Bernina railway
Coordinates: 46°24′32″N 10°1′11″E / 46.40889°N 10.01972°E
| Rhaetian Railway in the Albula / Bernina Landscapes | |
|---|---|
| Name as inscribed on the World Heritage List | |
 Two RhB ABe 4/4III multiple units with a Bernina Express train on the Bernina line, passing Lago Bianco | |
| Type | Cultural |
| Criteria | ii, iv |
| Reference | 1276 |
| UNESCO region | Europe and North America |
| Inscription history | |
| Inscription | 2008 (32nd Session) |
The Bernina railway is a single-track 1,000 mm (3 ft 3 3⁄8 in) metre gauge railway line forming part of the Rhaetian Railway (RhB). It links the spa resort of St. Moritz, in the Canton of Graubünden, Switzerland, with the town of Tirano, in the Province of Sondrio, Italy, via the Bernina Pass. Reaching a height of 2,253 metres (7,392 ft) above sea level, it is the highest railway crossing in Europe and the third highest railway in Switzerland. It also ranks as the highest adhesion railway of the continent, and – with inclines of up to 7% – as one of the steepest adhesion railways in the world.
On 7 July 2008, the Bernina Railway and the Albula Railway, which also forms part of the RhB, were recorded in the list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites, under the name Rhaetian Railway in the Albula / Bernina Landscapes. The whole site is regarded as a cross-border joint Swiss-Italian heritage area.
The most famous trains operating on the Bernina Railway are known as the Bernina Express.
History

In the year following the completion of the Albula Railway in 1904, the Bernina-Bahngesellschaft (BB) was established, with the objective of opening a railway line between St Moritz and Tirano, via the Bernina Pass. After obtaining a concession for such a line in 1906, the BB opened it from 1908 onwards, in several sections: on 1 July 1908 between Pontresina and Morteratasch, and between Tirano and Poschiavo; on 18 August of the same year between Pontresina and Celerina; and on 1 July 1909 between Celerina and St Moritz, and between Morteratsch and Bernina Suot. It was only on 5 July 1910 that the whole line could be opened, upon completion of the most difficult section between Bernina Suot and Poschiavo. The line was electrically operated with DC current from the start. In 1935 the voltage was increased from 750 to 1000 volts.
| Bernina Railway | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Winter scene near the top of the Bernina Pass. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overview | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Type | Heavy rail | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| System | Rhaetian Railway | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Open | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Locale |
Engadin / Poschiavo, Graubünden, Switzerland Valtellina, Province of Sondrio, Italy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Termini |
St. Moritz, Switzerland Tirano, Italy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stations | 22 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Services | Bernina Pass | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Website | Rhaetian Railway | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Opened | 1 July 1908 / 5 July 1910 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Owner | Rhaetian Railway | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operator(s) | Rhaetian Railway | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Depot(s) | Poschiavo | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Line length | 60.69 km (37.71 mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of tracks | single track | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Track gauge | 1,000 mm (3 ft 3 3⁄8 in) metre gauge | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum radius | 45 m (148 ft) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrification |
Overhead catenary, 1,000 V DC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Highest elevation |
2,253 m (7,392 ft) above sea level | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maximum incline | 7% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Originally, the Bernina Railway was intended for use only in summer, but in 1913/14 the BB commenced winter operations as well. This development was associated with major weather-related problems, necessitating further erection of avalanche barriers.
In the first years of its existence, the BB was always on the verge of bankruptcy. The costs of construction expenditure on the line to 1915 amounted to around 15 million Swiss francs. Even the introduction of a restaurant car in 1928, and packages for tourists, could not save the little railway from ruin. Due to its difficult financial situation, it was taken over by the Rhaetian Railway in 1943.
The RhB modernised the line fundamentally, also for military reasons, and completely renewed the section at the top of the pass. Previously, the line formation on the north ramp of the Bernina Pass had been laid out in curves giving passengers spectacular views, but also lying in the path of avalanche courses. The new parts of the line cut off those curves, the catenary and the flat bottomed rails of the old formation were removed, but the substructure is still visible in the high mountains.
Since the mid-1980s, the Rhaetian Railway has been marketing the natural and technical attractions of the Bernina Railway specifically to tourists. Thus, the section from Pontresina to Tirano forms part of the route of the Bernina Express. In October 2011, it was the first rail line in the world to be photographed and put on Google Street View.[1][2][3]
Description of the railway

