Dibenzofuran
 | |
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| 132-64-9 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:28145 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL277497 |
| ChemSpider | 551 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.612 |
| KEGG | C07729 |
| PubChem | 568 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H8O | |
| Molar mass | 168.19 g/mol |
| Appearance | white crystalline powder |
| Melting point | 81 to 85 °C (178 to 185 °F; 354 to 358 K) |
| Boiling point | 285 °C (545 °F; 558 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases | R51/53 |
| S-phrases | S24/25 S29 S61 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Furan Benzofuran Dibenzodioxin Dibenzothiophene Carbazole Polyozellin (compound with a kernel with two dibenzofurans that share the same benzene ring) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
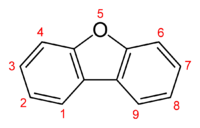
Dibenzofuran is a heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical structure shown at right. It is an aromatic compound that has two benzene rings fused to a central furan ring. All the numbered carbon atoms have a hydrogen atom bonded to each of them (not shown in the image). It is a volatile white solid that is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. It is obtained from coal tar, where it exists as a 1% component.[1]
Reactions
Dibenzofuran is thermally robust with a convenient liquid range. These properties together with its low toxicity, are exploited by the use of DBF as a heat transfer agent.[1]
It undergoes electrophilic reactions, such as halogenation and Friedel-Crafts reactions. Reaction of DBF with bultyl lithium results in dilithiation.[2]
Dibenzofuran is the precursor to the drug furobufen by Friedel-Crafts reaction with succinic anhydride.
Safety
Dibenzofuran is a relatively non-toxic compound as evidenced by rats being unaffected after a 200-day diet consisting of 0.025 – 0.4% of DBF.[1] The polychlorinated dibenzofurans are however controversial and potentially dangerous.
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Gerd Collin and Hartmut Höke "Benzofurans" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2007, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.l03_l01
- ↑ Ulrich Iserloh, Yoji Oderaotoshi, Shuji Kanemasa, and Dennis P. Curran "Synthesis of (R,R)-4,6-Dibenzofurandiyl-2,2'-Bis (4-Phenyloxazoline) (DBFOX/PH) – A Novel Trridentate Ligand" Org. Synth. 2003, volume 80, 46. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.080.0046