Drosera
| Drosera | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Drosera tokaiensis | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Eudicots |
| (unranked): | Core eudicots |
| Order: | Caryophyllales |
| Family: | Droseraceae |
| Genus: | Drosera L. |
| Subgenera | |
| |
Drosera, commonly known as the sundews, is one of the largest genera of carnivorous plants, with at least 194 species.[1] These members of the family Droseraceae lure, capture, and digest insects using stalked mucilaginous glands covering their leaf surfaces. The insects are used to supplement the poor mineral nutrition of the soil in which the plants grow. Various species, which vary greatly in size and form, are native to every continent except Antarctica.[2]
Both the botanical name (from the Greek δρόσος: drosos = "dew, dewdrops") and the English common name (sundew, derived from Latin ros solis, meaning "dew of the sun") refer to the glistening drops of mucilage at the tip of each tentacle that resemble drops of morning dew.
Characteristics

Sundews are perennial (or rarely annual) herbaceous plants, forming prostrate or upright rosettes between 1 and 100 cm (0.39 and 39.37 in) in height, depending on the species. Climbing species form scrambling stems which can reach much longer lengths, up to 3 m (9.8 ft) in the case of D. erythrogyne.[3] Sundews have been shown to be able to achieve a lifespan of 50 years.[4] The genus is so specialized for nutrient uptake through its carnivorous behavior, the pygmy sundew is missing the enzymes (nitrate reductase, in particular)[5] that plants normally use for the uptake of earth-bound nitrates.
Habit
The genus can be divided into several habits, or growth forms:
- Temperate sundews: These species form a tight cluster of unfurled leaves called a hibernaculum in a winter dormancy period (= Hemicryptophyte). All of the North American and European species belong to this group. Drosera arcturi from Australia (including Tasmania) and New Zealand is another temperate species that dies back to a horn-shaped hibernaculum.
- Subtropical sundews: These species maintain vegetative growth year-round under uniform or nearly uniform climatic conditions.
- Pygmy sundews: A group of roughly 40 Australian species, they are distinguished by miniature growth, the formation of gemmae for asexual reproduction, and dense formation of hairs in the crown center. These hairs serve to protect the plants from Australia's intense summer sun. Pygmy sundews form the subgenus Bryastrum.
- Tuberous sundews: These nearly 50 Australian species form an underground tuber to survive the extremely dry summers of their habitat, re-emerging in the autumn. These so-called tuberous sundews can be further divided into two groups, those that form rosettes and those that form climbing or scrambling stems. Tuberous sundews comprise the subgenus Ergaleium.
- Petiolaris complex: A group of tropical Australian species, they live in constantly warm but sometimes wet conditions. Several of the 14 species that comprise this group have developed special strategies to cope with the alternately drier conditions. Many species, for example, have petioles densely covered in trichomes, which maintain a sufficiently humid environment and serve as an increased condensation surface for morning dew. The Petiolaris complex comprises the subgenus Lasiocephala.
Although they do not form a single strictly defined growth form, a number of species are often put together in a further group:
- Queensland sundews: A small group of three species (D. adelae, D. schizandra and D. prolifera), all are native to highly humid habitats in the dim understories of the Australian rainforest.
Leaves and carnivory
Sundews are characterised by the glandular tentacles, topped with sticky secretions, that cover their laminae. The trapping and digestion mechanism usually employs two types of glands: stalked glands that secrete sweet mucilage to attract and ensnare insects and enzymes to digest them, and sessile glands that absorb the resulting nutrient soup (the latter glands are missing in some species, such as D. erythrorhiza). Small prey, mainly consisting of insects, are attracted by the sweet secretions of the peduncular glands. Upon touching these, the prey become entrapped by sticky mucilage which prevents their progress or escape. Eventually, the prey either succumb to death through exhaustion or through asphyxiation as the mucilage envelops them and clogs their spiracles. Death usually occurs within 15 minutes.[6] The plant meanwhile secretes esterase, peroxidase, phosphatase and protease enzymes.[7] These enzymes dissolve the insect and free the nutrients contained within it. This nutrient mixture is then absorbed through the leaf surfaces to be used by the rest of the plant.
