2100 Ra-Shalom
|
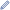
Light-curve based 3-D model of 2100 Ra-Shalom | |
| Discovery [1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | E. F. Helin |
| Discovery site | Palomar Obs. |
| Discovery date | 10 September 1978 |
| Designations | |
| MPC designation | 2100 Ra-Shalom |
Named after |
Ra and Shalom (composed name)[2] |
| 1978 RA · 1975 TB | |
| Aten · NEO | |
| Orbital characteristics [1] | |
| Epoch 14 April 2004 (JD 2453109.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 38.06 yr (13,902 days) |
| Aphelion | 1.1952 AU |
| Perihelion | 0.4688 AU |
| 0.8320 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.4365 |
| 0.76 yr (277 days) | |
| 81.749° | |
| Inclination | 15.756° |
| 170.88° | |
| 355.97° | |
| Earth MOID | 0.1492 AU |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions |
2.3±0.2 km[3] 2.04 km[4] 2.48 km[5] 2.78 km[6] 2.24 km[7] 2.22 km[8] 1.98±0.05 km[9] 2.79 km[10] |
|
19.797 h[11][lower-alpha 1] 19.79 h[12] 19.79±0.03 h[13] 19.79981 h[14] 19.793±0.001 h[3] 19.8201±0.00004 h[15] | |
|
0.13±0.03[3][7] 0.16[4] 0.125[5] 0.082[6][16] 0.14[8] 0.14±0.10[17] 0.177±0.009[9] 0.080[10] | |
|
B–V = 0.712 U–B = 0.310 C (Tholen)[1] Xc (SMASS)[1] C (CALL)[16] | |
| 16.05[1] | |
|
| |
2100 Ra-Shalom, provisional designation 1978 RA, is an eccentric, carbonaceous asteroid, classified as Aten asteroid and near-Earth object, about 2.7 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered by American astronomer Eleanor Helin at the U.S. Palomar Observatory in California, on 10 September 1978.[18]
It was the second Aten asteroid to be discovered after 2062 Aten, the family's namesake, also discovered by Helin in 1976. The group of Aten asteroids feature a semi-major axis of less than 1 AU. Of this group, "Ra-Shalom" has one of the smallest semi-major axes, just 0.832 AU. It comes within 30 gigameter (Gm) of Mars, Earth, Venus, and Mercury. The closest approaches are to Mercury, to about 0.0784 AU (11.7 Gm).[19]
The asteroid orbits the Sun at a distance of 0.5–1.2 AU once every 0 years and 9 months (277 days). Its orbit is tilted by 16 degrees to the plane of the ecliptic and shows a very high eccentricity of 0.44. It has a C-type and Xc-type spectrum on the Tholen and SMASS taxonomic scheme, respectively, and an Earth Minimum Orbit Intersection Distance (MOID) of slightly less than 0.14 AU, which is far too large to make it a potentially hazardous object.[1]
Over the last two decades, a large number of photometric light-curve observations have determined a concurring, well-defined rotation period of 19.8 hours, while the body's albedo varies from 0.08 to 0.16 and its diameter lies in the range of 1.98 to 2.79 kilometers (also see infobox). Among these differing results, the Collaborative Asteroid Lightcurve Link (CALL) considers an albedo of 0.082 with a diameter of 2.78 kilometers as the most reliable result.[16] In 1981, the asteroid was detected using radar, revealing a relatively smooth surface at decimeter scales.[12]
The minor planet's composed named was chosen by the discoverer to commemorate the Camp David Peace Accords between Egypt and Israel in September 1978, and as a symbol for the universal hope for peace. Ra is the Egyptian Sun-god, who symbolizes enlightenment and life, while Shalom is the traditional Hebrew greeting meaning peace.[2]
References
- ↑ Pravec (2003) web: rotation period 19.797 hours with a brightness amplitude of 0.34 in magnitude. Period Identical with Pravec's observation in 1998. Summary figures at Collaborative Asteroid Lightcurve Link (CALL) for (2100) Ra-Shalom
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 2100 Ra-Shalom (1978 RA)" (2013-10-25 last obs.). Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 11 January 2016.
- 1 2 Schmadel, Lutz D. (2003). Dictionary of Minor Planet Names – (2100) Ra-Shalom. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. p. 170. ISBN 978-3-540-29925-7. Retrieved 11 January 2016.
- 1 2 3 Shepard, Michael K.; Clark, Beth Ellen; Nolan, Michael C.; Benner, Lance A. M.; Ostro, Steven J.; Giorgini, Jon D.; et al. (January 2008). "Multi-wavelength observations of Asteroid 2100 Ra-Shalom". Icarus. 193 (1): 20–38. Bibcode:2008Icar..193...20S. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2007.09.006. Retrieved 11 January 2016.
- 1 2 Harris, Alan W. (February 1998). "A Thermal Model for Near-Earth Asteroids". Icarus. 131 (2): 291–301. Bibcode:1998Icar..131..291H. doi:10.1006/icar.1997.5865. Retrieved 11 January 2016.
- 1 2 Harris, Alan W.; Davies, John K.; Green, Simon F. (October 1998). "Thermal Infrared Spectrophotometry of the Near-Earth Asteroids 2100 Ra-Shalom and 1991 EE". Icarus. 135 (2): 441–450. Bibcode:1998Icar..135..441H. doi:10.1006/icar.1998.6002. Retrieved 11 January 2016.
