Ferdinand Konščak

Ferdinand Konščak (Spanish: Fernando Consag) (December 2, 1703 – September 10, 1759) was a Croatian Jesuit missionary, explorer and cartographer.
Education
Konščak was born in Varaždin, Croatia, and attended primary and secondary school in his native city. At sixteen he finished the expected grades and was admitted to the novitiate of the Society of Jesus in Trenčín, Slovakia, where he stayed for two years. He was then sent to Leoben in Styria to study classics, stylistics, and rhetoric. Later he studied philosophy in Graz, Austria and in 1725–1726 he lectured on the Elements of Grammar at the Jesuit Academy in Zagreb in Croatia. In 1726–1727 he taught classical studies at a secondary school in Buda in Hungary. In 1728 Konščak published a collection of poems titled Nagadia versibus latinus, which is kept at Budapest, Hungary. From 1727 to 1729 he studied theology at the University of Graz.
Missionary
In 1729, Konščak left for Cádiz in Spain, then went to North America, where he was active as a missionary on New Spain's Baja California Peninsula (today part of Mexico), from 1732 to the end of his life. His headquarters was at Mission San Ignacio. From 1748 he acted as the superior of the mission and later, in 1758, inspector of all missions in Baja California. Konščak spoke various dialects of the local Cochimí language. He directed and oversaw the building of new missions, aqueducts, embankments, drainage channels, and the first silver mines. He died at San Ignacio in 1759.
Expeditions
Konščak mounted three expeditions (in 1746, 1751 and 1753) systematically exploring previously unknown parts of the peninsula.
In June and July 1746 he was sent by sea to the head of the Gulf of California in order to investigate the disputed question of whether Baja California was an island. Although he closely followed the coast and reached the Colorado River, the issue continued to be in dispute for nearly another three decades
His second expedition comprised a journey by land across the peninsula to the Pacific coast. The third expedition went up the western side of the peninsula, to around 30 degrees of latitude near Bahía San Luis Gonzaga.
During his expeditions, Konščak recorded information on the peninsula's unknown topography, natural resources, and native inhabitants.
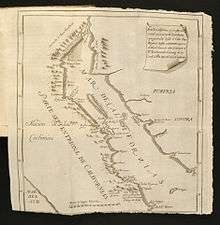
Maps and writings
On the basis of the data obtained, Konščak made a precise map of Baja California (1748) and a map of the Gulf of California (around 1750).
His maps of the regions explored were popular at the time frequently copied and used. Denis Diderot and D'Alembert used some of them within the French encyclopedia, where his name is cited as "P. Consaqua". Alexander von Humboldt used the maps in his work Carte generale ... de la Nouvelle Espagne, (Paris, 1804). The same is the case with Arrowsmith in his book Map of America, published in London in 1805.
His diaries, after his death translated and reprinted into many languages, were published during his lifetime by Villa-Senor y Sanchez, Ortega-Balthasar, and Venegas-Buriel.
The 1761 copy of his manuscript on California is held in the British Museum. His Carta del P. Fernando Consag de la Compania de Jesus, Visistaro de las Misiones de Californias are kept at:
- British Museum in London
- Library of Congress in Washington
- John Carter Library in Providence, Rhode Island
- Library of Pomona College in Pomona, California
- The Huntington Library in San Marino, California
Seven copies of maps are published by Ernest J. Burrus.
Konščak's name has also been associated with two anonymous accounts of Baja California: Descripción compendiosa de lo descubierto y conocido de la California and Adiciones to the same. Homer Aschmann in 1966 and Damir Zorić in 2000 suggested that Konščak was the author of the second of these, while Miguel León-Portilla in 1988 suggested that he wrote the first.
Memories
There is an outcrop in the northern Gulf of California named Roca Consag, located offshore near San Felipe. Konščak discovered many water springs so that even today there are shops and other facilities in California bearing his name like "Licores Konsag", (Liquor Store and Market, "Konsaqua" (purified water).
References
- Aschmann, Homer. 1959. The Central Desert of Baja California: Demography and Ecology. Iberoamericana, Vol. 42. University of California, Berkeley. ISBN 978-0-910950-01-5
- Aschmann, Homer. 1966. The Natural and Human History of Baja California. Dawson's Book Shop, Los Angeles.
- Burrus, Ernest J. 1967. La obra cartográfica de la Provincia Mexicana de la Compañía de Jesús, 1567–1967. J. Porrúa Turanzas, Madrid.
- Barco, Miguel del. 1988. Historia natural y crónica de la antigua California. Edited by Miguel León-Portilla. Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Mexico City. ISBN 968-36-8969-8
- Consag, Ferdinand. 1985. Descripción compendiosa de lo descubierto y conocido de la California, 1746. Edited by Catalina Velázquez Morales. Centro de Investigaciones Históricas UNAM-UABC, Mexicali, Mexico.
- Dunne, Peter Masten. 1952. Black Robes in Lower California. University of California Press, Berkeley. ISBN 0-520-00362-4
- Krmpotić, M. D. 1923. The Life and Works of the Reverend Ferdinand Konschak S.J. Stratford, Boston.
- Lazcano Sahagún, Carlos. 2001. Fernando Consag: textos y testimonios. Fundación Barco, Municipalidad de Varazdin, Museo de Historia de Ensenada, Seminario de Historia de Baja California, Ensenada, Mexico.
- Ortega, José de. 1944. Apostólicos afanes de la Compañía de Jesús en su provincia de México. Luis Álvarez y Álvarez de la Cadena, Mexico City.
- Venegas, Miguel. 1757. Noticia de la California y de su conquista temporal, y espíritual hasta el tiempo presente. 3 vols. M. Fernández, Madrid.
- Zevallos, Francisco. 1968. The Apostolic Life of Fernando Consag, Explorer of Lower California. Edited by Manuel P. Servin. Dawson's Book Shop, Los Angeles.
- Zorić, Damir. 2000. Misionar i kultura drugih: etnologijska istraživanja Ferdinanda Konšćaka (1703–1759) u donjoj Kaliforniji. HKD Napredak, Sarajevo, Bosnia. ISBN 9958-840-04-9