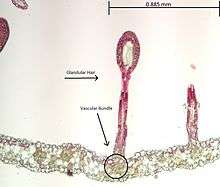
All species of sundew are able to move their tentacles in response to contact with edible prey. The tentacles are extremely sensitive and will bend toward the center of the leaf to bring the insect into contact with as many stalked glands as possible. According to Charles Darwin, the contact of the legs of a small gnat with a single tentacle is enough to induce this response.[6] This response to touch is known as thigmonasty, and is quite rapid in some species. The outer tentacles (recently coined as "snap-tentacles") of D. burmannii and D. sessilifolia can bend inwards toward prey in a matter of seconds after contact, while D. glanduligera is known to bend these tentacles in toward prey in tenths of a second.[8] In addition to tentacle movement, some species are able to bend their laminae to various degrees to maximize contact with the prey. Of these, D. capensis exhibits what is probably the most dramatic movement, curling its leaf completely around prey in 30 minutes. Some species, such as D. filiformis, are unable to bend their leaves in response to prey.[9]
A further type of (mostly strong red and yellow) emergence has recently been discovered in a few Australian species (D. hartmeyerorum, D. indica). Their function is not known yet, although they may help in attracting prey.
The leaf morphology of the species within the genus is extremely varied, ranging from the sessile ovate leaves of D. erythrorhiza to the bipinnately divided acicular leaves of D. binata.
Flowers and fruit

The flowers of sundews, as with nearly all carnivorous plants, are held far above the leaves by a long stem.This physical isolation of the flower from the traps was originally thought to be an adaptation meant to avoid trapping potential pollinators; a recent study, however, indicated Drosera species attract distinct types of insects as pollinators and prey, with little overlap.[10] Instead, the tall flower stalks probably help raise the flowers to a height where they are noticeable to pollinators. The mostly unforked inflorescences are spikes, whose flowers open one at a time and usually only remain open for a short period. Flowers open in response to light intensity (often opening only in direct sunlight), and the entire inflorescence is also helitropic, moving in response to the sun's position in the sky.
The radially symmetrical (actinomorphic) flowers are always perfect and have five parts (the exceptions to this rule are the four-petaled D. pygmaea and the eight to 12-petaled D. heterophylla). Most of the species have small flowers (<1.5 cm or 0.6 in). A few species, however, such as D. regia and D. cistiflora, have flowers 4 cm (1.6 in) or more in diameter.[9] In general, the flowers are white or pink. Australian species display a wider range of colors, including orange (D. callistos), red (D. adelae), yellow (D. zigzagia) or metallic violet (D. microphylla).
The ovary is superior and develops into a dehiscent seed capsule bearing numerous tiny seeds. The pollen grain type is compound, which means four microspores (pollen grains) are stuck together with a protein called callose.
Roots

The root systems of most Drosera are often only weakly developed. Serving mainly to absorb water and to anchor the plant to the ground, the roots are relatively useless for nutrient uptake. A few South African species use their roots for water and food storage. Some species have wiry root systems that remain during frosts if the stem dies. Some species, such as D. adelae and D. hamiltonii, use their roots for asexual propagation, by sprouting plantlets along their length. Some Australian species form underground corms for this purpose, which also serve to allow the plants to survive dry summers. The roots of pygmy sundews are often extremely long in proportion to their size, with a 1-cm (0.4-in) plant extending roots over 15 cm (5.9 in) beneath the soil surface. Some pygmy sundews, such as D. lasiantha and D. scorpioides, also form adventitious roots as supports. D. intermedia and D. rotundifolia have been reported to form arbuscular mycorrhizae, which penetrate the plant's tissues.[11]
Taxonomy and phylogenetics
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The unrooted cladogram to the right shows the relationship between various subgenera and classes as defined by the analysis of Rivadavia et al. in 2002.[12] The monotypic section Meristocaulis was not included in the study, so its place in this system is unclear. More recent studies have placed this group near section Bryastrum, so it is placed there below. Also of note, the placement of the section Regiae in relation to Aldrovanda and Dionaea is uncertain.[13] Since the section Drosera is polyphyletic, it shows up multiple times in the cladogram (*).
This phylogenetic study has made the need for a revision of the genus even clearer.
Reproduction
Many species of sundews are self-fertile; their flowers will often self-pollinate upon closing.[9] Often, numerous seeds are produced. The tiny black seeds germinate in response to moisture and light, while seeds of temperate species also require cold, damp, stratification to germinate. Seeds of the tuberous species require a hot, dry summer period followed by a cool, moist winter to germinate.
