Chinese economic reform
| History of the People's Republic of China (PRC) |
|---|
 |
| History of |
| Generations of leadership |
|
|
The Chinese economic reform (simplified Chinese: 改革开放; traditional Chinese: 改革開放; pinyin: Gǎigé kāifàng; literally: "reform and opening-up") refers to the program of economic reforms termed "Socialism with Chinese characteristics" in the People's Republic of China (PRC) that was started in December 1978 by reformists within the Communist Party of China, led by Deng Xiaoping.
China had one of the world's largest and most advanced economies prior to the nineteenth century.[1] In the 18th century, Adam Smith claimed China had long been one of the richest, that is, one of the most fertile, best cultivated, most industrious, most prosperous and most urbanized countries in the world.[2] The economy stagnated beginning in the 16th century[3] and even declined in absolute terms in the nineteenth and much of the twentieth century, with a brief recovery in the 1930s.[4]
Economic reforms introducing market principles began in 1978 and were carried out in two stages. The first stage, in the late 1970s and early 1980s, involved the decollectivization of agriculture, the opening up of the country to foreign investment, and permission for entrepreneurs to start businesses. However, most industry remained state-owned. The second stage of reform, in the late 1980s and 1990s, involved the privatization and contracting out of much state-owned industry and the lifting of price controls, protectionist policies, and regulations, although state monopolies in sectors such as banking and petroleum remained. The private sector grew remarkably, accounting for as much as 70 percent of China gross domestic product by 2005.[5] From 1978 until 2013, unprecedented growth occurred, with the economy increasing by 9.5% a year. The conservative Hu-Wen Administration more heavily regulated and controlled the economy after 2005, reversing some reforms.[6]
The success of China's economic policies and the manner of their implementation has resulted in immense changes in Chinese society. Large-scale government planning programs alongside market characteristics have minimized poverty, while incomes and income inequality have increased, leading to a backlash led by the New Left. In the academic scene, scholars have debated the reason for the success of the Chinese "dual-track" economy, and have compared them to attempts to reform socialism in the Eastern Bloc and the Soviet Union; as well as the growth of other developing economies.
Chinese economy prior to reform
During the 1930s, China developed a modern industrial sector, which stimulated modest but significant economic growth. Before the collapse of international trade that followed the onset of the Great Depression, China’s share of world trade and its ratio of foreign trade to GDP achieved levels that were not regained for over sixty years.[4]
The economy was heavily disrupted by the war against Japan and the Chinese Civil War from 1937 to 1949, after which the victorious communists installed a planned economy.[4] Afterwards, the economy largely stagnated and was disrupted by the Great Leap Forward famine which killed between 30 and 40 million people, and the purges of the Cultural Revolution further disrupted the economy. Urban Chinese citizens experienced virtually no increase in living standards from 1957 onwards, and rural Chinese had no better living standards in the 1970s than the 1930s.[7] One study noted that average pay levels in the catering sector exceeded wages in higher education.[8]
The economic performance of the People's Republic of China was poor in comparison with other East Asian countries, such as Japan, South Korea and rival Chiang Kai-shek's Republic of China. The economy was riddled with huge inefficiencies and malinvestments, and with Mao's death, the Communist Party of China (CPC) leadership turned to market-oriented reforms to salvage the failing economy.[9]
Course of reforms

Economic reforms began after Deng Xiaoping and his reformist allies ousted the Gang of Four Maoist faction. By the time Deng took power, there was widespread support among the elite for economic reforms. As the de facto leader, Deng's policies faced opposition from party conservatives but were extremely successful in increasing the country's wealth.
