Battle of Fraustadt
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Battle of Fraustadt was fought on 2 February 1706 (O.S.) / 3 February 1706 (Swedish calendar) / 13 February 1706 (N.S.) between Sweden and Saxony-Poland and their Russian allies near Fraustadt (present-day Wschowa) in Poland. During the Battle of Fraustadt on February 3, August II was only 120 kilometers away with a cavalry force about 8,000 men strong. This was one of the main reasons Swedish General Rehnskiöld hurried to engage Schulenburg. The battle is an example of a successfully executed pincer movement and was one of Sweden's greatest victories in the Great Northern War.
Background
Deployment
The Saxon army had not chosen its position carefully; Schulenburg had been maneuvered into a position chosen by the Swedes. Rehnskiöld withdrew his forces from Schlawa to Fraustadt. Rehnskiöld later stated in his journals, (Swedish) “Så resolverade jag att draga mig till Fraustadt tillbaka i den tanken att locka till mig fienden efter mig utur sin fördel, inbillandes honom att jag ville alldeles draga mig av” roughly translated as ”Thus I resolved to withdraw to Fraustadt with the thought to lure the enemy to me away from his advantageous position, deceiving him into thinking I was in full retreat”.
The Saxons, superior in numbers regarding infantry (9,000 Saxons and 6,300 Russians), but with less cavalry (4,000 Saxons) than the Swedes, took a strong defensive position behind lines of chevaux de frise littered by artillery. In two lines, with cavalry on both flanks, between the villages of Geyersdorf and Röhrsdorf and ahead of the town of Fraustadt, entrenched behind frozen lakes and marshes opposing the Saxon-Russian army, Rehnskiöld placed his infantry of 3,700 men in the center in three columns and his cavalry consisting of 5,700 units on both flanks.
The Battle
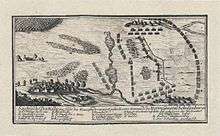
On the left flank, the Swedish cavalry under Hummerhielm had some trouble passing through a frozen swamp, but the Saxon cavalry did not use that advantage. After regrouping, the Swedes charged the Saxon Garde du Corps and Chevaliers Garde regiments three times, utterly routing them. Colonel von Krassow, commander of the Swedish cavalry on the right flank, passed outside the left Russian flank with 12 dragoon squadrons, near the village of Rörsdorf, and engaged the Saxon Cavalry covering the Russian flank. After witnessing the destruction of the Saxon right flank, the left flank fled, and were routed by the Swedish dragoons. Colonel von Krassow's cavalry then wheeled clock-wise into the Saxon-Russian rear, which caused several of the Saxon regiments to break formation.
On the Saxon left flank, facing Rehnskiöld's infantry, the Russians were deployed with their uniforms inside-out so they would look more like Saxons with their red colors instead of the Russian-standard green. This was however an order from Schulenburg who questioned their battle skills to reveal the weakness of the flank.[5] The Swedish infantry assaulted the Saxon-Russian line frontally, under heavy cannon and musket fire. Upon discovering that the left wing of the enemy line was held by the Russian troops, Rhenskiöld directed his infantry to assault their positions, which were also being attacked from the rear by colonel von Krassow's cavalry. The Russian infantry were quickly surrounded and dispersed.
The Saxon middle had its flank and rear exposed, and its regiments buckled and broke formation in short order under the pressure along its left flank. The Saxon right flank initially held, inflicting some damage to the Swedish infantry until the cavalry in the frozen swamp attacked their rear. The Saxon-Russian army fell apart and the main body fled to the south through Fraustadt. The Swedish cavalry, previously bogged down in the swamp, raced ahead on the open terrain, and met the fleeing Saxons and Russians on the far outskirts of the town. Trapped by Swedish cavalry to their front and infantry to their rear, the defeated Saxon-Russian forces surrendered en masse.