Vegetative reproduction occurs naturally in some species that produce stolons or when roots come close to the surface of the soil. Older leaves that touch the ground may sprout plantlets. Pygmy sundews reproduce asexually using specialized scale-like leaves called gemmae. Tuberous sundews can produce offsets from their corms.[9]
In culture, sundews can often be propagated through leaf, crown, or root cuttings, as well as through seeds.[9]
Distribution


The range of the sundew genus stretches from Alaska in the north to New Zealand in the south. The centers of diversity are Australia, with roughly 50% of all known species, and South America and southern Africa, each with more than 20 species. A few species are also found in large parts of Eurasia and North America. These areas, however, can be considered to form the outskirts of the generic range, as the ranges of sundews do not typically approach temperate or Arctic areas. Contrary to previous supposition, the evolutionary speciation of this genus is no longer thought to have occurred with the breakup of Gondwana through continental drift. Rather, speciation is now thought to have occurred as a result of a subsequent wide dispersal of its range.[12] The origins of the genus are thought to have been in Africa or Australia.[12]
Europe is home to only three species: D. intermedia, D. anglica, and D. rotundifolia. Where the ranges of the two latter species overlap, they sometimes hybridize to form the sterile D. × obovata. In addition to the three species and the hybrid native to Europe, North America is also home to four additional species; D. brevifolia is a small annual native to coastal states from Texas to Virginia, while D. capillaris, a slightly larger plant with a similar range, is also found in areas of the Caribbean. The third species, D. linearis, is native to the northern United States and southern Canada. D. filiformis has two subspecies native to the East Coast of North America, the Gulf Coast, and the Florida panhandle.
This genus is often described as cosmopolitan, meaning it has worldwide distribution. The botanist Ludwig Diels, author of the only monograph of the family to date, called this description an "arrant misjudgment of this genus' highly unusual distributional circumstances (arge Verkennung ihrer höchst eigentümlichen Verbreitungsverhältnisse)", while admitting sundew species do "occupy a significant part of the Earth's surface (einen beträchtlichen Teil der Erdoberfläche besetzt)".[14] He particularly pointed to the absence of Drosera species from almost all arid climate zones, countless rainforests, the American Pacific Coast, Polynesia, the Mediterranean region, and North Africa, as well as the scarcity of species diversity in temperate zones, such as Europe and North America.[14]
Habitat

Sundews generally grow in seasonally moist or more rarely constantly wet habitats with acidic soils and high levels of sunlight. Common habitats include bogs, fens, swamps, marshes, the tepuis of Venezuela, the wallums of coastal Australia, the fynbos of South Africa, and moist streambanks. Many species grow in association with sphagnum moss, which absorbs much of the soil's nutrient supply and also acidifies the soil, making nutrients less available to plant life. This allows sundews, which do not rely on soil-bound nutrients, to flourish where more dominating vegetation would usually outcompete them.
The genus, though, is very variable in terms of habitat. Individual sundew species have adapted to a wide variety of environments, including atypical habitats, such as rainforests, deserts (D. burmannii and D. indica), and even highly shaded environments (Queensland sundews). The temperate species, which form hibernacula in the winter, are examples of such adaptation to habitats; in general, sundews tend to inhabit warm climates, and are only moderately frost-resistant.
Conservation status

Although none of the Drosera species in the United States are federally protected, all are listed as threatened or endangered in some states.[15] Additionally, many of the remaining native populations lie on protected land, such as national parks or wildlife preserves. Drosera species are protected by law in many European countries, such as Germany,[16] Austria, Switzerland, the Czech Republic, Finland,[16] Hungary,[16] France,[16] and Bulgaria.[16] Currently, the largest threat in Europe and North America is habitat destruction for development projects, as well as the draining of bogs for agricultural uses and peat harvesting. In many regions, this has led to the extirpation of some species from parts of their former range. Reintroduction of plants into such habitats is usually difficult or impossible, as the ecological needs of certain populations is closely tied to their geographical location. Through increased legal protection of bogs and moors, as well as a concentrated effort to renaturalize such habitats, the threat to these plants' survival might be curbed, although most species would remain endangered. The relatively unimpressive image of these plants, as well as their small, low growth, makes them difficult to protect. As part of the landscape, sundews are often overlooked or not recognized at all.