1978–84
Deng's first reforms began in agriculture, a sector long neglected by the Communist Party. By the late 1970s, food supplies and production had become so deficient that government officials were warning that China was about to repeat the "disaster of 1959", the famines which killed tens of millions during the Great Leap Forward.[10] Deng responded by decollectivizing agriculture and emphasizing the household-responsibility system, which divided the land of the People's communes into private plots. Farmers were able to keep the land's output after paying a share to the state. This move increased agricultural production, increased the living standards of hundreds of millions of farmers and stimulated rural industry.[11] The bottom-up approach of the reforms promoted by Deng, in contrast to the top-down approach of the perestroika in the former Soviet Union, is considered an important factor contributing to the success of China’s economic transition.[12]
Reforms were also implemented in urban industry to increase productivity. A dual-price system was introduced, in which (State-owned enterprise reform 1979) state-owned industries were allowed to sell any production above the plan quota, and commodities were sold at both plan and market prices, allowing citizens to avoid the shortages of the Maoist era. Moreover, the adoption of Industrial Responsibility System 1980s further promote the development of state-owned enterprise by allowing individuals or groups to manage the enterprise by contract. Private businesses were allowed to operate for the first time since the Communist takeover, and they gradually began to make up a greater percentage of industrial output.[13] Price flexibility was also increased, expanding the service sector.[14]
The country was opened to foreign investment for the first time since the Kuomintang era. Deng created a series of special economic zones for foreign investment that were relatively free of the bureaucratic regulations and interventions that hampered economic growth. These regions became engines of growth for the national economy.[14]
1984–93
During this period, Deng Xiaoping's policies continued beyond the initial reforms. Controls on private businesses and government intervention continued to decrease, and there was small-scale privatization of state enterprises which had become unviable. A notable development was the decentralization of state control, leaving local provincial leaders to experiment with ways to increase economic growth and privatize the state sector.[15] Township and village enterprises, firms nominally owned by local governments but effectively private, began to gain market share at the expense of the state sector.[16] Conservative elder opposition, led by Chen Yun, prevented many major reforms which would have damaged the interests of special interest groups in the government bureaucracy.[17] Corruption and increased inflation increased discontent, contributing to the Tiananmen Square protests of 1989 and a conservative backlash after that event which ousted several key reformers and threatened to reverse many of Deng's reforms.[18] However, Deng stood by his reforms and in 1992, he affirmed the need to continue reforms in his southern tour.[17] He also reopened the Shanghai Stock Exchange closed by Mao 40 years earlier.
Although the economy grew quickly during this period, economic troubles in the inefficient state sector increased. Heavy losses had to be made up by state revenues and acted as a drain upon the economy.[19] Inflation became problematic in 1985, 1988 and 1992.[18] Privatizations began to accelerate after 1992, and the private sector grew as a percentage of GDP. China's government slowly expanded recognition of the private economy, first as a "complement" to the state sector (1988) and then as an "important component" (1999) of the socialist market economy.[20]
1993–2005
In the 1990s, Deng forced many of the conservative elders such as Chen Yun into retirement, allowing radical reforms to be carried out.[17] Despite Deng's death in 1997, reforms continued under his handpicked successors, Jiang Zemin and Zhu Rongji, who were ardent reformers. In 1997 and 1998, large-scale privatization occurred, in which all state enterprises, except a few large monopolies, were liquidated and their assets sold to private investors. Between 2001 and 2004, the number of state-owned enterprises decreased by 48 percent.[16] During the same period, Jiang and Zhu also reduced tariffs, trade barriers, and regulations; reformed the banking system; dismantled much of the Mao-era social welfare system; forced the PLA to divest itself of military-run businesses;[21] reduced inflation; and joined the World Trade Organization. These moves invoked discontent among some groups, especially laid-off workers of state enterprises that had been privatized.[22]