- 1 2 Delbó, Marco; Harris, Alan W.; Binzel, Richard P.; Pravec, Petr; Davies, John K. (November 2003). "Keck observations of near-Earth asteroids in the thermal infrared". Icarus. 166 (1): 116–130. Bibcode:2003Icar..166..116D. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2003.07.002. Retrieved 11 January 2016.
- 1 2 Harris, A. W.; Mommert, M.; Hora, J. L.; Mueller, M.; Trilling, D. E.; Bhattacharya, B.; et al. (March 2011). "ExploreNEOs. II. The Accuracy of the Warm Spitzer Near-Earth Object Survey". The Astronomical Journal. 141 (3): 10. Bibcode:2011AJ....141...75H. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/141/3/75. Retrieved 11 January 2016.
- 1 2 Trilling, D. E.; Mueller, M.; Hora, J. L.; Harris, A. W.; Bhattacharya, B.; Bottke, W. F.; et al. (September 2010). "ExploreNEOs. I. Description and First Results from the Warm Spitzer Near-Earth Object Survey". The Astronomical Journal. 140 (3): 770–784. Bibcode:2010AJ....140..770T. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/140/3/770. Retrieved 11 January 2016.
- 1 2 Usui, Fumihiko; Kuroda, Daisuke; Müller, Thomas G.; Hasegawa, Sunao; Ishiguro, Masateru; Ootsubo, Takafumi; et al. (October 2011). "Asteroid Catalog Using Akari: AKARI/IRC Mid-Infrared Asteroid Survey". Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan. 63 (5): 1117–1138. Bibcode:2011PASJ...63.1117U. doi:10.1093/pasj/63.5.1117. Retrieved 11 January 2016.
- 1 2 Delbo, Marco; Walsh, Kevin; Mueller, Michael; Harris, Alan W.; Howell, Ellen S. (March 2011). "The cool surfaces of binary near-Earth asteroids". Icarus. 212 (1): 138–148. Bibcode:2011Icar..212..138D. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2010.12.011. Retrieved 11 January 2016.
- ↑ Pravec, Petr; Wolf, Marek; Sarounová, Lenka (November 1998). "Lightcurves of 26 Near-Earth Asteroids". Icarus. 136 (1): 124–153. Bibcode:1998Icar..136..124P. doi:10.1006/icar.1998.5993. Retrieved 11 January 2016.
- 1 2 Ostro, S. J.; Harris, A. W.; Campbell, D. B.; Shapiro, I. I.; Young, J. W. (November 1984). "Radar and photoelectric observations of asteroid 2100 Ra-Shalom". Icarus: 391–403. Bibcode:1984Icar...60..391O. doi:10.1016/0019-1035(84)90198-2. ISSN 0019-1035. Retrieved 11 January 2016.
- ↑ Harris, A. W.; Young, J. W.; Dockweiler, Thor; Gibson, J.; Poutanen, M.; Bowell, E. (January 1992). "Asteroid lightcurve observations from 1981". Icarus: 115–147.ResearchsupportedbyLowellObservatoryEndowmentandNASA. Bibcode:1992Icar...95..115H. doi:10.1016/0019-1035(92)90195-D. ISSN 0019-1035. Retrieved 11 January 2016.
- ↑ Kaasalainen, Mikko; Pravec, Petr; Krugly, Yurij N.; Sarounová, Lenka; Torppa, Johanna; Virtanen, Jenni; et al. (January 2004). "Photometry and models of eight near-Earth asteroids". Icarus. 167 (1): 178–196. Bibcode:2004Icar..167..178K. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2003.09.012. Retrieved 11 January 2016.
- ↑ Durech, J.; Vokrouhlický, D.; Baransky, A. R.; Breiter, S.; Burkhonov, O. A.; Cooney, W.; et al. (November 2012). "Analysis of the rotation period of asteroids (1865) Cerberus, (2100) Ra-Shalom, and (3103) Eger - search for the YORP effect". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 547: 9. arXiv:1210.2219
 . Bibcode:2012A&A...547A..10D. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201219396. Retrieved 11 January 2016.
. Bibcode:2012A&A...547A..10D. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201219396. Retrieved 11 January 2016. - 1 2 3 "LCDB Data for (2100) Ra-Shalom". Asteroid Lightcurve Database (LCDB). Retrieved 11 January 2016.
- ↑ Thomas, C. A.; Trilling, D. E.; Emery, J. P.; Mueller, M.; Hora, J. L.; Benner, L. A. M.; et al. (September 2011). "ExploreNEOs. V. Average Albedo by Taxonomic Complex in the Near-Earth Asteroid Population". The Astronomical Journal. 142 (3): 12. Bibcode:2011AJ....142...85T. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/142/3/85. Retrieved 11 January 2016.
- ↑ "2100 Ra-Shalom (1978 RA)". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 11 January 2016.
- ↑ "JPL Close-Approach Data: 2100 Ra-Shalom (1978 RA)" (2013-10-25 last obs). Retrieved 2009-05-05.
External links
- Asteroid Lightcurve Database (LCDB), query form (info)
- Dictionary of Minor Planet Names, Google books
- Asteroids and comets rotation curves, CdR – Observatoire de Genève, Raoul Behrend
- Discovery Circumstances: Numbered Minor Planets (1)-(5000) – Minor Planet Center
- 2100 Ra-Shalom at the JPL Small-Body Database
.png)