In South Africa and Australia, two of the three centers of species diversity, the natural habitats of these plants are undergoing a high degree of pressure from human activities. Expanding population centers (such as Queensland, Perth, and Cape Town) threaten many such habitats, as does the draining of moist areas for agriculture and forestry in rural areas. The droughts that have been sweeping Australia over the last 10 years also pose a threat to many species by drying up previously moist areas.
Those species endemic to a very limited area are often most threatened by the collection of plants from the wild. D. madagascariensis is considered endangered in Madagascar because of the large-scale removal of plants from the wild for exportation; 10 - 200 million plants are harvested for commercial medicinal use annually.[16]
Uses

As a medicinal plant
Sundews were used as medicinal herbs as early as the 12th century, when an Italian doctor from the School of Salerno, Matthaeus Platearius, described the plant as an herbal remedy for coughs under the name herba sole. It has been used commonly in cough preparations in Germany and elsewhere in Europe. Sundew tea was especially recommended by herbalists for dry coughs, bronchitis, whooping cough, asthma and "bronchial cramps".[17] A modern study has shown that Drosera exhibits antitussive properties.[18]
Culbreth's 1927 Materia Medica listed D. rotundifolia, D. anglica and D.linearis as being used as stimulants and expectorants, and "of doubtful efficacy" for treating bronchitis, whooping cough, and tuberculosis.[19] Sundews have also been used as an aphrodisiac and to strengthen the heart, as well as to treat sunburn, toothache,[20] and prevent freckles. They are still used today in some 200-300 registered medications, usually in combination with other herbal ingredients. Today, Drosera is usually used to treat ailments such as asthma, coughs, lung infections, and stomach ulcers.
Medicinal preparations are primarily made using the roots, flowers, and fruit-like capsules.[21] Since all native sundews species are protected in many parts of Europe and North America, extracts are usually prepared using cultivated fast-growing sundews (specifically D. rotundifolia, D. intermedia, D. anglica, D. ramentacea and D. madagascariensis) or from plants collected and imported from Madagascar, Spain, France, Finland and the Baltics.[16]
As ornamental plants
Because of their carnivorous nature and the beauty of their glistening traps, sundews have become favorite ornamental plants; however, the environmental requirements of most species are relatively stringent and can be difficult to meet in cultivation. As a result, most species are unavailable commercially. A few of the hardiest varieties, however, have made their way into the mainstream nursery business and can often be found for sale next to Venus flytraps. These most often include D. capensis, D. aliciae, and D. spatulata.[22]
Cultivation requirements vary greatly by species. In general, though, sundews require high environmental moisture content, usually in the form of a constantly moist or wet soil substrate. Most species also require this water to be pure, as nutrients, salts, or minerals in their soil can stunt their growth or even kill them. Commonly, plants are grown in a soil substrate containing some combination of dead or live sphagnum moss, sphagnum peat moss, sand, and/or perlite, and are watered with distilled, reverse osmosis, or rain water.[9]
Nanobiotechnology
The mucilage produced by Drosera has remarkable elastic properties and has made this genus a very attractive subject in biomaterials research. In one recent study, the adhesive mucilages of three species (D. binata, D. capensis, and D. spatulata) were analyzed for nanofiber and nanoparticle content.[23] Using atomic force microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, researchers were able to observe networks of nanofibers and nanoparticles of various sizes within the mucilage residues. In addition, calcium, magnesium, and chlorine – key components of biological salts - were identified.[23] These nanoparticles are theorized to increase the viscosity and stickiness of the mucilage, in turn increasing the effectiveness of the trap. More importantly for biomaterials research, however, is the fact that, when dried, the mucin provides a suitable substrate for the attachment of living cells. This has important implications for tissue engineering, especially because of the elastic qualities of the adhesive. Essentially, a coating of Drosera mucilage on a surgical implant, such as a replacement hip or an organ transplant, could drastically improve the rate of recovery and decrease the potential for rejection, because living tissue can effectively attach and grow on it. The authors also suggest a wide variety of applications for Drosera mucin, including wound treatment, regenerative medicine, or enhancing synthetic adhesives.[23] Also of note, because this mucilage can stretch to nearly a million times its original size and is readily available for use, it can be an extremely cost-efficient source of biomaterial.