The domestic private sector first exceeded 50% of GDP in 2005 and has further expanded since. Also in 2005, China was able to surpass Japan as the largest economy in Asia.[23] However, some state monopolies still remained, such as in petroleum and banking.[24]
2005–present
The conservative Hu-Wen Administration began to reverse some of Deng Xiaoping's reforms in 2005. Observers note that the government adopted more egalitarian and populist policies.[25] It increased subsidies and control over the health care sector,[26] halted privatization,[6] and adopted a loose monetary policy, which led to the formation of a U.S.-style property bubble in which property prices tripled.[27] The privileged state sector was the primary recipient of government investment, which under the new administration, promoted the rise of large "national champions" which could compete with large foreign corporations.[6]
Economic performance since reform
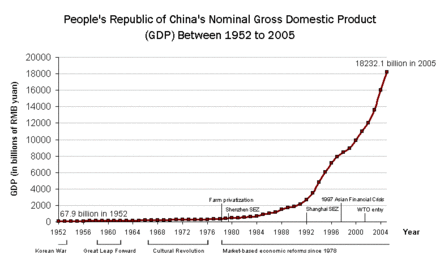
China's economic growth since the reform has been very rapid, exceeding the East Asian Tigers. Economists estimate China's GDP growth from 1978 to 2013 at between 9.5% to around 11.5% a year. Since the beginning of Deng Xiaoping's reforms, China's GDP has risen tenfold.[28] The increase in total factor productivity (TFP) was the most important factor, with productivity accounting for 40.1% of the GDP increase, compared with a decline of 13.2% for the period 1957 to 1978—the height of Maoist policies. For the period 1978–2005, Chinese GDP per capita increased from 2.7% to 15.7% of U.S. GDP per capita, and from 53.7% to 188.5% of Indian GDP per capita. Per capita incomes grew at 6.6% a year.[29] Average wages rose sixfold between 1978 and 2005,[30] while absolute poverty declined from 41% of the population to 5% from 1978 to 2001.[31] Some scholars believed that China's economic growth has been understated, due to large sectors of the economy not being counted.[32]
Impact on world growth
China is widely seen as an engine of world and regional growth.[33] Surges in Chinese demand account for 50, 44 and 66 percent of export growth of Hong Kong, Japan and Taiwan respectively, and China's trade deficit with the rest of East Asia helped to revive the economies of Japan and Southeast Asia.[33] Asian leaders view China's economic growth as an "engine of growth for all Asia".[34]
Reforms in specific sectors
After three decades of reform, China's economy experienced one of the world's biggest booms. Agriculture and light industry have largely been privatized, while the state still retains control over some heavy industries. Despite the dominance of state ownership in finance, telecommunications, petroleum and other important sectors of the economy, private entrepreneurs continue to expand into sectors formerly reserved for public enterprise. Prices have also been liberalized.[35]
Agriculture
During the pre-reform period, Chinese agricultural performance was extremely poor and food shortages were common.[36] After Deng Xiaoping implemented the household responsibility system, agricultural output increased by 8.2% a year, compared with 2.7% in the pre-reform period, despite a decrease in the area of land used.[36] Food prices fell nearly 50%, while agricultural incomes rose.[37]
A more fundamental transformation was the economy's growing adoption of cash crops instead of just growing rice and grain.[37] Vegetable and meat production increased to the point that Chinese agricultural production was adding the equivalent of California’s vegetable industry every two years. Growth in the sector slowed after 1984, with agriculture falling from 40% of GDP to 16%; however, increases in agricultural productivity allowed workers to be released for work in industry and services, while simultaneously increasing agricultural production.[38] Trade in agriculture was also liberalized and China became an exporter of food, a great contrast to its previous famines and shortages.[39]
Industry
In the pre-reform period, industry was largely stagnant and the socialist system presented few incentives for improvements in quality and productivity. With the introduction of the dual-price system and greater autonomy for enterprise managers, productivity increased greatly in the early 1980s.[40] Foreign enterprises and newly formed Township and Village Enterprises, owned by local government and often de facto private firms, competed successfully with state-owned enterprises. By the 1990s, large-scale privatizations reduced the market share of both the Township and Village Enterprises and state-owned enterprises and increased the private sector's market share. The state sector's share of industrial output dropped from 81% in 1980 to 15% in 2005.[41] Foreign capital controls much of Chinese industry and plays an important role.[16]