St Moritz is the terminus of both the Albula Railway and the Bernina Railway. As the two railways are powered by different electrification systems, they meet at the same station, but operate on separate lines from separate platforms. The Bernina Railway leaves St Moritz station in an easterly direction, and crosses the Inn River on a 64 m (210 ft) long viaduct. It then passes through the 689 m (2,260 ft) long Charnadüra-Tunnel II, the longest tunnel on the entire route. The next station, Celerina Staz, is, at 1,716 m (5,630 ft) above sea level, the lowest point on the north side of the Bernina Pass. From there until Ospizio Bernina, the line will now climb almost continuously. After returning to the banks of the Inn, the line reaches the small station Punt Muragl Staz. At this point is the valley station of the funicular to Muottas Muragl, opened in 1907.
The next station in Pontresina represents, together with St Moritz station, a curiosity in the network of the RhB: two completely different electrification systems meet here. The 11 kV AC powered trains, which enter the station on the line from Samedan, use tracks 1 to 3, while the 1,000 V DC powered Bernina trains use tracks 3 to 7. Track 3 has a catenary that can be switched from alternating current to direct current, and a special signal to display to train crews the type of current being used. By means of track 3, the trains using the core network (from Samedan) and the Bernina line trains can use the same line, despite their differing electrification systems. On track 3 is also the exchange of locomotives for the famous Bernina Express, which operates between Chur or Davos Platz and Tirano.
The line now turns to the south east. After crossing the Rosegbach, passing through the Surovas station (which was previously called "Sans Souci" (Carefree)), and crossing the Berninabach, it finally reaches Morteratsch station, about 2 km (1.2 mi) below the Morteratsch Glacier. Past the other end of the station is the world famous Montebello Curve, where the line meets the road over the pass. The line and the road will now accompany each other as far as Ospizio Bernina. At the recently modernised Bernina Suot passing loop, the tree line has already been reached. The next stations are Diavolezza and Bernina Lagalb; both are departure points of cableways.
The next section is probably the most interesting on the north side of the pass. Here, the route is very winding, and moves from one side of the valley to the other. First, the Berninabach is crossed, using the 37 m (121 ft) long Lower Berninabach Bridge, and then the line crosses the Arlasbach, a tributory of the Berninabach. On the Upper Berninabach Bridge, the line moves back to the eastern side of the valley. Southwest of here, the Piz Bernina and the Piz Palü rise majestically. Next follows the 175 m (574 ft) long Arlas Gallery, which provides protection against snow drifts. On the southwestern side are the small lakes known as Lej Pitschen and Lej Nair. Directly behind them towers the 15 m (49 ft) high and 283 m (928 ft) long Lago Bianco dam, which also marks the watershed between the Danube and the Po.
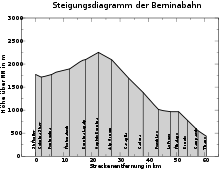
The railway now runs along the eastern bank of the lake, and, near Ospizio Bernina, reaches its highest point, at 2,253 m (7,392 ft) above sea level. The Bernina Railway is thereby (mountainside railways excluded) the highest railway line in the Alps, operating as a public railway with year round traffic. As the section from here to Poschiavo is particularly badly affected by drifting snow, countless engineering structures have been erected from the southern dam wall onwards: the 140 m (460 ft) long Scala Gallery, the 192 m (630 ft) long Scala Tunnel, the Sassal Mason Gallery, even longer at 348 m (1,142 ft), and the 54 m (177 ft) long Drago Tunnel.