Other uses
The corms of the tuberous sundews native to Australia are considered a delicacy by the Australian Aborigines.[24] Some of these corms were also used to dye textiles,[25] while another purple or yellow dye was traditionally prepared in the Scottish Highlands using D. rotundifolia.[26] A sundew liqueur is also still produced using a recipe from the 14th century. It is made using fresh leaves from mainly D. capensis, D. spatulata, and D. rotundifolia.[25]
Chemical constituents
Several chemical compounds with potential biological activities are found in sundews, including flavonoids (kaempferol, myricetin, quercetin and hyperoside),[27] quinones (plumbagin,[28] hydroplumbagin glucoside[29] and rossoliside (7–methyl–hydrojuglone–4–glucoside)[30]), and other constituents such as carotenoids, plant acids (e.g. butyric acid, citric acid, formic acid, gallic acid, malic acid, propionic acid), resin, tannins and ascorbic acid (vitamin C).
Notes
- ↑ McPherson, S.R. 2010. Carnivorous Plants and their Habitats. 2 volumes. Redfern Natural History Productions Ltd., Poole.
- ↑ McPherson, S.R. 2008. Glistening Carnivores. Redfern Natural History Productions Ltd., Poole.
- ↑ Mann, Phill (2001). The world's largest Drosera; Carnivorous Plant Newsletter, Vol 30, #3: pg 79.
- ↑ Barthlott et al., Karnivoren, p. 102
- ↑ Karlsson PS, Pate JS (1992). "Contrasting effects of supplementary feeding of insects or mineral nutrients on the growth and nitrogen and phosphorus economy of pygmy species of Drosera". Oecologia. 92: 8–13. doi:10.1007/BF00317256.
- 1 2 Charles Darwin (1875). Insectivorous Plants. ISBN 1-4102-0174-0. Archived from the original on 2005-07-20.
- ↑ Barthlott et al., Karnivoren, p. 41
- ↑ Hartmeyer, I. & Hartmeyer, S., (2005) Drosera glanduligera: Der Sonnentau mit "Schnapp-Tentakeln", DAS TAUBLATT (GFP) 2005/2: 34-38
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 D'Amato, Peter (1998). The Savage Garden: Cultivating Carnivorous Plants. Berkeley, California: Ten Speed Press. ISBN 0-89815-915-6.
- ↑ Murza, Gillian L; Heaver, Joanne R; Davis, Arthur R (2006). "Minor pollinator-prey conflict in the carnivorous plant, Drosera anglica". Plant Ecology. 184 (1): 43–52. doi:10.1007/s11258-005-9050-y.
- ↑ B. Wang; Y.-L. Qiu (2006). "Phylogenetic distribution and evolution of mycorrhizas in land plants". Mycorrhiza. 16 (5): 299–363. doi:10.1007/s00572-005-0033-6. PMID 16845554.
- 1 2 3 Rivadavia, Fernando; Kondo, Katsuhiko; Kato, Masahiro und Hasebe, Mitsuyasu (2003). "Phylogeny of the sundews, Drosera (Droseraceae), based on chloroplast rbcL and nuclear 18S ribosomal DNA Sequences". American Journal of Botany. 90 (1): 123–130. doi:10.3732/ajb.90.1.123. PMID 21659087.
- ↑ http://www.amjbot.org/cgi/content/full/89/9/1503
- 1 2 Diels, Ludwig: Droseraceae, in Engler, A. (Hrsg.): Pflanzenr. 4, 112 : 109, 1906
- ↑ USDA, Threatened and Endangered; Results for Genus Drosera; Results compiled from multiple publications. (Retrieved 04:30, May 16, 2006)
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 World Wildlife Fund Germany, TRAFFIC Germany (eds.), Drosera spp. - Sonnentau, 2001, p. 5, PDF Online
- ↑ Schilcher, H.; Elzer, M. (1993). "Drosera (Sundew): A proven antitussive". Zeitschrift für Phytotherapie. 14 (50): 4.
- ↑ Oliver-Bever B. Plants in Tropical West Africa. Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 1986: 129.
- ↑ Culbreth, David M. R. Materia Medica and Pharmacology. Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia, 1927.
