Energy in Armenia
Energy in Armenia describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Armenia.
Armenia has no proven reserves of oil or natural gas and currently imports nearly all of it from Russia. The new Iran-Armenia Natural Gas Pipeline has the capacity to provide twice the country's 2008 natural gas consumption and has the potential to provide energy security for Armenia as an alternative to the Russian-dominated imports that flow through the Georgian border.
Despite a lack of fossil fuel, Armenia has significant domestic electricity generation resources. The Armenian electrical energy sector has had a surplus capacity ever since emerging from a severe post-Soviet crisis in the mid-1990s thanks to the reopening of the nuclear power station at Metsamor.[1] The Metsamor Nuclear Power Plant provides 42.9% of the country's electricity. Armenia has plans to build a new NPP in order to replace the aging Metsamor which was built in 1979. The country also has eleven hydroelectric power plants and has plans to build a geothermal power plant in Syunik. Most of the rest of Armenia's electricity is generated by the natural gas-fired thermal power plants in Yerevan (completed in 2010) and Hrazdan.
Wind power in Armenia is underdeveloped and as of 2008, Armenia has only one wind power farm located in the Lori marz. The Armenian and Iranian energy sectors are currently jointly constructing the Iran-Armenia Wind Farm which is set to become the country's largest wind farm.[2]
Armenia is a partner country of the EU INOGATE energy programme, which has four key topics: enhancing energy security, convergence of member state energy markets on the basis of EU internal energy market principles, supporting sustainable energy development, and attracting investment for energy projects of common and regional interest.[3]
It is estimated that nearly 80 percent of Armenia's energy system is under Russian control.[4]
Oil
Armenia has no oil reserves. Most of its oil demands are met through imports from Russia. In Soviet times, this fuel made its way to Armenia via a direct rail link from Armenia-Georgia-Russia, but since the Abkhazia-Georgia border is closed fuel is transported across the Black Sea to Georgia from where it makes its way to Armenia via rail cars. Armenian oil demand is constrained, in large part, due to an economic embargo maintained by Azerbaijan to the East, and Turkey to the West. The embargo began shortly after the secession of Nagorno-Karabakh, an Armenian populated Azerbaijani enclave within Azerbaijan in 1988, and has held, despite a cease fire declared in 1994.[5]
Iran-Armenia oil pipeline
Armenian and Iranian authorities have for years been discussing an oil pipeline (distinct from the existing Iran-Armenia natural gas pipeline) that will pump Iranian oil products to Armenia; however, as of early 2011, no concrete dates have been set for the construction.[6] Armenian Energy Minister Armen Movsisian has said that the construction will take two years and cost Armenia about $100 million.[6] Iran's Oil Minister has said that the 365-kilometer pipeline could go on stream by 2014.[6] Iran plans to export 1.5 million liters of gasoline and diesel fuel a day to Armenia through the pipeline; Armenia’s annual demand for refined oil products stands at around 400,000 metric tons.[6]
Natural Gas
Natural gas represents a large portion of total energy consumption in Armenia, accounting for 50%. Armenia receives all of its natural gas from Russia (which has the world's largest reserves of natural gas and controls nearly 80% of the country's energy network).[4] Armrosgazprom holds a monopoly over the import and distribution of natural gas in Armenia.
Armenia's thermal power stations (which supply approximately 24% of Armenia's electricity needs) run on natural gas, making Armenia (at the present time) dependent on imported Russian gas to meeting its electricity needs.[7] Furthermore, natural gas is the primary means of winter heating in the country.
