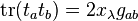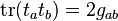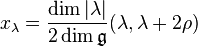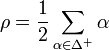Dynkin index
In mathematics, the Dynkin index
of a representation with highest weight  of a compact simple Lie algebra
of a compact simple Lie algebra 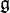 that has a highest weight
that has a highest weight 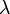 is defined by
is defined by
evaluated in the representation  . Here
. Here  are the matrices representing the generators, and
are the matrices representing the generators, and
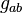 is given by
is given by
evaluated in the defining representation.
By taking traces, we find that
where the Weyl vector
is equal to half of the sum of all the positive roots of 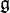 . The expression
. The expression 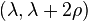 is the value quadratic Casimir in the representation
is the value quadratic Casimir in the representation  . The index
. The index 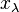 is always a positive integer.
is always a positive integer.
In the particular case where 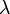 is the highest root, meaning that
is the highest root, meaning that  is the adjoint representation,
is the adjoint representation, 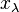 is equal to the dual Coxeter number.
is equal to the dual Coxeter number.
References
- Philippe Di Francesco, Pierre Mathieu, David Sénéchal, Conformal Field Theory, 1997 Springer-Verlag New York, ISBN 0-387-94785-X
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 1/20/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.