- ↑ Lewis, Walter H., 1977 Medical Botany - Plants Affecting Man's Health; John Wiley & Sons, St. Louis, Missouri. pg. 254. Plant decoction of "Drosera sp.." used in Mexico to treat toothache.
- ↑ Wichtl M.; Herbal Drugs and Phytopharmacetuicals; Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 1994, 178;81.
- ↑ Rice, Barry. 2006. Growing Carnivorous Plants. Timber Press: Portland, Oregon.
- 1 2 3 Zhang, M.; Lenaghan, S.C.; Xia, L.; Dong, L.; He, W.; Henson, W.R.; Fan, X. (2010). "Nanofibers and nanoparticles from the insect capturing adhesive of the Sundew (Drosera) for cell attachment". Journal of Nanobiotechnology. 8 (20): 20. doi:10.1186/1477-3155-8-20
- ↑ Barthlott et al., Karnivoren, p. 100
- 1 2 Plantarara (2001): Artzneimittle, Tee, und Likör aus fleischfressenden Pflanzen
- ↑ Dwelly, Edward; "Dwelly’s [Scottish] Gaelic Dictionary" (1911) (Dath)
- ↑ Ayuga C; et al. (1985). "Contribución al estudio de flavonoides en D. rotundifolia L". An R Acad Farm. 51: 321–326.
- ↑ Wagner H; et al. (1986). "Immunological investigations of naphthoquinone – containing plant extracts, isolated quinones and other cytostatic compounds in cellular immunosystems". Phytochem Soc Eur Symp: 43.
- ↑ Vinkenborg, J; Sampara-Rumantir, N; Uffelie, OF (1969). "The presence of hydroplumbagin glucoside in Drosera rotundifolia L". Pharmaceutisch weekblad. 104 (3): 45–9. PMID 5774641.
- ↑ Sampara-Rumantir N. (1971). "Rossoliside". Pharm Weekbl. 106 (35): 653–664. PMID 5566922.
Sources
Much of the content of this article comes from the equivalent German-language Wikipedia article (retrieved April 30, 2006).
- Barthlott, Wilhelm; Porembski, Stefan; Seine, Rüdiger; Theisen, Inge: Karnivoren. Stuttgart, 2004, ISBN 3-8001-4144-2
- Correa A., Mireya D.; Silva, Tania Regina Dos Santos: Drosera (Droseraceae), in: Flora Neotropica, Monograph 96, New York, 2005
- Darwin, Charles: Insectivorous Plants, 1875
- Lowrie, Allen: Carnivorous Plants of Australia, Vol. 1-3, English, Nedlands, Western Australia, 1987–1998
- Lowrie, Allen: A taxonomic revision of Drosera section Stolonifera (Droseraceae) from south-west Western Australia, 2005, Nuytsia 15(3):355-393. (Online: http://science.calm.wa.gov.au/nuytsia/15/3/355-394.pdf)
- Olberg, Günter: Sonnentau, Natur und Volk, Bd. 78, Heft 1/3, pp. 32–37, Frankfurt, 1948
- Rivadavia, Fernando; Kondo, Katsuhiko; Kato, Masahiro und Hasebe, Mitsuyasu: Phylogeny of the sundews, Drosera (Droseraceae), based on chloroplast rbcL and nuclear 18S ribosomal DNA Sequences, American Journal of Botany. 2003;90:123-130. (Online: http://www.amjbot.org/cgi/content/full/90/1/123)
- Seine, Rüdiger; Barthlott, Wilhelm: Some proposals on the infrageneric classification of Drosera L., Taxon 43, 583 - 589, 1994
- Schlauer, Jan: A dichotomous key to the genus Drosera L. (Droseraceae), Carnivorous Plant Newsletter, Vol. 25 (1996)
External links
-
 Media related to Sundew (Drosera) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Sundew (Drosera) at Wikimedia Commons -
 Data related to Sundew (Drosera) at Wikispecies
Data related to Sundew (Drosera) at Wikispecies -
 The dictionary definition of Sundew at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of Sundew at Wiktionary - A key to Drosera species, with distribution maps and growing difficulty scale
- A virtually exhaustive listing of Drosera pictures on the web
- International Carnivorous Plant Society
- Carnivorous Plant FAQ
- The Sundew Grow Guides
- Sundew images from smugmug
- Botanical Society of America, Drosera - the Sundews