From virtually an industrial backwater in 1978, China is now the world's biggest producer of concrete, steel, ships and textiles, and has the world's largest automobile market. Chinese steel output quadrupled between 1980 and 2000, and from 2000 to 2006 rose from 128.5 million tons to 418.8 million tons, one-third of global production.[42] Labor productivity at some Chinese steel firms exceeds Western productivity.[42] From 1975 to 1992, China's automobile production rose from 139,800 to 1.1 million, rising to 9.35 million in 2008.[43] Light industries such as textiles saw an even greater increase, due to reduced government interference. Chinese textile exports increased from 4.6% of world exports in 1980 to 24.1% in 2005. Textile output increased 18-fold over the same period.[44]
This increase in production is largely the result of the removal of barriers to entry and increased competition; the number of industrial firms rose from 377,300 in 1980 to nearly 8 million in 1990 and 1996; the 2004 economic census, which excluded enterprises with annual sales below RMB 5 million, counted 1.33 million manufacturing firms, with Jiangsu and Zhejiang reporting more firms than the nationwide total for 1980.[45] Compared to other East Asian industrial growth spurts, China's industrial performance exceeded Japan's but remained behind South Korea and Taiwan's economies.[46]
Trade and foreign investment
Scholars find that China has attained a degree of openness that is unprecedented among large and populous nations, with competition from foreign goods in almost every sector of the economy. Foreign investment helped to greatly increase quality, knowledge and standards, especially in heavy industry. China's experience supports the assertion that globalization greatly increases wealth for poor countries.[45] Throughout the reform period, the government reduced tariffs and other trade barriers, with the overall tariff rate falling from 56% to 15%. By 2001, less than 40% of imports were subject to tariffs and only 9 percent of import were subject to licensing and import quotas. Even during the early reform era, protectionist policies were often circumvented by smuggling.[47] When China joined the WTO, it agreed to considerably harsher conditions than other developing countries.[48] Trade has increased from under 10% of GDP to 64% of GDP over the same period.[49] China is considered the most open large country; By 2005, China’s average statutory tariff on industrial products was 8.9 percent. For Argentina, Brazil, India, and Indonesia, the respective percentage figures are 30.9, 27.0, 32.4, and 36.9 percent.[50]
China's trade surplus is considered by some in the United States as threatening American jobs. In the 2000s, the Bush administration pursued protectionist policies such as tariffs and quotas to limit the import of Chinese goods. Some scholars argue that China's growing trade surplus is the result of industries in more developed Asian countries moving to China, and not a new phenomenon.[34] China's trade policy, which allows producers to avoid paying the Value Added Tax (VAT) for exports and undervaluation of the currency since 2002, has resulted in an overdeveloped export sector and distortion of the economy overall, a result that could hamper future growth.[51]
Foreign investment was also liberalized upon Deng's ascension. Special Economic Zones (SEZs) were created in the early 1980s to attract foreign capital by exempting them from taxes and regulations. This experiment was successful and SEZs were expanded to cover the whole Chinese coast. Although FDI fell briefly after the 1989 student protests, it increased again to 160 billion by 2004.[52]
Services

In the 1990s, the financial sector was liberalized.[53] After China joined the World Trade Organization (WTO), the service sector was considerably liberalized and foreign investment was allowed; restrictions on retail, wholesale and distribution ended.[54] Banking, financial services, insurance and telecommunications were also opened up to foreign investment.[55]
