cannot be precisely specified — models place GQ Lupi b's mass anywhere between a few Jupiter masses and 36 Jupiter masses.[2] At the highest end of this range, GQ Lupi b could be classified as a small brown dwarf rather than an exoplanet. As of 2006, the International Astronomical Union Working Group on Extrasolar Planets described GQ Lupi b as a "possible planetary-mass companion to a young star."[5]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 GQ Lupi, entry, SIMBAD. Accessed on line June 13, 2008.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Astrometric and photometric monitoring of GQ Lupi and its sub-stellar companion, Ralph Neuhäuser, Markus Mugrauer, Andreas Seifahrt, Tobias Schmidt, and Nikolaus Vogt, Astronomy and Astrophysics 484, #1 (2008), pp. 281–291. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078493. Bibcode: 2008A&A...484..281N
- ↑ Planet : GQ Lup b, Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia. Accessed on line June 13, 2008
- 1 2 Is this a Brown Dwarf or an Exoplanet? New Young Sub-stellar Companion Imaged with the VLT, ESO Press Release 09/05, April 7, 2005. Accessed on line June 13, 2008.
- ↑ Lists of Extrasolar Planets, IAU Working Group on Extrasolar Planets, August 28, 2006. Accessed on line June 13, 2008.
External links
![]() Media related to GQ Lupi b at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to GQ Lupi b at Wikimedia Commons
- "GQ Lup b". Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia. Retrieved 2008-06-09.
- "V* GQ Lup". SIMBAD. Retrieved 2008-06-09.
- Young, Kelly (2005-04-04). "First image of exoplanet orbiting Sun-like star". New Scientist. Retrieved 2008-06-09.
- "Telescopes see 'distant planet'". BBC News. 2005-04-04. Retrieved 2008-06-09.
- Britt, Robert Roy (2005-04-30). "Fresh Debate over First Photo of Extrasolar Planet". SPACE.com. Retrieved 2008-06-09.