Russia-Georgia-Armenia pipelines
The Russian gas export monopoly Gazprom supplies Armenia with gas through a pipeline that runs through Georgia.[8] In 2007, Gazprom provided Armenia with just under 2 billion cubic meters of natural gas. As a transit fee, Armenia pays Georgia approximately 10% of the gas that was destined to reach Armenia.[9] Russian natural gas supplies to Georgia and Armenia are provided by two main pipelines: the North Caucasus-Transcaucasus pipeline (1,200 mm diameter) and the Mozdok-Tbilisi pipeline (700 mm diameter).[10]
In 2008, Armenia imported 2.2 billion cubic meters of natural gas from Russia.[11]
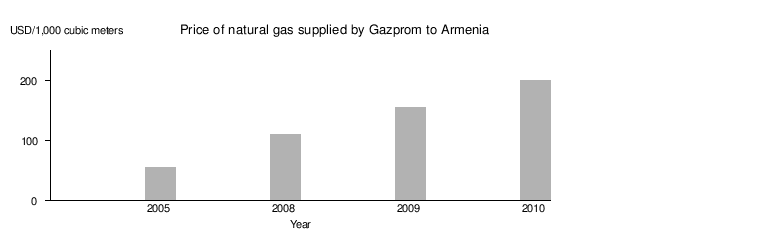
Iran-Armenia gas pipeline
A new gas pipeline, the Iran-Armenia Natural Gas Pipeline, was completed in October, 2008. It is owned and operated by ArmRosGazProm and links Armenia to neighboring Iran, which has the world's second largest natural gas reserve after Russia.[12] It has a capacity to pump 2.3-2.5 billion cubic meters of Iranian gas per year. However, although Iran is ready to export gas to Armenia, the Armenian Ministry of Energy claimed in October 2008 that it "does not yet have a need" for Iranian gas.[4] Analysts have said that Armenia's reluctance to import Iranian gas is a result of pressure from Russia which maintains a monopoly over Armenia's natural gas market.[4]
ArmRosGazProm (68% of which is owned by the Russian gas giant Gazprom) owns the natural gas pipeline network within Armenia that supplies gas to consumers and businesses. Furthermore, Gazprom wholly owns a crucial 24-mile section of the pipeline which Armenia surrendered in exchange for natural gas supplies from Russia at prices well below the European average until 2009. According to an analyst, Armenia "effectively bargained away its future prospects for energy sources in return for cheaper prices now." While Armenia could diversify its gas supply, with control of the Iran-Armenia gas pipeline, Gazprom now controls the competitors' supply.[12]
In 2009 Armenia was importing 1-1.5 million cubic meters of Iranian natural gas, paying for this by electricity exports.[11] In 2010 Iran will sell about 150 million cubic meters of natural gas to Armenia. A natural gas measuring center was installed late 2009/early 2010 at the Armenian-Iranian border to replace a provisional gas measuring station.[11]
Electricity
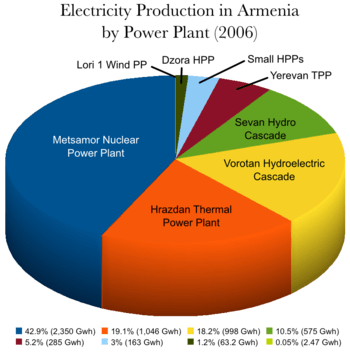
Despite a lack of fossil fuel, Armenia has significant domestic electricity generation resources. In 2006, non-thermal domestic electricity generation accounted for 76% of total generation: 43% nuclear and 33% hydroelectric. In comparison, in 2002, these numbers were 56%, 32%, and 26%.
In 2006, Armenia's power plants generated a total of 5,940.9 million KWh of electricity of which 5,566.7 million KWh were delivered (374.2 million KWh – or 6.3% – was consumed by the producing plants).[13] Thus, in 2006, Armenia's power plants on average generated 678.2 MW of power, while the country's electricity consumption rate on average was 635.5 MW.
Armenia has a total of 11 power stations and 17 220 kV substations. A map of Armenia's National Electricity Transmission Grid can be found at the website of the Global Energy Network Institute here .
United Energy Systems of Russia owns 70% of Electricity Networks of Armenia, the company that owns and manages Armenia's electricity grid.[14]
Nuclear Power Plant and Nuclear Fuel

Armenia's controversial Metsamor Nuclear Power Plant, constructed in 1979, has an installed capacity of 815 MW, though only one unit of 407.5 MW is currently in operation.[15] In 2006, it provided about 42.9% of the country's domestic electricity generation by generating 2,640.3 GWh of electricity (a yearly average of 301.4 MW of power).[13] Nuclear fuel must be flown in from Russia and then taken along a dirt road from Yerevan because Armenia's border with Turkey is closed.[5] While the Republic of Armenia is the sole owner of the plant, the Russian company United Energy Systems (UES) manages the Metsamor NPP.[4][16] Metsamor's resources will be exhausted by 2016.