China's banking sector is dominated by four large state-owned banks, which are largely inefficient and monopolistic.[56] China's largest bank, ICBC, is the largest bank in the world. The financial sector is widely seen as a drag on the economy due to the inefficient state management.[57] Non-performing loans, mostly made to local governments and unprofitable state-owned enterprises for political purposes,[58] especially the political goal of keeping unemployment low, are a big drain on the financial system and economy, reaching over 22% of GDP by 2000, with a drop to 6.3% by 2006 due to government recapitalization of these banks. In 2006, the total amount of non-performing loans was estimated at $160 billion.[59] Observers recommend privatization of the banking system to solve this problem, a move that was partially carried out when the four banks were floated on the stock market.[60] China's financial markets, the Shanghai Stock Exchange and Shenzhen Stock Exchange, are relatively ineffective at raising capital, as they comprise only 11% of GDP.[61]
Due to the weakness of the banks, firms raise most of their capital through an informal, nonstandard financial sector developed during the 1980s and 1990s, consisting largely of underground businesses and private banks.[62] Internal finance is the most important method successful firms use to fund their activities.[62]
By the 1980s much emphasis was placed on the role of advertising in meeting the modernization goals being promoted by Deng. Lip service was still paid to old Maoist ideals of egalitarianism, but it did not inhibit the growth of consumerism.[63]
Government finances
In the pre-reform era, government was funded by profits from state-owned enterprises, much like the Soviet Union.[64] As the state sector fell in importance and profitability, government revenues, especially that of the central government in Beijing, fell substantially and the government relied on a confused system of inventory taxes. Government revenues fell from 35% of GDP to 11% of GDP in the mid-1990s, excluding revenue from state-owned enterprises, with the central government's budget at just 3% of GDP.[65] The tax system was reformed in 1994 when inventory taxes were unified into a single VAT of 17% on all manufacturing, repair, and assembly activities and an excise tax on 11 items, with the VAT becoming the main income source, accounting for half of government revenue. The 1994 reform also increased the central government's share of revenues, increasing it to 9% of GDP.[66]
Reasons for success
Scholars have proposed a number of theories to explain the success of China's economic reforms in its move from a planned economy to a socialist market economy despite unfavorable factors such as the troublesome legacies of socialism, considerable erosion of the work ethic, decades of anti-market propaganda, and the "lost generation" whose education disintegrated amid the disruption of the Cultural Revolution.[67]
One notable theory is that decentralization of state authority allowed local leaders to experiment with various ways to privatize the state sector and energize the economy.[15] Although Deng was not the originator of many of the reforms, he gave approval to them. Another theory focuses on internal incentives within the Chinese government, in which officials presiding over areas of high economic growth were more likely to be promoted. Scholars have noted that local and provincial governments in China were "hungry for investment" and competed to reduce regulations and barriers to investment to boost economic growth and the officials' own careers. A third explanation believes that the success of the reformists are attributable to Deng's cultivation of his own followers in the government.[68] Herman Kahn explained the rise of Asian economic power saying the Confucian ethic was playing a "similar but more spectacular role in the modernization of East Asia than the Protestant ethic played in Europe".[69]
China's success is also due to the export-led growth strategy used successfully by the Four Asian Tigers beginning with Japan in the 1960s–1970s and other Newly industrialized counties.[70]
The collapse of the Soviet Bloc and centrally planned economies in 1989 provided renewed impetus for China to further reform its economy through different policies in order to avoid a similar fate.[71] China also wanted to avoid the Russian ad-hoc experiments with market capitalism under Boris Yeltsin resulting in the rise of powerful oligarchs, corruption, and the loss of state revenue which exacerbated economic disparity.[72]
Effect on inequality
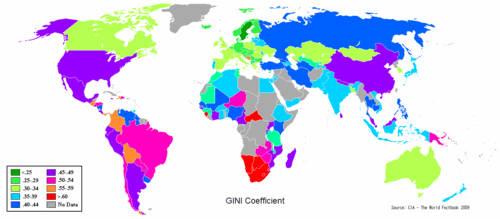
The economic reforms have increased inequality dramatically within China. Despite rapid economic growth which has virtually eliminated poverty in urban China and reduced it greatly in rural regions and the fact that living standards for everyone in China have drastically increased in comparison to the pre-reform era, the Gini coefficient of China is estimated to be above 0.45, comparable to some Latin American countries and the United States.[73]