After the Grüm Gallery, the attractive Alp Grüm station is reached. It not only is located at the tree line, but also marks the last station before the Italian linguistic border. From here onwards, the line clambers, with a gradient of up to 7%, and via multiple s-bends, downwards into the Poschiavo valley. That this occurs without the assistance of a rack railway system makes the Bernina Railway one of the steepest adhesion railways in the world.
Immediately behind the Alp Grüm station, the line winds in a tight 180° bend, and passes below Alp Grüm through the Upper Palü Gallery. In a further 180° bend, it heads through the Palü Tunnel and subsequently through the Lower Palü Gallery. A further four half circle loops follow, until the line reaches the Cavaglia station. Since about 2000, there has also been a new automatic passing loop, Stablini, between Alp Grüm and Cavaglia. It bisects a portion of the line that was previously prone to traffic delays. In zigzag fashion, the line continues from Cavaglia further down into the valley via Cadera to Privilasco. From there, the line leaves the tight bends behind, and, still at its maximum gradient, reaches the Poschiavo Valley. In Poschiavo it finally meets up once again with the Bernina Pass road.
At the request of the Poschiavo community, the station at Poschiavo was built just outside the village boundaries. It has a railway depot and workshop, in which a few historic railcars of the Bernina Railway are also stored. The remaining section of line of approximately 17 km (11 mi) to Tirano are laid partially still as a mountain railway, but also partially in the manner of a tramway system. After the stopping point Li Curt, erected only in 1977, the line ends on a street in the village of Le Prese. Between Le Prese and Miralago the line passes along the banks of the Poschiavo Lake, thus remaining at the lake's altitude of 965 m (3,166 ft) above sea level.
Below Brusio, the railway has, as its last highlight, the Brusio spiral viaduct, which serves only to adjust the altitude of the line. The spiral viaduct is followed by the stopping point for the village of Campascio, which still belongs to Brusio. Beyond the border station of Campocologno, which is unusually large due to its customs facilities, the line finally reaches Italy, and, after crossing the main square of Tirano, its terminal station. Here, the Bernina Railway meets the standard gauge station and line of the Italian state rail infrastructure company Rete Ferroviaria Italiana (RFI), which links Tirano through Valtellina to Milan.
Rolling stock and traffic
Today, the following classes of railcar and locomotive are used in scheduled commercial services on the Bernina Railway: fifteen ABe 8/12I starting service in 2010, to replace the old series of engines, such as four ABe 4/4I and nine ABe 4/4II. Still in service also six ABe 4/4III and two Gem 4/4 that can operate without electrical feeding, thanks their diesel-generator inside (double engine locomotives).
This fleet, consisting of railcars, also carries freight traffic. Some freight cars are added to passenger trains until the maximum towing capacity of such trains of 140 tonnes is reached. For reasons of safety, due to the presence of dangerous goods, other freight cars are operated in pure freight trains. Despite being set up originally only for tourist traffic, the Bernina Railway now also assists trade with Italy by carrying considerable quantities of freight, consisting mostly of heating oil, fuels and timber. Additionally, the regional shopping businesses of the Poschiavo valley are served partly by rail.
The timetable is tightly designed, with year round services of one passenger train per hour in each direction. The flagship services are the now fully panorama car equipped Bernina Express and the Trenino Rosso travelling in the opposite direction.