Despite an abundance of renewable energy sources in the country, the government of Armenia is currently discussing the issue of constructing a new nuclear power plant of either 1,000 MW[17] or 1,200 MW,[18] with a projected cost of $4 billion and $5.2-7.2 billion dollars respectively. Armenian Deputy Minister of Energy and natural Resources Areg Galstyan said that the construction of the new nuclear power plant may start in 2011. The new NPP is expected to be commissioned in 2017.[18]
Thermal Power Plants
As of April 2010, thermal power plants (running on imported natural gas from Russia and Iran) provided about one-third of Armenia's electricity.[19]
Thermal power plants (running on natural gas) in Armenia have an established capacity of 1,756 MW.[15]
The following table lists the three thermal power plants which together account for 24% of Armenia's domestic electricity generation.[20]
| Plant | Year built | Operational capacity (MW) | Official Usage (MW) | 2006 Electricity Generation[13] (GWh) | 2006 Average Usage[13] (MW) | Ownership | Management |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vanadzor Thermal Power Plant | 1966-1976[21] | 96 | 0[21] | 0 | 0 | Zakneftegazstroy-Prometey[22] | |
| Hrazdan Thermal Power Plant | 1966–1974; 2012 | 1,110[23] + 480[24] | 1,138.3 | 129.9 | Hrazdan Energy Company (RazTES) (owned by the Russian Federation)[15][25][26] | Unified Energy System of Russia (since December, 2003)[23] | |
| Yerevan Thermal Power Plant | 1963-1967[27] | 550 | 50[28] | 337.0 | 38.5 |
New thermal power plants

In April 2010, a new natural gas-fired thermal power plant was inaugurated in Yerevan, making it the first major energy facility built in the country since independence.[19] The plant will reportedly allow Armenia to considerably cut back on use of natural gas for electricity production, because officials say it will also be twice as efficient as the plant’s decommissioned unit and four other Soviet-era facilities of its kind functioning in the central Armenian town of Hrazdan.[19] With a capacity of 242 megawatts, its gas-powered turbine will be able to generate approximately one-quarter of Armenia’s current (as of 2010) electricity output.[19] The state-of-the-art plant was built in Yerevan in place of an obsolete facility with a $247 million loan provided by the Japanese government through the Japan Bank of International Cooperation (JBIC). The long-term loan was disbursed to the Armenian government on concessional terms in 2007.[19]
Armenia’s energy sector will expand further after the ongoing construction of the Hrazdan thermal plant’s new and even more powerful Fifth Unit.[19] Russia’s Gazprom monopoly acquired the incomplete facility in 2006 as part of a complex agreement with the Yerevan government that raised its controlling stake in the Armenian gas distribution network to a commanding 80 percent. The Russian giant pledged to spend more than $200 million on finishing its protracted construction by 2011.[19]
The new Yerevan and Hrazdan facilities will pave the way for large-scale Armenian imports of natural gas from neighboring Iran through a pipeline constructed in late 2008. Armenia began receiving modest amounts of Iranian gas in May 2009. With Russian gas essentially meeting its domestic needs, it is expected that the bulk of that gas will be converted into electricity and exported to the Islamic Republic.[19]
In late-December 2010, the Armenian Energy Ministry announced that the fifth block of the Hrazdan thermal power plant will go online by April 2011.[1] Although construction on the fifth block began in the late 1980s, the Armenian government tried to unsuccessfully finish it in the late 1990s. The current project is part of a 2006 deal between Gazprom and the Armenian government, in which Gazprom acquired the incomplete facility and increased its stake in Armenia's gas distribution network, in turn pledging to spend $200 million in completing the project by 2011.[1]
Hydroelectric Power Plants

Hydropower plants have an established capacity of 1,038 MW.[15]
The economically justified hydropower potential of Armenia is around 3.600 GWh/year. From this amount, 1.500 GWh/year (or about 42% of economically justified hydropower potential) has been developed already.[29]
Armenia has 9 hydroelectric power plants which together accounted for 33% of its domestic electricity generation. The plants are grouped along two cascades: the Sevan–Hrazdan Cascade and the Vorotan Cascade.[29] The following table lists the details of each cascade:[20][29]
| Plant | Year built | Installed Capacity (MW) | Annual Average Production (GWh) | Ownership | Management |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sevan-Hrazdan Cascade | 1936-1961 | 556 | 936 (reduced to 487 because of the level of Lake Sevan) |