Increased inequality is attributed to the disappearance of the welfare state and differences between coastal and interior provinces, the latter being burdened by a larger state sector.[74] Some Western scholars have suggested that reviving the welfare state and instituting a re-distributive income tax system is needed to relieve inequality,[75] while some Chinese economists have suggested that privatizing state monopolies and distributing the proceeds to the population can reduce inequality.[76]
Comparison to other developing economies

China's transition from a planned economy to a socialist market economy has often been compared with economies in Eastern Europe that are undergoing a similar transition. China's performance has been praised for avoiding the major shocks and inflation that plagued the Eastern Bloc.[77] The Eastern bloc economies saw declines of 13% to 65% in GDP at the beginning of reforms, while Chinese growth has been very strong since the beginning of reform.[78] China also managed to avoid the hyperinflation of 200 to 1,000% that Eastern Europe experienced.[79] This success is attributed to the gradualist and decentralized approach of the Chinese government, which allowed market institutions to develop to the point where they could replace state planning. This contrasts with the "big bang" approach of Eastern Europe, where the state-owned sector was rapidly privatized with employee buyouts, but retained much of the earlier, inefficient management.[80] Other factors thought to account for the differences are the greater urbanization of the CIS economies and differences in social welfare and other institutions.[81] Another argument is that, in the Eastern European economies, political change is sometimes seen to have made gradualist reforms impossible, so the shocks and inflation were unavoidable.[82]
China's economic growth has been compared with other developing countries, such as Brazil, Mexico, and India. GDP growth in China outstrips all other developing countries, with only India after 1990 coming close to China's experience.[83] Scholars believe that high rates of investments, especially increases in capital invested per worker, have contributed to China's superior economic performance.[83] China's relatively free economy, with less government intervention and regulation, is cited by scholars as an important factor in China's superior performance compared to other developing countries.[84]
Legacy and criticism
The government retains monopolies in several sectors, such as petroleum and banking. The recent reversal of some reforms have left some observers dubbing 2008 the "third anniversary of the end of reforms".[6] Nevertheless, observers believe that China's economy can continue growing at rates of 6–8 percent until 2025,[85] though a reduction in state intervention is considered to be necessary for sustained growth.[86]
Despite reducing poverty and increasing China's wealth, Deng's reforms have been criticized by the Chinese New Left for increasing inequality and allowing private entrepreneurs to purchase state assets at reduced prices. These accusations were especially intense during the Lang-Gu dispute, in which New Left academic Larry Lang accused entrepreneur Gu Sujung of usurping state assets, after which Gu was imprisoned.[87] The Hu-Wen Administration adopted some New Left policies, such as halting privatizations and increasing the state sector's importance in the economy, and Keynesian policies that have been criticized by some Chinese economists who advocate a policy of deregulation, tax cuts and privatization.[76]
Other criticisms focus on the effects of rapid industrialization on public health and the environment. However, scholars believe that public health issues are unlikely to become major obstacles to the growth of China’s economy during the coming decades, and studies have shown that air quality and other environmental measures in China are better than those in developed countries, such as the United States and Japan, at the same level of development.[88]
See also
- Economy of China
- Economic history of China (pre-1911)
- Economic history of China (1912–1949)
- Deng Xiaoping Theory
- Great Divergence
- Doi Moi
References
- ↑ Dahlman, Carl J; Aubert, Jean-Eric. China and the Knowledge Economy: Seizing the 21st century. WBI Development Studies. World Bank Publications. Accessed January 30, 2008.
- ↑ The Wealth of Nations, Adam Smith, 1776
- ↑ Maddison, Angus (2007): "Contours of the World Economy, 1–2030 AD. Essays in Macro-Economic History", Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-922721-1, p. 382, table A.7.
- 1 2 3 Brandt 2008, p. 4
- ↑ Engardio, Peter (21 August 2005). "'China Is a Private-Sector Economy'". Bloomberg Businessweek.
- 1 2 3 4 Scissors, Derek (May–June 2009). "Deng Undone: The Costs of Halting Market Reform in China". Foreign Affairs. 88 (3).