In winter, an old 1913 steam rotary snowplow is regularly in service, but also two electrical rotary snowplows from 1968 and also two modern engines from 2010 are used as well. Their operation is also a tourist attraction that draws in railway enthusiasts from all over the world, especially for the steam one. The two Gem 4/4 assure the shunt of the rotary snowplow.
In connection with the danger of avalanches on the Bernina Railway, the Rhaetian Railway has developed an unusual procedure for the removal of these high alpine hazards. In late winter, when the risk of avalanche is greatest, artillery is fired at the points of origin of avalanches, to bring some control to their occurrence.
References
Notes
- ↑ "Street View hits the stunning Swiss Alps railways". Google Official Blog. 20 October 2011. Retrieved 2014-04-06.
- ↑ "Street View Rhaetian Railway". Rhaetian Railway. Retrieved 2014-04-06.
- ↑ Google Street View on Bernina Railway, Netzwelt, October 19th, 2011 (german)
Bibliography
- Gion Caprez, Peter Pfeiffer: Die Goldenen Jahre der Berninabahn. AS Verlag & Buchkonzept AG, Zürich 2000, ISBN 3-905111-48-9.
- Moser, Beat; Pfeiffer, Peter (2004). Die RhB. Teil 2: Berninabahn • St. Moritz – Tirano [The RhB. Part 2: Berninabahn • St. Moritz – Tirano]. Eisenbahn Journal Special-Ausgabe 2/2004. Fürstenfeldbruck: Eisenbahn Journal. ISBN 3896101285. (German) ISSN 0171-3671.
- Mit der Rhätischen Bahn von St. Moritz nach Tirano. A photographic description of probably one of the most beautiful alpine railways. Published by BahnGalerie. FotoReise-CD Bernina 2002.
- Christian Tarnuzzer: Die Bernina-Bahn. Illustrated with original photographs by D. Mischol, with a 1:100,000 map of the Bernina Railway. Ebner & Cie, Chur und St. Moritz. [1909]
- Paul Caminada: "Der Bau der Rhätischen Bahn", Orell Füssli Verlag, Zürich, 1980.
- Andrea Tognina: Arbeiter am Bernina. Sozialgeschichte eines Bahnbaus, 1906–1910, Chur, Desertina, 2010; Andrea Tognina: Gli operai del Bernina. Storia sociale di un cantiere ferroviario, Coira, Desertina, 2010).
Audio-visual material
- "Von Pontresina, Oberengadin, nach Bernina Hospiz", Welt-Kinematograph, Freiburg i. Br., Germany 1909 or 1910.
- "Mit der Berninabahn", Welt-Kinematograph, Freiburg i. Br., Germany 1910.
- "Le Ferrovie del Bernina", Pasquali e C., Turin, Italy 1911.
- "The Bernina Railway (Switzerland)", Urbanora, Great Britain 1912.
- "La Ferrovia del Bernina", Regie: Giovanni Vitrotti, Società Anonima Ambrosio, Turin, Italy 1913.
- "Europe's Winter Playground", Director: Frederick Burlingham, British & Colonial Kinematograph Company, Great Britain 1913.
- "Dallo Spluga al Bernina", Luca Comerio, Milan, Italy 1914.
- "Eine Fahrt mit der Bernina-Bahn (Schweiz)", Sascha-Filmfabrik, Vienna, Austria 1914.
- The TV program "Die schönsten Bahnstrecken Europas", which was shown on Germany's ARD network (see also Das Erste), included a cab ride on the Bernina Railway.
Images
-

A Rhaetian Railway train in Tirano.
-

An RhB Regio train to Tirano between Lagalb and Ospizio Bernina.
-

Bernina Express panorama cars in Tirano.
-

Lei Pitschen in winter.
-
Regional train on the Bernina line on the shores of Lake Nero in the Lago Bianco to the Bernina Pass
-

Crossing the upper Berninabach Bridge.
-
Grüm Galery at Alp Grüm.
-

A down valley train at Poschiavo station.
-

Rhaetian Railway station in Tirano.
-

ABe 4/4 I 30 and 34 below Alp Grüm.
-

Hybrid loco Gem 4 / 4 in service at the head of a Regio train to Tirano.
-

Rotary snowplow Xrotd 9213 with dual-mode Gem 4 / 802 4 in action
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bernina Railway. |
- Images of the Bernina Railway
- Photos of the Bernina Railway in BahnGalerie
- Timetable of the Bernina Railway 2009(pdf; 986 kB)
- Photos of the Bernina Railway