Casualties and losses
In the end 7,377 Saxons and Russians had been killed and over 7,300 taken prisoner where of 2,000 of them were wounded. Sweden suffered some 400 killed, (amongst them, commander of the Kronoberg Regiment, colonel Gabriel Lilliehöök) and 1,000 wounded. Schulenburg managed to escape, despite having suffered a bullet wound to his hip.[5] 71 banners, the whole Saxon artillery, 11,000 rapiers and equally as many muskets had also been captured. Rehnskiöld executed about 500 Russian prisoners; it is debated whether he did this in retaliation for Russian atrocities in Courland[6]:699 or because he believed their inside-out coats were an attempt to be recognized as Saxons, who were given better terms in captivity. Hiding your own identity and claiming to be something else was frowned upon at the time, and sometimes considered reason enough to be denied quarter. [4]
Analysis
The Swedish success in the battle was mainly due to Rehnskiöld effectively neutralising the Saxon infantry, who were superior in number at the start of the battle, combined with the pincer movement performed by the Swedish cavalry under Hummerhielm and von Krassow. Schulenburg also made two grave mistakes: first by being lured into terrain not to his advantage and then underestimating the mobility of the Swedish cavalry, especially on the flanks. It is known from Rehnskiöld's personal journals that he had intended a double envelopment from the beginning. The Battle of Fraustadt is one of the most classic double envelopments in military history. It is probable that Rehnskiöld had studied the Battle of Cannae 216 BC although it is uncertain if he intended to copy it.
Aftermath
The captured Russians (some 500) were, according to some historians, executed by an order from Rehnskiöld, although involvement of the latter has been disputed.[7] The authors further quotes Lieutenant Colonel Nils Gyllenstierna of the Norra Skånska cavalry regiment about the fate of the Russian infantry, (Swedish) “på några 100 när massakrerat, emedan vi inte i begynnelsen kunde giva kvarter, eftersom vår vänstra flygel ännu stod i full eld” roughly translated as “all but a few hundred were massacred, as initially quarters could not be given, since our left flank was still in full assault”.
The road to Saxony was open for King Charles XII of Sweden. King August II of Poland gave up his claim on the Polish crown, although he remained Elector Frederick Augustus I of Saxony. He would later regain the Polish throne in 1709. The prisoners taken by the Swedes during the battle that were of German, French and Swiss nationality were immediately reorganized into the ranks of the Swedish army. The Saxon prisoners were shipped to Sweden, where they formed a regiment and three battalions. This regiment made a good effort at the Battle of Helsingborg 1710.
The battle was the subject of the Sabaton song "Killing Ground" in their album Carolus Rex.
See also
References
- ↑ Ericson, Lars m.fl (2003). Svenska slagfält (in Swedish). Värnamo: Wahlström & Widstrand. p. 274. ISBN 91-46-21087-3.
- ↑ Sjöström, Oskar (2008). Fraustadt 1706. Ett fält färgat rött (in Swedish). Lund: Historiska Media. pp. 132–133. ISBN 978-91-85507-90-0.
- ↑ Беспалов А. В. (Alexander V. Bespalov) Русский вспомогательный корпус на службе Саксонии в эпоху Великой Северной войны // Северная Европа: проблемы истории. Вып.5. М., 2005. С. 245.
- 1 2 Sjöström, Oskar (2008). Fraustadt 1706. Ett fält färgat rött (in Swedish). Lund: Historiska Media. pp. 145–146. ISBN 978-91-85507-90-0.
- 1 2 Slaget vid Fraustadt, Youtube
- ↑ Tucker, S.C., 2010, A Global Chronology of Conflict, Vol. Two, Santa Barbara: ABC-CLIO, LLC, ISBN 9781851096671
- ↑ Svenska Slagfält, 2003, (Walhlström & Widstrand) ISBN 91-46-21087-3
- http://www.wfgamers.org.uk/resources/C18/fraustadt.htm Orders of Battle
Coordinates: 51°48′00″N 16°19′00″E / 51.800000°N 16.316667°E