- ↑ Brandt 2008, pp. 5–6
- ↑ Brandt 2008, p. 6
- ↑ Brandt 2008, pp. 7–8
- ↑ Brandt 2008, p. 8
- ↑ Brandt 2008, p. 9
- ↑ Cited by Susan L. Shirk in The Political Logic of Economic Reform in China, University of California, Berkeley and Los Angeles, 1993. ISBN 0-520-07706-7
- ↑ Brandt 2008, p. 10
- 1 2 Brandt 2008, p. 11
- 1 2 Brandt 2008, pp. 17–18
- 1 2 3 Rawski 2008, p. 573
- 1 2 3 Naughton 2008, p. 114
- 1 2 Naughton 2008, p. 105
- ↑ Brandt 2008, p. 22
- ↑ Brandt 2008, p. 19
- ↑ Naughton 2008, p. 116
- ↑ Brandt 2008, p. 128
- ↑ Schoenleber, H. (23 September 2006). "China's Private Economy Grows Up". 8km.de.
- ↑ "China names key industries for state control", China Daily, (2006)
- ↑ Naughton 2008, p. 129
- ↑ "China's New Healthcare could cover millions more", Time magazine.
- ↑ Chovanec, Patrick (2009-06-08). "China's Real Estate Riddle". Far East Economic Review. Retrieved 13 March 2010.
- ↑ China has socialist market economy in place (People's Daily Online, 2005).
- ↑ Heston 2008, p. 28
- ↑ Fang 2008, p. 184
- ↑ Brandt 2008, p. 2
- ↑ Perkins 2008, p. 834
- 1 2 Branstetter 2008, p. 668
- 1 2 Branstetter 2008, p. 669
- ↑ Brandt 2008, p. 3
- 1 2 Huang 2008, p. 478
- 1 2 Huang 2008, p. 480
- ↑ Huang 2008, pp. 481–482
- ↑ Huang 2008, p. 483
- ↑ Rawski 2008, p. 572
- ↑ Perkins 2008, p. 862
- 1 2 Rawski 2008, p. 593
- ↑ "China poised to be world’s largest auto market". MSNBC. 2009-02-04.
- ↑ Rawski 2008, p. 588
- 1 2 Brandt 2008, p. 13
- ↑ Rawski 2008, p. 570
- ↑ Branstetter 2008, pp. 635–638
- ↑ Branstetter 2008, p. 655
- ↑ Brandt 2008, pp. 1–3
- ↑ Branstetter 2008, p. 656
- ↑ Branstetter 2008, p. 676
- ↑ Branstetter 2008, pp. 640–642
- ↑ Haggard, Stevens et al (2008), 339
- ↑ Branstetter 2008, p. 657
- ↑ Branstetter 2008, pp. 658–659
- ↑ Allen 2008, p. 522
- ↑ Perkins 2008, p. 866
- ↑ Allen 2008, p. 523
- ↑ Allen 2008, p. 528
- ↑ Allen 2008, p. 530
- ↑ Allen 2008, p. 514
- 1 2 Allen 2008, p. 556
- ↑ Xin Zhao and Russell W. Belk, "Politicizing Consumer Culture: Advertising's Appropriation of Political Ideology in China's Social Transition," Journal of Consumer Research (2008) 35#2 pp 231-244
- ↑ Wong 2008, p. 431
- ↑ Wong 2008, p. 440
- ↑ Wong 2008, p. 434
- ↑ Calhoun, Craig; Wasserstrom, Jeffrey N. (2003), "The Cultural Revolution and the Democracy Movement of 1989: Complexity in Historical Connections", in Law, Kam-yee, The Chinese cultural revolution reconsidered: beyond purge and holocaust, Palgrave Macmillan, p. 247, ISBN 978-0-333-73835-1, retrieved 2011-10-20
- ↑ Brandt 2008, pp. 18–19
- ↑ Kahn 1979, pp. 455
- ↑ Sharma, Shalendra D. (Winter–Spring 2007). "China's Economic Transformation". Global Dialogue. 9 (1–2).
- ↑ Dorn, James A. (Fall 2002). "Economic Development and Freedom: The Legacy of Peter Bauer" (PDF). Cato Journal. Cato Institute. 22 (2).
- ↑ Remnick, David (January–February 1997). "Can Russia Change?". Foreign Affairs. 76 (1).
