Axon hillock
| Axon hillock | |
|---|---|
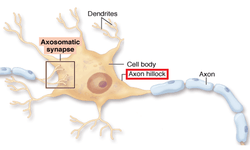 red labeled is pointing directly at the axon hillock. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Colliculus axonis |
| Code | TH H2.00.06.1.00006 |
The axon hillock is a specialized part of the cell body (or soma) of a neuron that connects to the axon.
The axon hillock is the last site in the soma where membrane potentials propagated from synaptic inputs are summated before being transmitted to the axon. For many years, it had been believed that the axon hillock was the usual site of action potential initiation. It is now thought that the earliest site of action potential initiation is found just adjacent, in the initial (unmyelinated) segment of the axon.[1] However, the positive point, at which the action potential starts, varies between cells. It can also be altered by hormonal stimulation of the neuron, or by second messenger effects of neurotransmitters.
The axon hillock also functions as a tight junction, since it acts as a barrier for lateral diffusion of transmembrane proteins, GPI anchored proteins such as thy1, and lipids embedded in the plasma membrane.
Structure
The axon hillock has a number of specialized properties that make it capable of action potential generation, including adjacency to the axon and a much higher density of voltage-gated ion channels than is found in the rest of the cell body.[2] In dorsal root ganglion cells, the cell body is thought to have approximately 1 voltage-gated sodium channel per square micrometre, while the axon hillock and initial segment of the axon have about ~100–200 voltage-gated sodium channels per square micrometre; in comparison, the nodes of Ranvier along the axon are thought to have ~1000–2000 such channels per square micrometre.[3] This clustering of voltage-gated ion channels is a consequence of plasma-membrane and cytoskeletal associating proteins such as ankyrin.[4]
In electrophysiological models, the axon hillock is included with the initial segment of the axon where membrane potentials propagate from synaptic inputs to the dendrites or cell body are summed.
Function
Both inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) and excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) are summed in the axon hillock and once a triggering threshold is exceeded, an action potential propagates through the rest of the axon (and "backwards" towards the dendrites as seen in neural backpropagation). The triggering is due to positive feedback between highly crowded voltage-gated sodium channels, which are present at the critical density at the axon hillock (and nodes of ranvier) but not in the soma.
In its resting state, a neuron is polarized, with its inside at about -70 mV relative to its surroundings. When an excitatory neurotransmitter is released by the presynaptic neuron and binds to the postsynaptic dendritic spines, ligand-gated ion channels open, allowing sodium ions to enter the cell. This may make the postsynaptic membrane depolarized (less negative). This depolarization will travel towards the axon hillock, diminishing exponentially with time and distance. If several such events occur in a short time, the axon hillock may become sufficiently depolarized for the voltage-gated sodium channels to open. This initiates an action potential that then propagates down the axon.
As sodium enters the cell, the cell membrane potential becomes more positive, which activates even more sodium channels in the membrane. The sodium influx eventually overtakes the potassium efflux (via the potassium leak channels), initiating a positive feedback loop (rising phase). At around +40 mV, the voltage-gated sodium channels begin to close (peak phase) and the voltage-gated potassium channels begin to open, moving potassium down its electrochemical gradient and out of the cell (falling phase).
The potassium channels exhibit a delayed reaction to the membrane repolarisation, and, even after the resting potential is achieved, some potassium continues to flow out, resulting in an intracellular fluid that is more negative than the resting potential, and during which no action potential can begin (undershoot phase/refractory period). This undershoot phase ensures that the action potential propagates down the axon and not back up it.
Once this initial action potential is initiated, principally at the axon hillock, it propagates down the length of the axon. Under normal conditions, the action potential would attenuate very quickly due to the porous nature of the cell membrane. To ensure faster and more efficient propagation of action potentials, the axon is myelinated. Myelin, a derivative of cholesterol, acts as an insulating sheath and ensures that the signal cannot escape through the ion or leak channels. There are, nevertheless, gaps in the insulation (nodes of ranvier), which boost the signal strength. As the action potential reaches a node of Ranvier, it depolarises the cell membrane. As the cell membrane is depolarised, the voltage-gated sodium channels open and sodium rushes in, triggering a fresh new action potential.
See also Initiation Action
References
- ↑ Clark BD, Goldberg EM & Rudy B (December 2009). "Electrogenic Tuning of the Axon Initial Segment". Neuroscientist. 15 (6): 651–668. doi:10.1177/1073858409341973. PMC 2951114
 . PMID 20007821. Retrieved 2010-05-02.
. PMID 20007821. Retrieved 2010-05-02. - ↑ Wollner D & Catterall WA (November 1986). "Localization of sodium channels in axon hillocks and initial segments of retinal ganglion cells". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 83 (21): 8424–28. doi:10.1073/pnas.83.21.8424. PMC 386941
 . PMID 2430289.
. PMID 2430289. - ↑ Safronov BV, Wolff M, Vogel W (February 1, 1999). "Axonal expression of sodium channels in rat spinal neurones during postnatal development". J Physiol. 514 (3): 729–34. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.729ad.x. PMC 2269106
 . PMID 9882745.
. PMID 9882745. - ↑ Zhou D, Lambert S, Malen PL, Carpenter S, Boland LM, Bennett V (November 30, 1998). "AnkyrinG Is Required for Clustering of Voltage-gated Na Channels at Axon Initial Segments and for Normal Action Potential Firing". The Journal of Cell Biology. 143 (5): 1295–304. doi:10.1083/jcb.143.5.1295. PMC 2133082
 . PMID 9832557.
. PMID 9832557.
External links
- Histology image: 3_09 at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center - "Slide 3 Spinal cord"