International Energy Corporation CJSC (privatized in June 2003)[15] (IEC is 90% owned by United Energy System of Russia)[14] | International Energy Corporation CJSC |
| Sevan Hydro Power Plant | 1949 | 34.2 | 50 | ||
| Atarbekyan Hydro Power Plant (Hrazdan) | 1959 | 81.6 | 136 | ||
| Gyumush Hydro Power Plant (Argel) | 1953 | 224 | 378 | ||
| Arzni Hydro Power Plant | 1956 | 70.5 | 13 | ||
| Kanaker Hydro Power Plant | 1936 | 102 | 151 | ||
| Yerevan 1 Hydro Power Plant | 1961 | 44 | 83 | ||
| Vorotan Cascade | 1970-1984 | 405.46 | 1010.7 | publicly owned[29] | |
| Spandaryan Hydro Power Plant | 1984 | 76 | 154 | ||
| Shamb Hydro Power Plant | 1977 | 171 | 272 | ||
| Tatev Hydro Power Plant | 1970 | 157.2 | 580 |
Planned projects
By 2020, it is expected that the Meghri HPP (also known as the Araks Hydro Power Plant) with 140 MW capacity and the Loriberd HPP with 60 MW capacity will be built with the cumulative generation of 1,012 million kWh/year.[30] The Meghri Hydro Power Plant is a joint Armenian-Iranian project to be constructed on the Araks River near Armenia's southern border town of Meghri.[31]
In 2010, the energy ministers of Armenia and Iran signed a document on the long-anticipated construction of two hydropower stations on the Arax River. The agreement stipulates that the $323 million project will be fundamentally financed and operated by Iran, 793 million kWh of energy transported to Iran annually, and the stations transferred to Armenia’s ownership 15 years later. Construction is expected to commence in 2011 and take five years to complete.[32]
Small hydroelectric power plants
According to a USAID sponsored report, 313 small hydroelectric power plants (small HPPs) with an installed capacity of 243.366 MW and an average yearly electricity production of 737.38 GWh are installed in the country.[30] In 2006, the small HPPs produced 166.6 GWh of electricity.[13]
| Name of water reservoir | Number of HPP units | Total installed capacity (MW) | Average yearly production (GWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Debed River | 79 | 35.501 | 123.47 |
| Aghstev River | 67 | 58.270 | 159.27 |
| Akhuryan River | 14 | 24.985 | 79.75 |
| Kasakh River | 14 | 7.905 | 19.16 |
| Hrazdan River | 13 | 9.070 | 27.37 |
| Lake Sevan | 20 | 22.965 | 66.03 |
| Azat River and Vedi River | 20 | 18.215 | 56.15 |
| Arpa River | 26 | 35.410 | 88.58 |
| Meghri River and Voghdji River | 53 | 21.245 | 72.63 |
| Vorotan River | 8 | 9.800 | 44.97 |
| Total | 313 | 243.366 | 737.38 |
Wind power

According to a study sponsored by the United States Department of Energy (DOE) and the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) in 2002-2003, the theoretical wind power potential of Armenia is 4,900 MWe in 4 zones with a total area of 979 km2.[33]
As of 2008, the Lori 1 Wind power plant is Armenia's only wind power plant. Completed in December 2005 by the Iranian company "Sunir" with funding from Iran, it consists of 4 wind turbines and has a capacity of 2.64 MWe. It is located along the Bazum Mountains at Pushkin Pass (40°54′41.36″N 44°25′52.86″E / 40.9114889°N 44.4313500°E) in Armenia's northern region of Lori. In 2006, the Lori 1 WPP generated only 2.6 GWh of electricity (a yearly average of 296.8 KWe—about 11% of installed capacity).[13]
The Armenian and Iranian energy sectors are currently jointly constructing the Iran-Armenia Wind Farm which is set to become the country's largest wind farm, having an installed electric capacity of 90 MW.[2]
Solar power
According to the report of Renewable Energy Roadmap for Armenia ([34]) the technical potential of the solar energy in the country is exceeding 1000 MW. Such a high number is due to the rather high average solar radiation over the country (around 1700 kWh/m2 annually). Yet the solar energy utilization in the country remains at very small scales and the developments are only at a research level.
Geothermal power
Armenia is constructing the Jermaghbyur Geothermal Power Plant which will be the country's largest geothermal power plant having an installed electric capacity of 150 MW.[35]
Thermal Energy
In addition to generating electricity, both the Yerevan Thermal Power Plant and the Hrazdan Thermal Power Plants can provide thermal energy to consumers and industry.[36]
Notes
- 1 2 3 "New Armenian Power Plant Set For Launch", Armenia Liberty (RFE/RL), December 21, 2010.
- 1 2 Iran-Armenia Wind Farm, Renewable Development Initiative.
- ↑ INOGATE website
- 1 2 3 4 5 ARMENIA: NEW PROJECTS A STAB AT INDEPENDENCE FROM MOSCOW?, EurasiaNet.org, October 17, 2008.