- ↑ Benjamin 2008, p. 730
- ↑ Benjamin 2008, pp. 730–731
- ↑ Benjamin 2008, p. 774
- 1 2 Weiyin, Zhang, "Completely bury Keynesianism", (February 17, 2009)
- ↑ Svejnar 2008, p. 68
- ↑ Svejnar 2008, p. 74
- ↑ Svejnar 2008, p. 76
- ↑ Svejnar 2008, pp. 69–70
- ↑ Svejnar 2008, p. 72
- ↑ Naughton 2008, p. 96
- 1 2 Heston 2008, p. 37
- ↑ Heston 2008, p. 46
- ↑ Perkins 2008, p. 879
- ↑ Perkins 2008, p. 865
- ↑ "The Lang-Gu debate: a debate that has not yet ended", 30 October 2008
- ↑ Perkins 2008, pp. 870–871
Sources
- Allen, Franklin; et al. (2008), "China's Financial system: Past, present and future", in Brandt, Loren; Rawski, G. Thomas, China's Great Transformation, Cambridge: Cambridge university press
- Cardenal, Juan Pablo; Araújo, Heriberto (2011), La silenciosa conquista china (in Spanish), Barcelona: Crítica, ISBN 9788498922578
- Benjamin, Dwayne; et al. (2008), "Income inequality during China's Economic Transition", in Brandt, Loren; Rawski, G. Thomas, China's Great Transformation, Cambridge: Cambridge university press
- Brandt, Loren; et al. (2008), "China's Great Transformation", in Brandt, Loren; Rawski, G. Thomas, China's Great Transformation, Cambridge: Cambridge university press
- Bransetter, Lee; et al. (2008), "China's embrace of globalization", in Brandt, Loren; Rawski, G. Thomas, China's Great Transformation, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
- Cai, Fang; et al. (2008), "The Chinese labor market in the reform era", in Brandt, Loren; Rawski, G. Thomas, China's Great Transformation, Cambridge: Cambridge university press
- Haggard, Stevens; et al. (2008), "The political economy of private-sector development in China", in Brandt, Loren; Rawski, G. Thomas, China's Great Transformation, Cambridge: Cambridge university press
- Herston, Alan; et al. (2008), "China and Development economics", in Brandt, Loren; Rawski, G. Thomas, China's Great Transformation, Cambridge: Cambridge university press
- Huang, Jikun; et al. (2008), "Agriculture in China's Development: Past Disappointments, Recent Successes, and Future Challenges", in Brandt, Loren; Rawski, G. Thomas, China's Great Transformation, Cambridge: Cambridge university press
- Naughton, Barry; et al. (2008), "A Political Economy of China's Economic Transitionin China's Great Transformation", in Brandt, Loren; Rawski, G. Thomas, China's Great Transformation, Cambridge: Cambridge university press
- Perkins, Dwight; et al. (2008), "Forecasting China's growth to 2025", in Brandt, Loren; Rawski, G. Thomas, China's Great Transformation, Cambridge: Cambridge university press
- Rawski, G. Thomas; et al. (2008), "China's Industrial Development", in Brandt, Loren; Rawski, G. Thomas, China's Great Transformation, Cambridge: Cambridge university press
- Svejnar, Jan; et al. (2008), "China in light of other transition economies", in Brandt, Loren and Rawski, G. Thomas, China's Great Transformation, Cambridge: Cambridge university press
- Wong, P.W. Christine; et al. (2008), "China's Fiscal system: a work in progress", in Brandt, Loren; Rawski, G. Thomas, China's Great Transformation, Cambridge: Cambridge university press
- Zhao, Xin, and Russell W. Belk. (2008) "Politicizing Consumer Culture: Advertising's Appropriation of Political Ideology in China's Social Transition," Journal of Consumer Research 35#2 pp 231–244
External links
- Fengbo Zhang: Speech at “Future China Global Forum 2010”, Remembering China’s Reform and Open Policy on the 30th Anniversary