- 1 2 Official Energy Statistics from the U.S. Government - Caucasus Region, Energy Information Administration of the U.S. Department of Energy
- 1 2 3 4 "No Firm Date Set For Work On Another Armenian-Iranian Pipeline", Armenia Liberty (RFE/RL), February 15, 2011.
- ↑ "Armenian Power Utility Rules Out Price Rise", Armenian Liberty (RFE/RL), July 28, 2008.
- ↑ "ARMENIA: GAS PRICE HIKE POSES CHALLENGE FOR GOVERNMENT", EurasiaNet, April 24, 2008.
- ↑ "Georgia/Russia: Both Sides Move Closer On Gas Issues", Armenian Liberty (RFE/RL), December 21, 2005.
- ↑ Russian Gas Supplies to Georgia, Armenia Cut Over Pipeline Blasts - Ministry, RIA Novosti, January 22, 2006.
- 1 2 3 Armenia to import gas from Iran, Interfax-Ukraine (December 22, 2009)
- 1 2 Resolving a Supply Dispute, Armenia to Buy Russian Gas, New York Times, April 7, 2006.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 2006Q4 Electric Power: Main Indicators, Public Services Regulatory Commission of The Republic of Armenia, 2007.
- 1 2 THE ANNUAL REPORT RAO "UES OF RUSSIA" 2007, United Energy System of Russia, 2007.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Electric Power in Asia and the Pacific 2001 - 2002: Armenia", United Nations ESCAP.
- ↑ Armenian Government, ZAO "INTER RAO UES" Sign Agreement, United Energy System of Russia, September 18, 2003.
- ↑ Construction of Armenian NPP’S New Power Generating Unit May Cost $4 Bln, Energy Minister Says, ARKA News Agency, September 16, 2008.
- 1 2 Russian Academician: New NPP to Give Armenia Geopolitical Advantage, ARKA News Agency, October 23, 2008.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "Armenia Inaugurates New Power Plant", Armenia Liberty (RFE/RL), April 20, 2010.
- 1 2 Map of Armenian Electricity Grid, Global Energy Network Institute, September, 2000.
- 1 2 "Power Systems: Heat Energy", Ministry of Energy and Natural Resources of the Republic of Armenia.
- ↑ "PIPES, PATRIOTISM AND PROFITS: TWO GENERATIONS OF GEVORKIANS HEAD ONE OF RUSSIA'S LARGEST COMPANIES", AGBU News, April 1, 2006.
- 1 2 ZAO INTER RAO UES to Run ZAO "Razdanskaya TPP", Unified Energy System of Russia, December 3, 2003.
- ↑ http://energyland.info/news-show-tek-electro-107681
- ↑ The first four units of the Hrazdan TPP was given to Russia under a 2002-debit-for-equity deal. See GAS PRICES PROMPT ARMENIA TO DEBATE ALLIANCE WITH RUSSIA, Eurasianet.org, January 30, 2006.
- ↑ In April 2006, the fifth -- incomplete, but modern -- unit of the Hrazdan TPP was purchased by Gazprom from the Armenian government for $249 million. See Analysis: Russian-Armenian Gas Talks Inconclusive, RFE/RL, May 23, 2008.
- ↑ "General Information on Armenian Power Sector", Renewable Energy Armenia (Danish Energy Management A/S).
- ↑ "Power System: Yerevan TPP", Ministry of Energy and Natural Resources of the Republic of Armenia.
- 1 2 3 4 "Hydropower Potential of Armenia", Renewable Energy Armenia (Danish Energy Management A/S).
- 1 2 3 National Program on Energy Saving and Renewable Energy of Republic of Armenia, Scientific Research Institute of Energy for the Alliance to Save Energy, 2007.
- ↑ US CONCERNED BY ARMENIA’S ENERGY TIES WITH IRAN, EurasiaNet, June 21, 2007.
- ↑ Armenia in 2010. A Year of Uncertainty (PDF). Yerevan: The Civilitas Foundation. 2010. ISBN 978-99941-2-503-6. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-04-21.
- ↑ "Wind Power Potential", Renewable Energy Armenia (Danish Energy Management A/S).
- ↑
- ↑ New Geothermal Plant for Armenia, Renewable Development Initiative.
- ↑ Thermal Energy: Licensed companies, Public Services Regulatory Commission of The Republic of Armenia, 2008. (Armenian)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Energy in Armenia. |
- Ministry of Energy and Natural Resources of Armenia
- Renewable Energy Armenia
- Public Services Regulatory Commission of The Republic of Armenia (statistics on electricity generation & consumption, natural gas consumption, and thermal energy generation)
- Hrazdan Energy Company